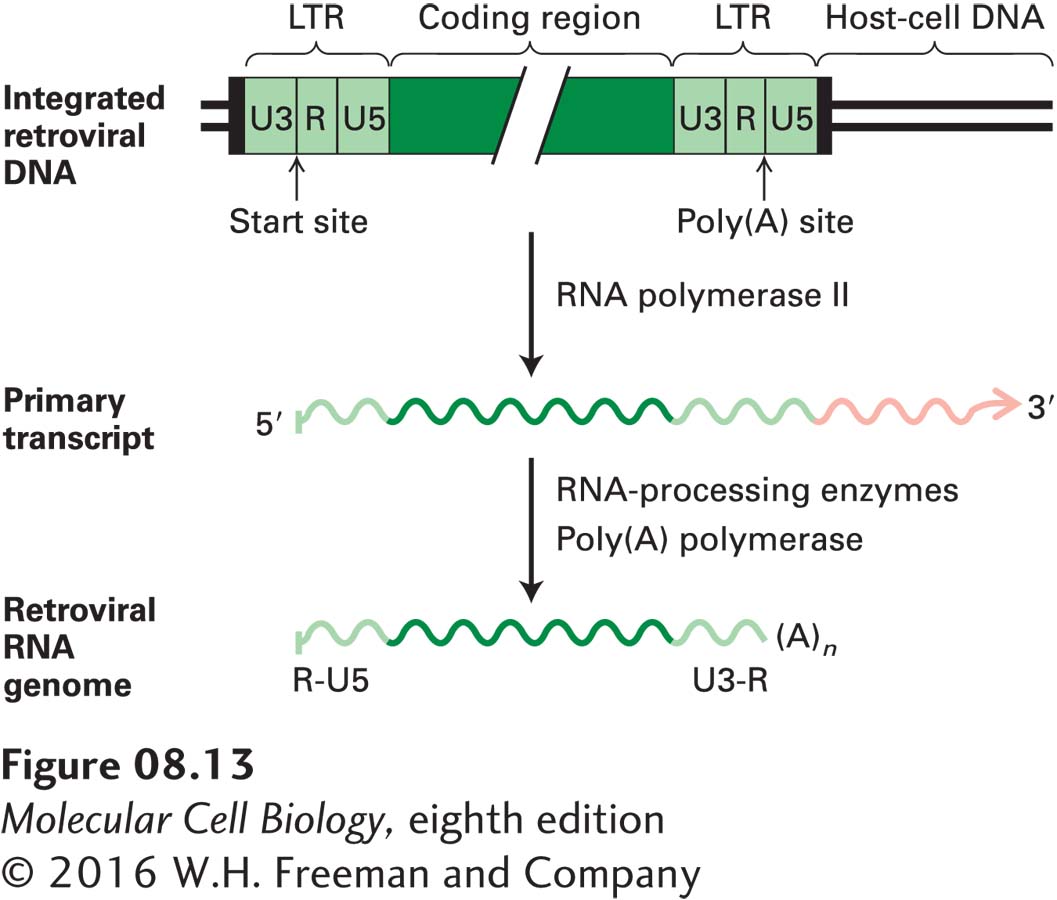
FIGURE 8- 13 Generation of retroviral genomic RNA from integrated retroviral DNA. The left LTR directs cellular RNA polymerase to initiate transcription at the first nucleotide of the left R region. The resulting primary transcript extends beyond the right LTR. The right LTR, now present in the RNA primary transcript, directs cellular enzymes to cleave the primary transcript at the last nucleotide of the right R region and to add a poly(A) tail, yielding a retroviral RNA genome with the structure shown at the top of Figure 8- 14 . The R sequence is repeated precisely at the 5′ and 3′ end [before the poly(A) tail] of the viral genomic RNA. U5 and U3 refer to sequences at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the viral RNA that are not repeated in the genomic retroviral RNA and hence are unique (see Figure 8- 14 ). A similar mechanism is thought to generate the RNA intermediate during transposition of retrotransposons. The short direct repeat sequences (black) of target- site DNA are generated during integration of the retroviral DNA into the host- cell genome.
[Leave] [Close]