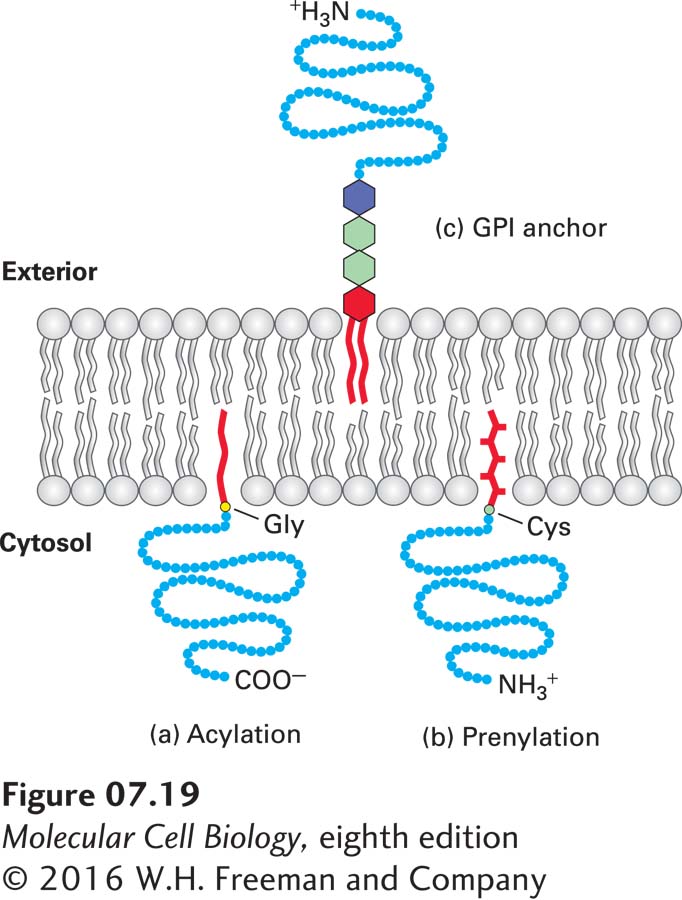
FIGURE 7- 19 Anchoring of plasma- membrane proteins to the phospholipid bilayer by covalently linked hydrocarbon groups. (a) Cytosolic proteins such as v- Src are associated with the plasma membrane through a single fatty acyl chain attached to the N- terminal glycine (Gly) residue of the polypeptide. Myristate (C14) and palmitate (C16) are common acyl anchors. (b) Other cytosolic proteins (e.g., Ras and Rab proteins) are anchored to the membrane by prenylation of one or two cysteine (Cys) residues at or near the C- terminus. The anchors are farnesyl (C15) and geranylgeranyl (C20) groups, both of which are unsaturated. (c) The lipid anchor on the exoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane is glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI). The phosphatidylinositol part (red) of this anchor contains two fatty acyl chains that extend into the bilayer. The phosphoethanolamine unit (purple) in the anchor links it to the protein. The two green hexagons represent sugar units, which vary in number, nature, and arrangement in different GPI anchors. The complete structure of a yeast GPI anchor is shown in Figure 13- 15 . See H. Sprong et al., 2001, Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2:504.
[Leave] [Close]