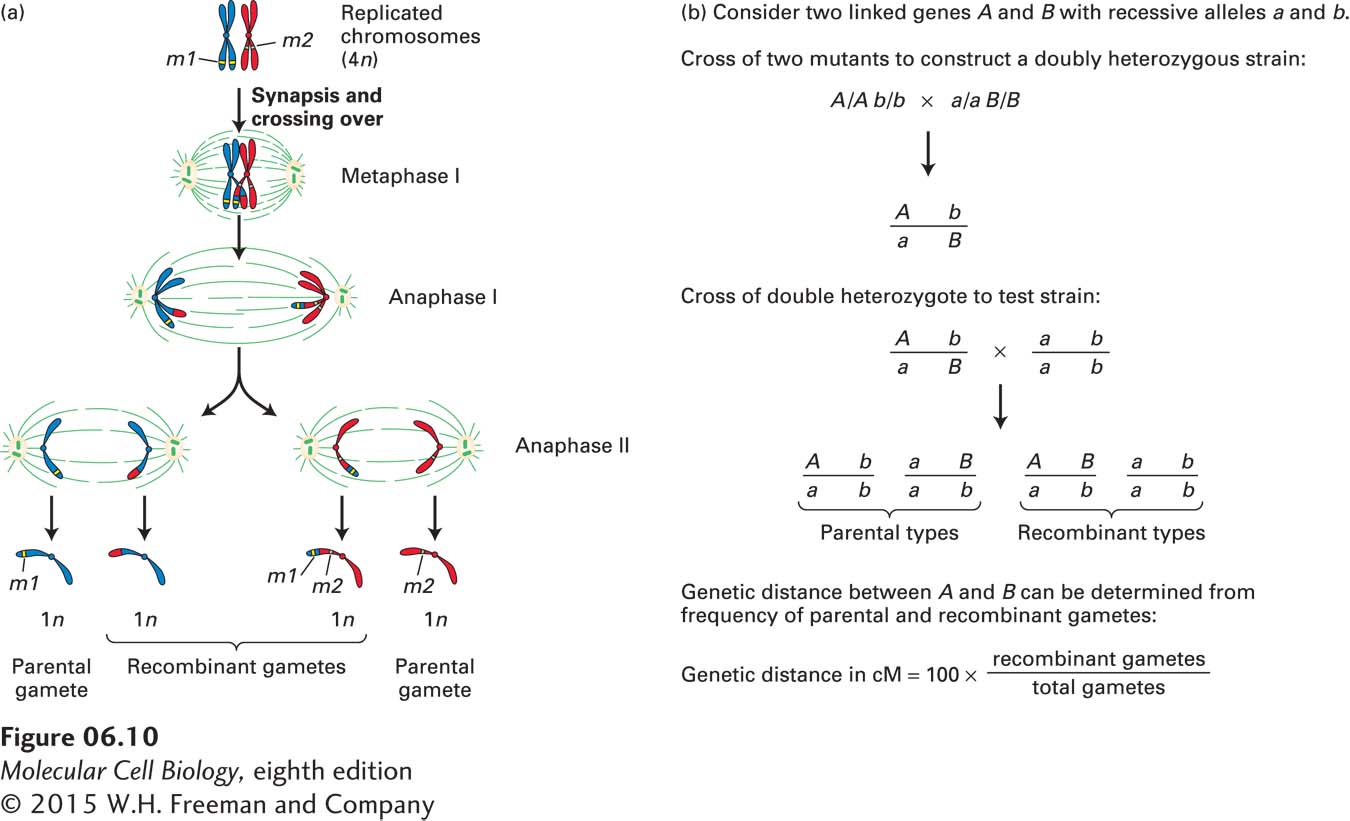
FIGURE 6- 10 Recombination during meiosis can be used to map the positions of genes. (a) Consider the gametes produced by an individual that carries two mutations, designated m1 (yellow) and m2 (green), that are on the maternal and paternal versions of the same chromosome, respectively. If crossing over occurs at an interval between m1 and m2 before the first meiotic division, then two types of recombinant gametes are produced; one carries both m1 and m2, whereas the other carries neither mutation. The longer the distance between two mutations on a chromatid, the more likely they are to be separated by recombination, and the greater the proportion of recombinant gametes produced. (b) In a typical mapping experiment, a strain that is heterozygous for two different genes is constructed. The frequency of parental or recombinant gametes produced by this strain can be determined from the phenotypes of the progeny in a testcross to a homozygous recessive strain. The genetic map distance in centimorgans (cM) is given as the percentage of the gametes that are recombinant.
[Leave] [Close]