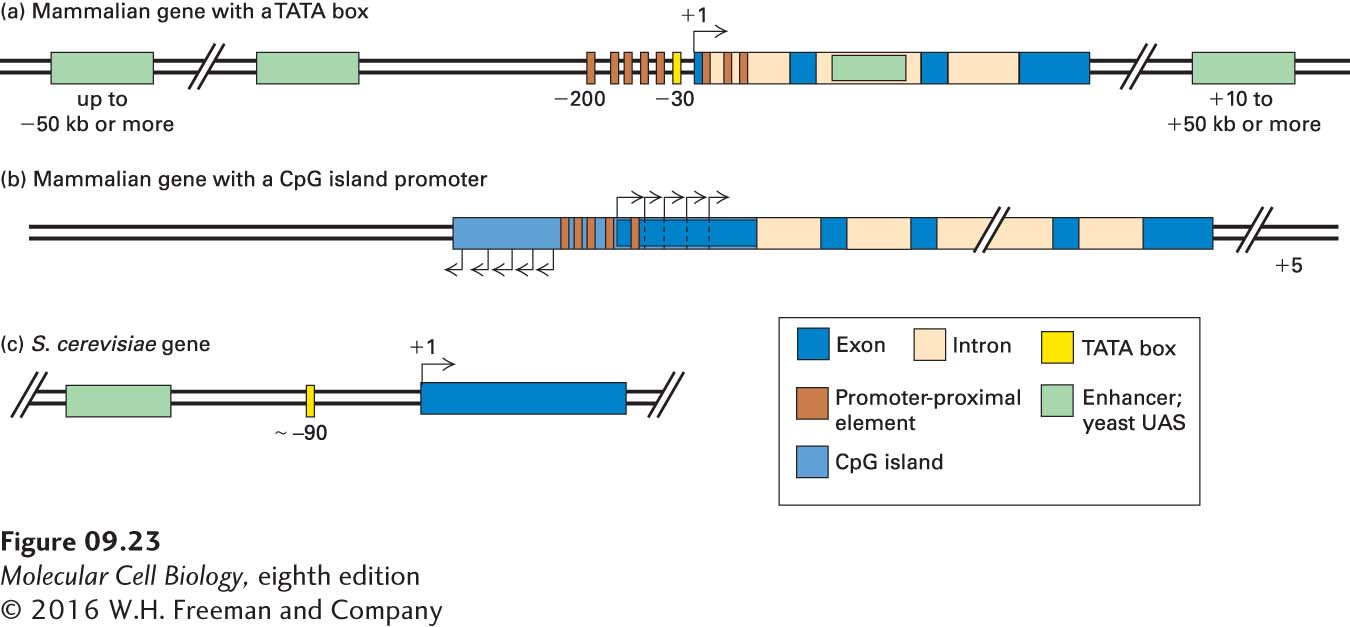
FIGURE 9- 23 General organization of control elements that regulate gene expression in multicellular eukaryotes and yeast. (a) Mammalian genes with a TATA box promoter are regulated by promoter- proximal elements and enhancers. The promoter elements shown in Figure 9- 16 position RNA polymerase II to initiate transcription at the start site and influence the rate of transcription. Enhancers may be either upstream or downstream and as far away as hundreds of kilobases from the transcription start site. In some cases, enhancers lie within introns. Promoter- proximal elements are found upstream and downstream of transcription start sites at equal frequency in mammalian genes. (b) For mammalian genes with a CpG island promoter, transcription initiates at several sites in both the sense and antisense directions from the ends of the CpG- rich region. Transcripts in the sense direction are elongated and are processed into mRNAs by RNA splicing. These genes express mRNAs with alternative 5′ exons determined by the transcription start site. Genes with CpG island promoters contain promoter- proximal control elements. Currently, it is not clear whether they are also regulated by distant enhancers. (c) Most S. cerevisiae genes contain only one regulatory region, called an upstream activating sequence (UAS), and a TATA box, which is about 90 bp upstream from the transcription start site.
[Leave] [Close]