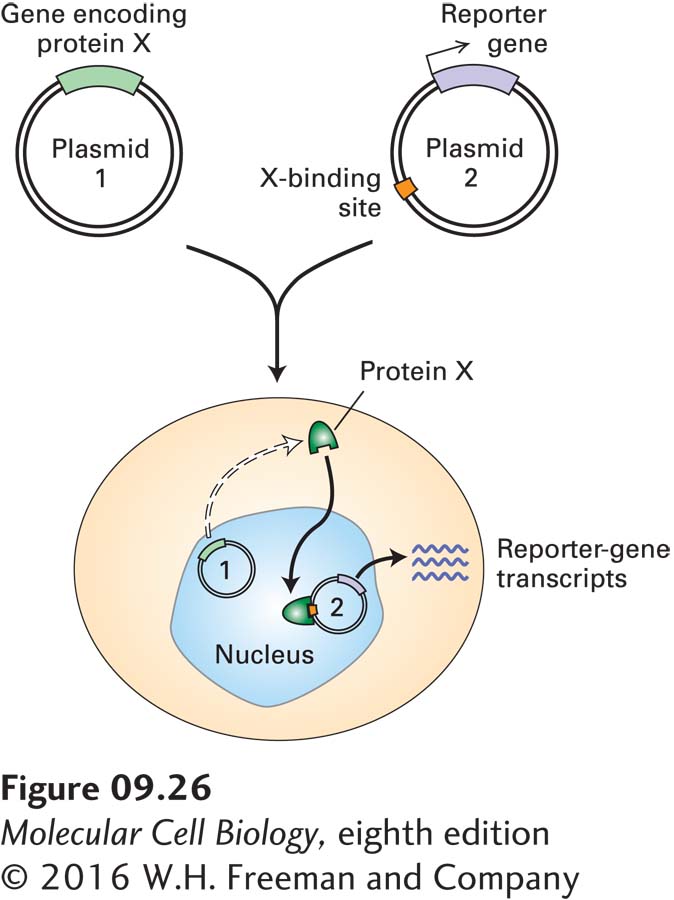
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 9- 26 An in vivo transfection assay measures transcription activity to evaluate proteins believed to be transcription factors. The assay system requires two plasmids. One plasmid contains the gene encoding the putative transcription factor (protein X). The second plasmid contains a reporter gene (e.g., luciferase) and one or more binding sites for protein X. Both plasmids are simultaneously introduced into cells that lack the gene encoding protein X. The production of reporter- gene RNA transcripts is measured; alternatively, the activity of the encoded protein can be assayed. If reporter- gene transcription is greater in the presence of the X- encoding plasmid than in its absence, then the protein is an activator; if transcription is less, then it is a repressor. By use of plasmids encoding a mutated or rearranged transcription factor, important domains of the protein can be identified.
[Leave] [Close]