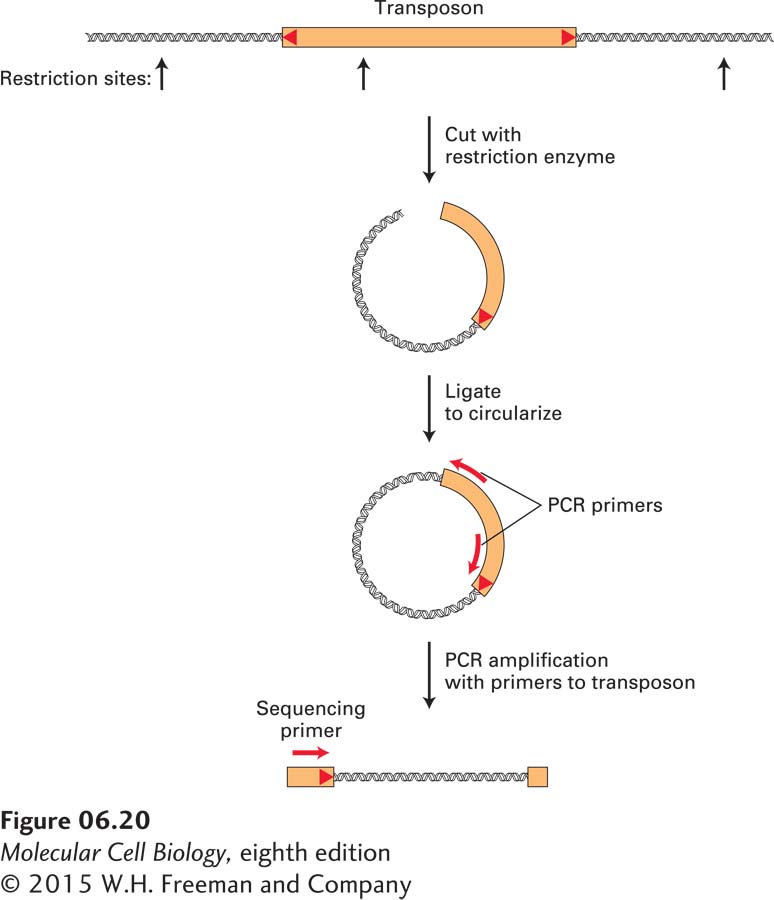
FIGURE 6- 20 The genomic sequence at the insertion site of a DNA transposon is revealed by PCR amplification and sequencing. To obtain the DNA sequence of the insertion site of a P element, it is necessary to amplify the junction between known transposon sequences and unknown flanking chromosomal sequences. One way to achieve this is to cleave genomic DNA with a restriction enzyme that cuts once within the transposon sequence. Ligation of the resulting restriction fragments will generate circular DNA molecules. By using appropriately designed DNA primers that match transposon sequences, it is possible to amplify the desired junction fragment using PCR. Finally, a DNA sequencing reaction (see Figures 6- 21 and 6- 22 ) is performed using the amplified fragment as a template and an oligonucleotide primer that matches sequences near the end of the transposon to obtain the sequence of the junction between the transposon and chromosome.
[Leave] [Close]