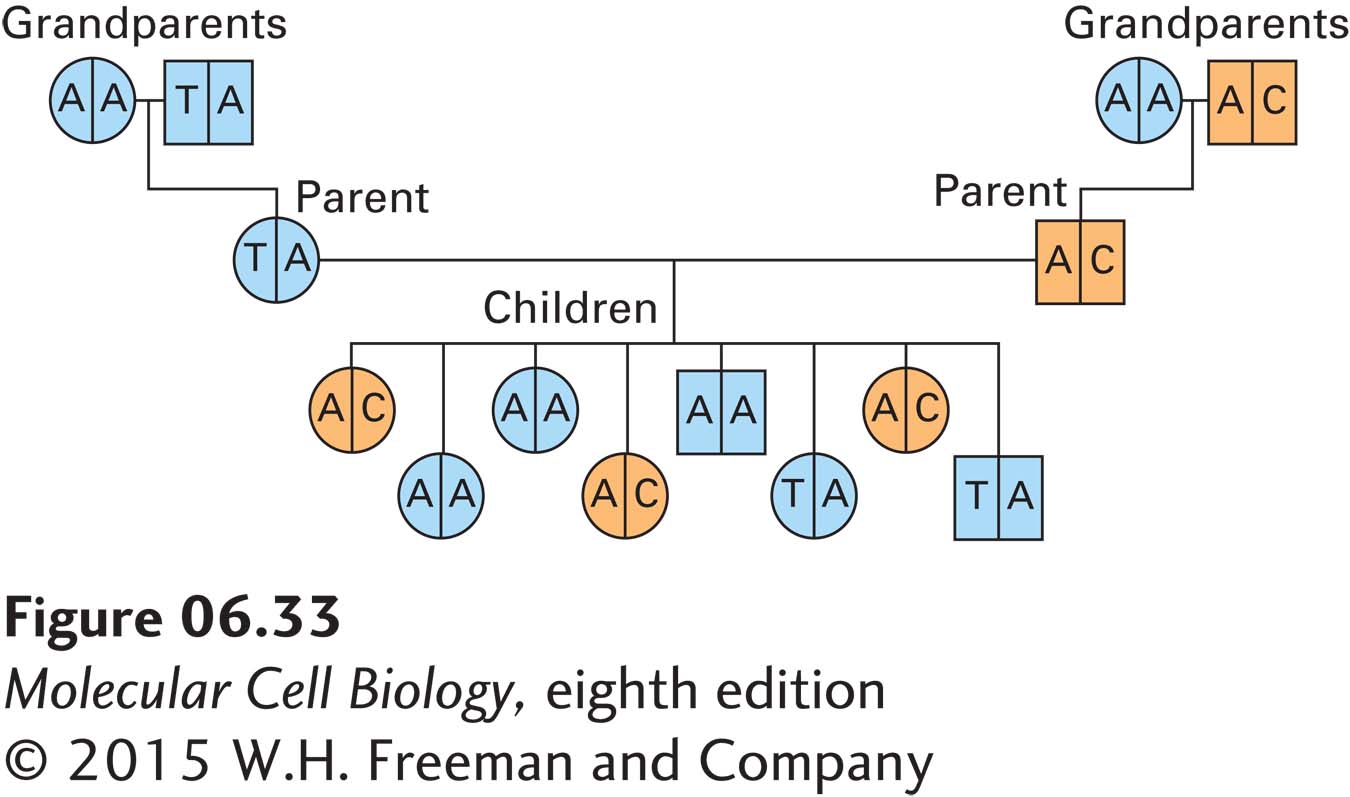
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 6- 33 Single- nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be followed like genetic markers. A hypothetical pedigree based on SNP analysis of the DNA from a region of a chromosome. In this family, the SNP exists as an A, T, or C nucleotide. Each individual has two alleles: some contain an A on both chromosomes, and others are heterozygous at this site. Circles indicate females; squares indicate males. Blue indicates unaffected individuals; orange indicates individuals with the trait of interest. Analysis reveals that the trait segregates with a C at the SNP.
[Leave] [Close]