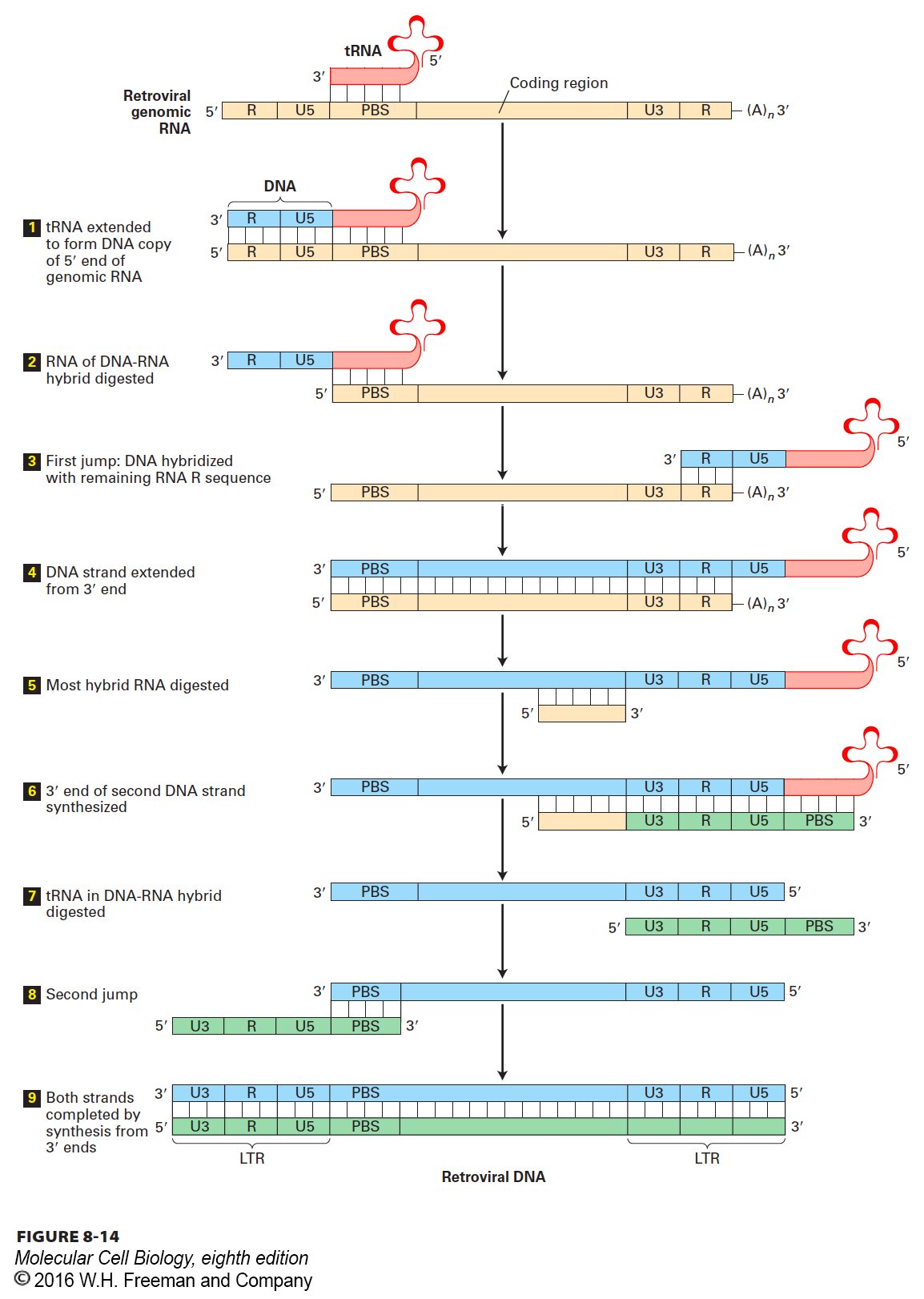
FIGURE 8- 14 Model for reverse transcription of retroviral genomic RNA into DNA. In this model, a complicated series of nine events generates a double- stranded DNA copy of the single- stranded RNA genome of a retrovirus. The genomic RNA is packaged in the virion with a retrovirus- specific cellular tRNA hybridized to a complementary sequence near its 5′ end, called the primer- binding site (PBS). The retroviral RNA has a short direct repeat terminal sequence (R) at each end. The overall reaction is carried out by reverse transcriptase, which catalyzes polymerization of deoxyribonucleotides. RNaseH, also encoded in the viral RNA and packaged into the virion particle, digests the RNA strand in a DNA- RNA hybrid. The entire process yields a double- stranded DNA molecule that is longer than the template RNA and has a long terminal repeat (LTR) at each end. The different regions are not shown to scale. The PBS and R regions are actually much shorter than the U5 and U3 regions, and the central coding region is very much longer than the other regions. See E. Gilboa et al., 1979, Cell 18:93.
[Leave] [Close]