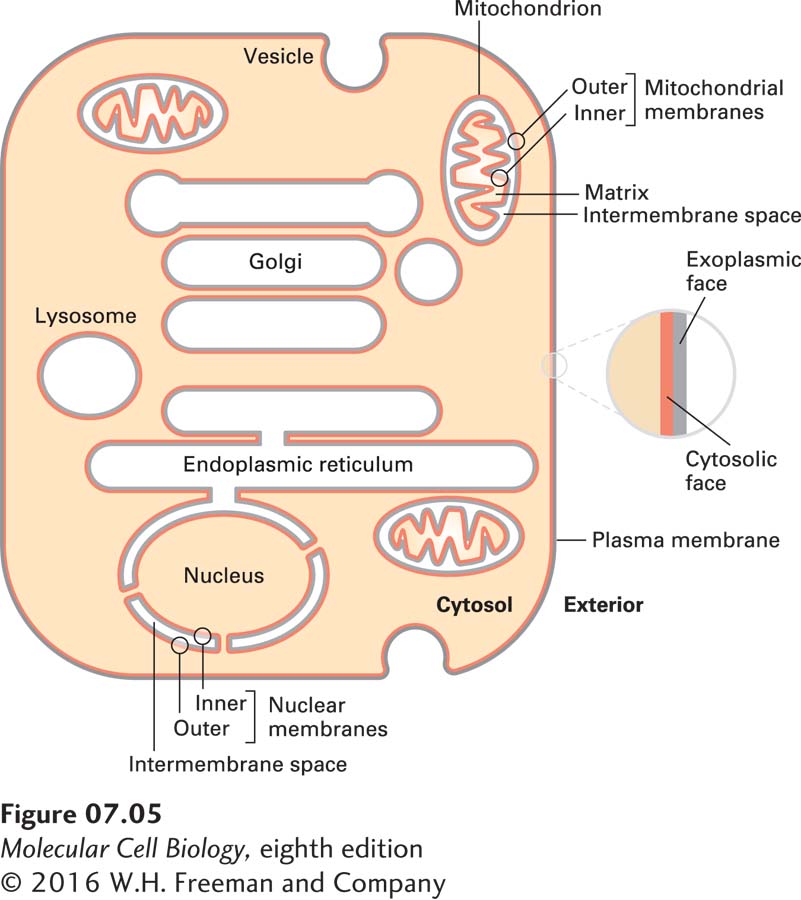
FIGURE 7- s—