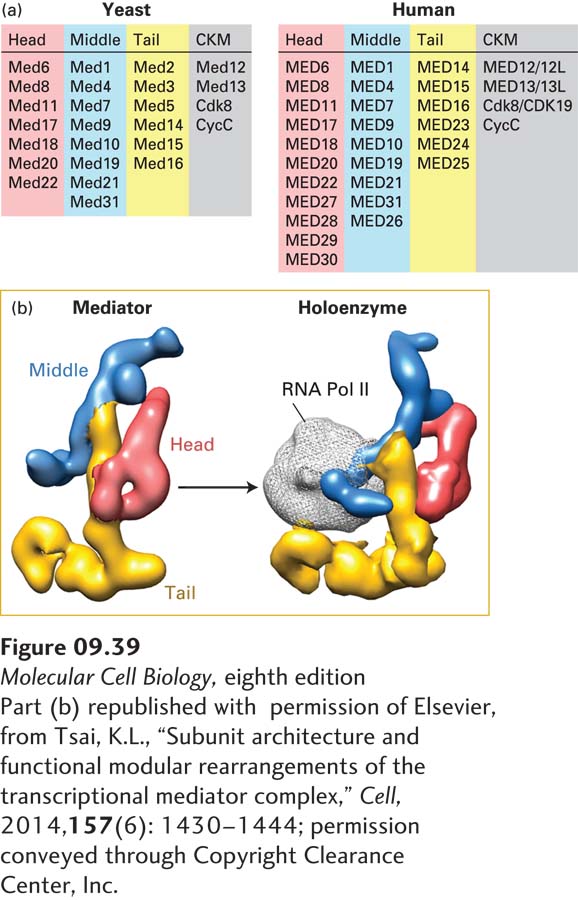
FIGURE 9- 8- r-
[Part (b) republished with permission of Elsevier, from Tsai, K.L., “Subunit architecture and functional modular rearrangements of the transcriptional mediator complex,” Cell, 2014, 157(6): 1430–