
Chapter 14. Examining KDEL in a GFP Construct
Introduction

Analyze the Data 14-2: Examining KDEL in a GFP Construct
You have genetically engineered a green fluorescent protein (GFP) construct containing a KDEL sequence. When the construct is transfected into normal human fibroblasts and examined using fluorescence microscopy, the fluorescence appears throughout the cytoplasm, as diagrammed below.
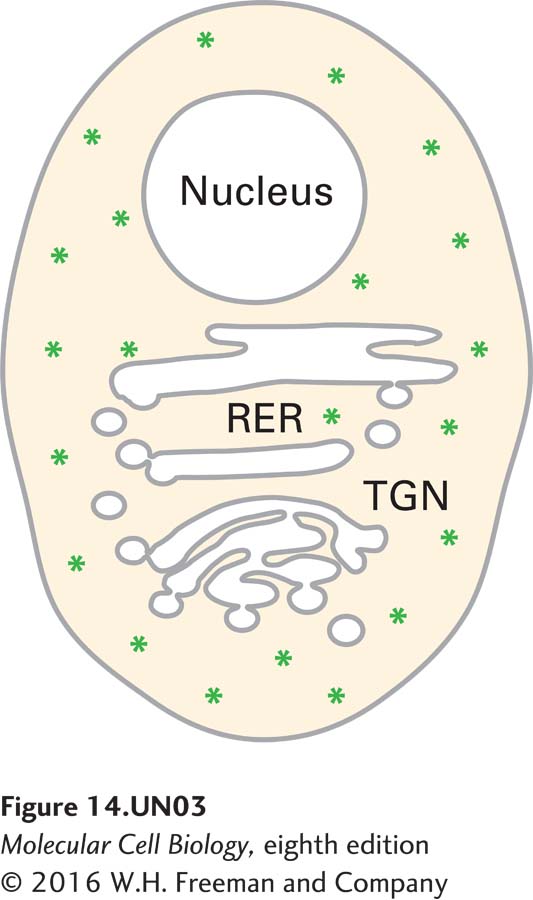
a. How would you explain this pattern given that KDEL is supposed to be an ER-specific sorting sequence?
b. To analyze the results further, fractions of different organelles and the cytoplasm are collected from cells expressing this KDEL-containing GFP construct and then examined on Western blots using antibodies against GFP (27 kDa) and protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), a resident rough ER (RER) protein of approximately 55 kDa.
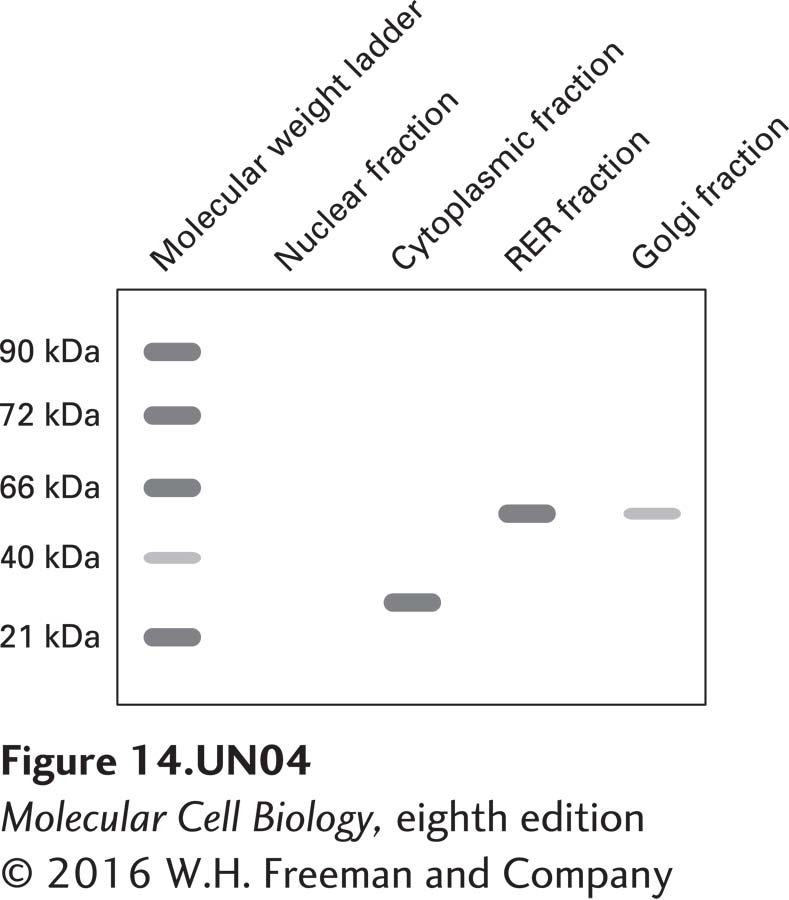

The blot confirms the presence of GFP exclusively in the cytoplasm, and as expected, a PDI signal in the RER fraction. How would you explain the PDI band, albeit weak, in the Golgi fraction? Given the function of PDI proteins, what would you expect if both alleles of a PDI gene were knocked out in mice?
c. The antibodies used above do not detect any signals in the nuclear fraction, which indicates their specificity or the fact that no proteins were isolated and loaded in the nuclear fraction lane. What antibody could be used to show there were nuclear proteins present in this sample?
Activity results are being submitted...