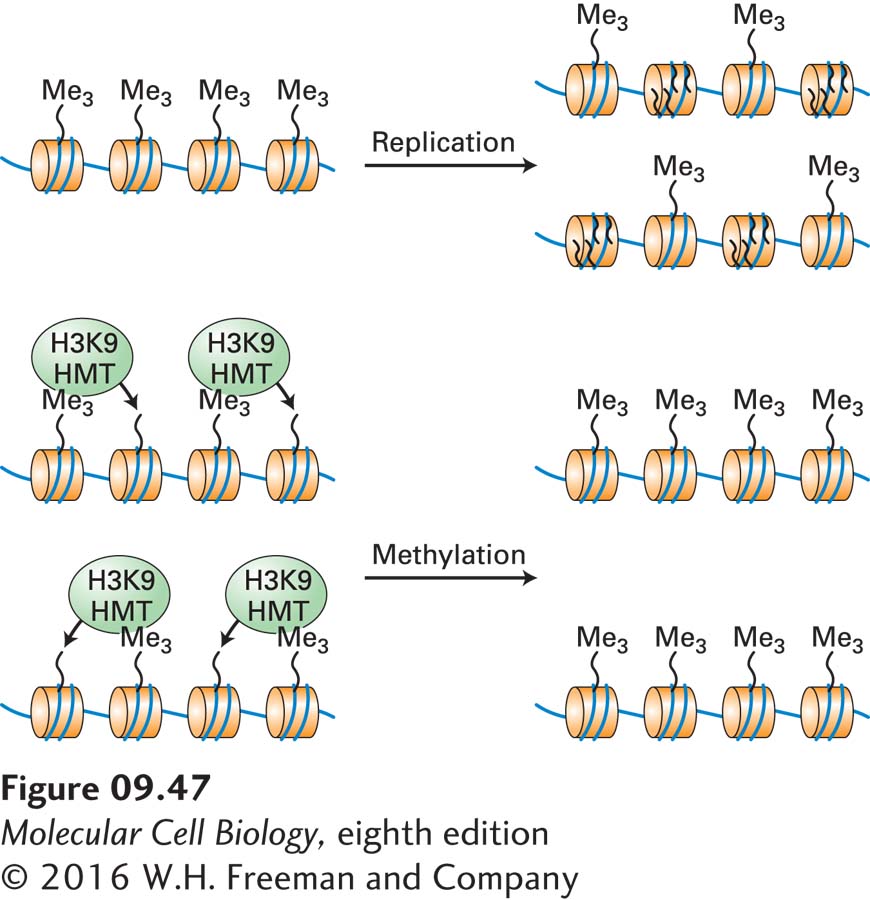
FIGURE 9- i-