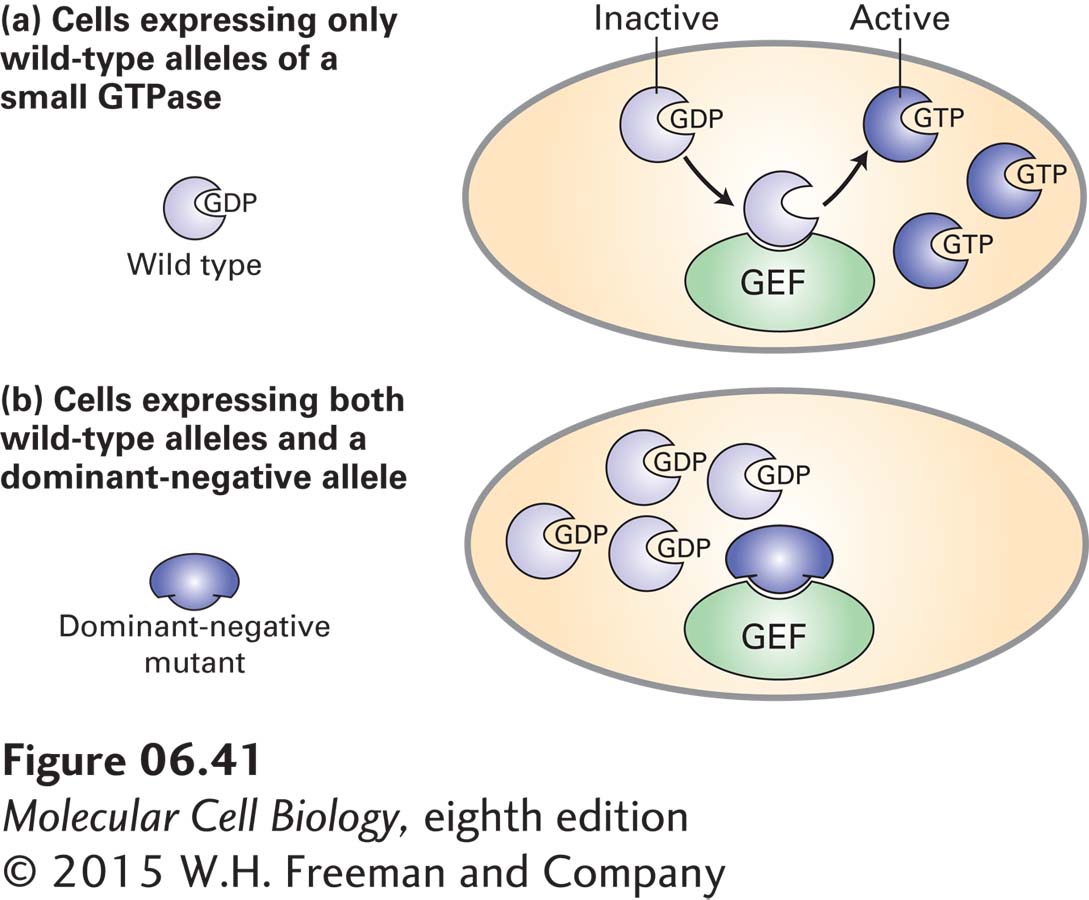
FIGURE 6- 41 Inactivation of the function of a wild- type GTPase by the action of a dominant- negative mutant allele. (a) Small (monomeric) GTPases (purple) are activated by their interaction with a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), which catalyzes the exchange of GDP for GTP. (b) Introduction of a dominant- negative allele of a small GTPase gene into cultured cells or transgenic animals leads to expression of a mutant GTPase that binds to and inactivates the GEF. As a result, endogenous wild- type copies of the same small GTPase are trapped in the inactive GDP- bound state. A single dominant- negative allele thus causes a loss- of- function phenotype in heterozygotes similar to that seen in homozygotes carrying two recessive loss- of- function alleles.
[Leave] [Close]