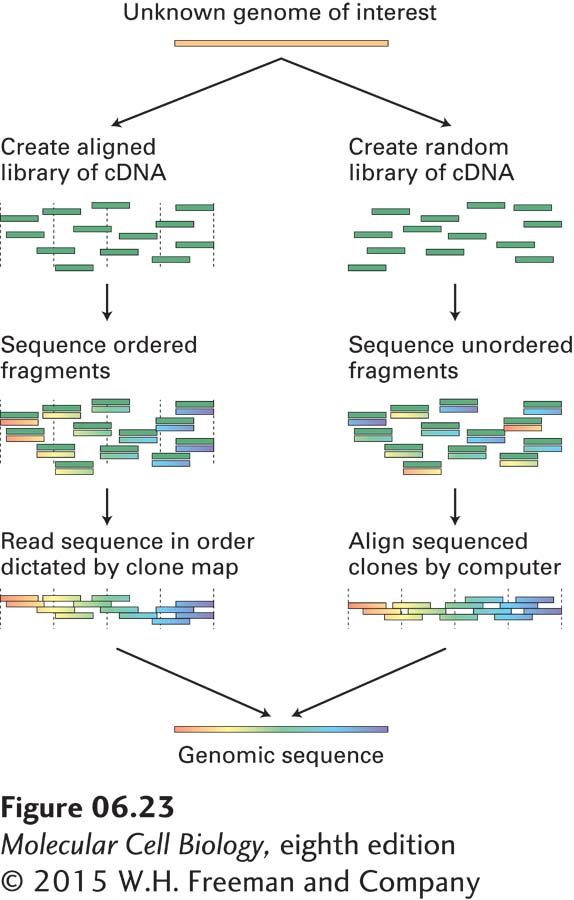
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 6- 23 Two strategies for assembling whole genome sequences. One method (left) depends on isolating and assembling a set of cloned DNA fragments that span the genome. This can be done by matching cloned fragments by hybridization or by alignment of restriction- site maps. The DNA sequence of the ordered clones can then be assembled into a complete genomic sequence. The alternative method (right) depends on the relative ease of automated DNA sequencing and bypasses the laborious step of ordering a DNA library. By sequencing enough random clones from the library so that each segment of the genome is represented from 3 to 10 times, it is possible to reconstruct the genomic sequence by computer alignment of the very large number of sequence fragments.
[Leave] [Close]