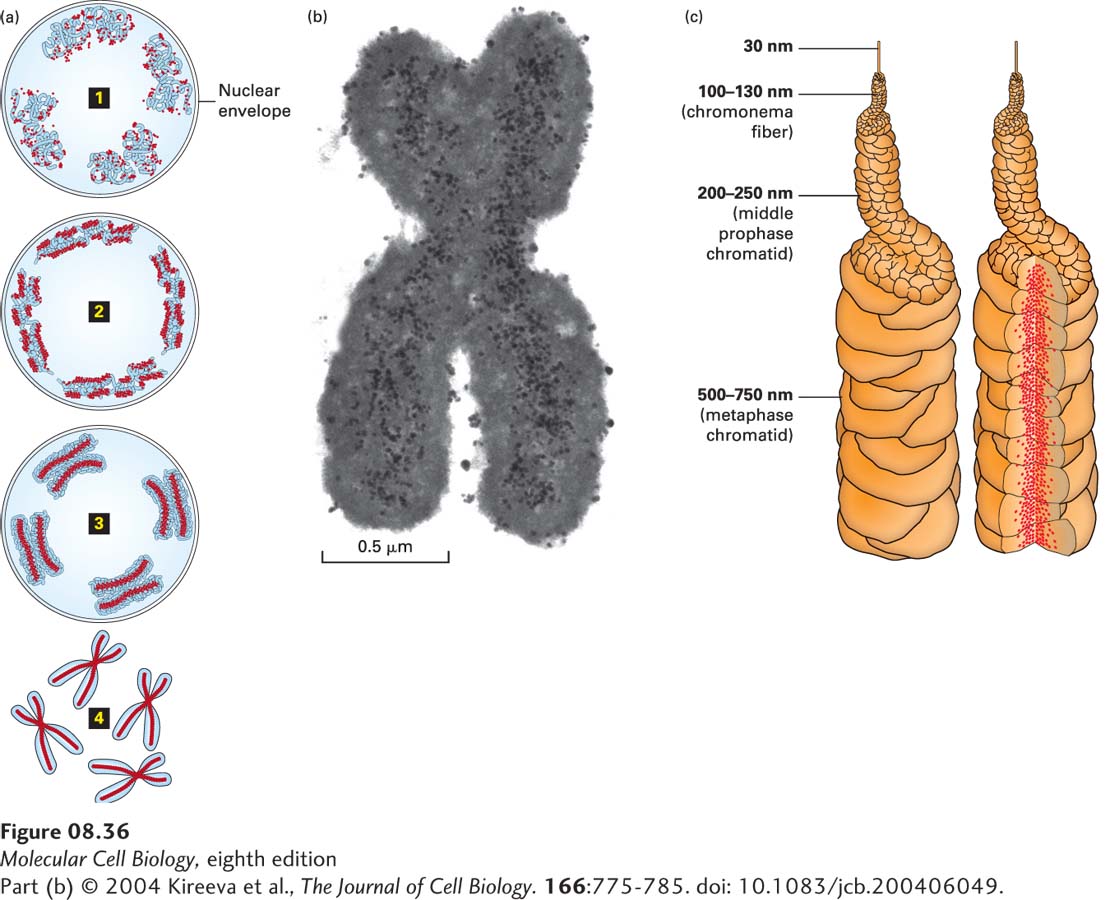
FIGURE 8- 36 Model for mitotic chromosome condensation. (a) Stages of chromosome condensation during mitosis. Changes in large- scale chromatin folding (blue) versus distribution of Smc2, a subunit of condensin (red), from early prophase 1 to middle prophase 2 to late prophase 3 to metaphase 4. (b) Transmission electron micrograph of immunogold staining of Smc2 in a section through a metaphase chromosome reveals axial staining of Smc2 of about 0.15– 0.2 µm in width. (c) “Hierarchical folding, axial glue” model of metaphase chromosome structure. (Left) 30- nm fiber folds into 100– 130- nm chromonema fiber, which folds into 200– 250- nm middle prophase chromatid, which folds into 500– 750- nm metaphase chromatid. Only one chromatid is shown. (Right) Axial condensin distribution (red) occupies approximately one- third of the chromatid diameter, acting as a cross- linking “glue” to stabilize the structure of the metaphase chromosome.
[Part (b) © 2004 Kireeva et al., The Journal of Cell Biology. 166:775- 785. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200406049.]
[Leave] [Close]