
Chapter 19. Xnf7 and APC/C in Xenopus
Introduction

Analyze the Data 19-1: Xnf7 and APC/C in Xenopus
Many of the proteins that regulate transit through the cell cycle have been characterized. Xnf7, identified in extracts of Xenopus eggs, binds to the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C). To elucidate the function of this protein, studies have been undertaken in which Xnf7 either has been depleted from extracts using an antibody raised against it or has been augmented in the extracts through addition of extra Xnf7. The consequences for transit through mitosis have then been assessed (see J. B. Casaletto et al., 2005, J. Cell Biol. 169:61–71).
a.Xenopus egg extracts, arrested in metaphase, were either depleted of Xnf7 or were mock depleted (subjected to the same treatment as the first extracts, but without Xnf7 antibody), then released from metaphase arrest by addition of Ca2+. Aliquots of the extract were then sampled at various times after Ca2+ addition and the amounts of mitotic cyclin in those samples were determined. The results are shown on the Western blot below. What information do these data provide about a possible function for Xnf7?

Cyclin B is degraded more quickly when Xnf7 is depleted from the extracts. Thus, these studies suggest that Xnf7 functions in some way to delay cyclin degradation and perhaps the onset of anaphase. Because Xnf7 binds to APC/C, it is possible that Xnf7 normally inhibits APC/C. If so, depletion of Xnf7 would allow APC/C to be activated and target cyclin B for destruction sooner, as observed here.
b. In additional studies, exogenous Xnf7 was added to Xenopus egg extracts arrested at metaphase, so that the total amount of this protein in the extracts was higher than normal. The extracts, released from arrest by Ca2+ addition, were then assessed at various times after release for mitotic cyclin ubiquitinylation (cyclin-Ub conjugates). What is the rationale for examining ubiquitinylation? Using the following figure, determine what information these studies add beyond that obtained from part (a).
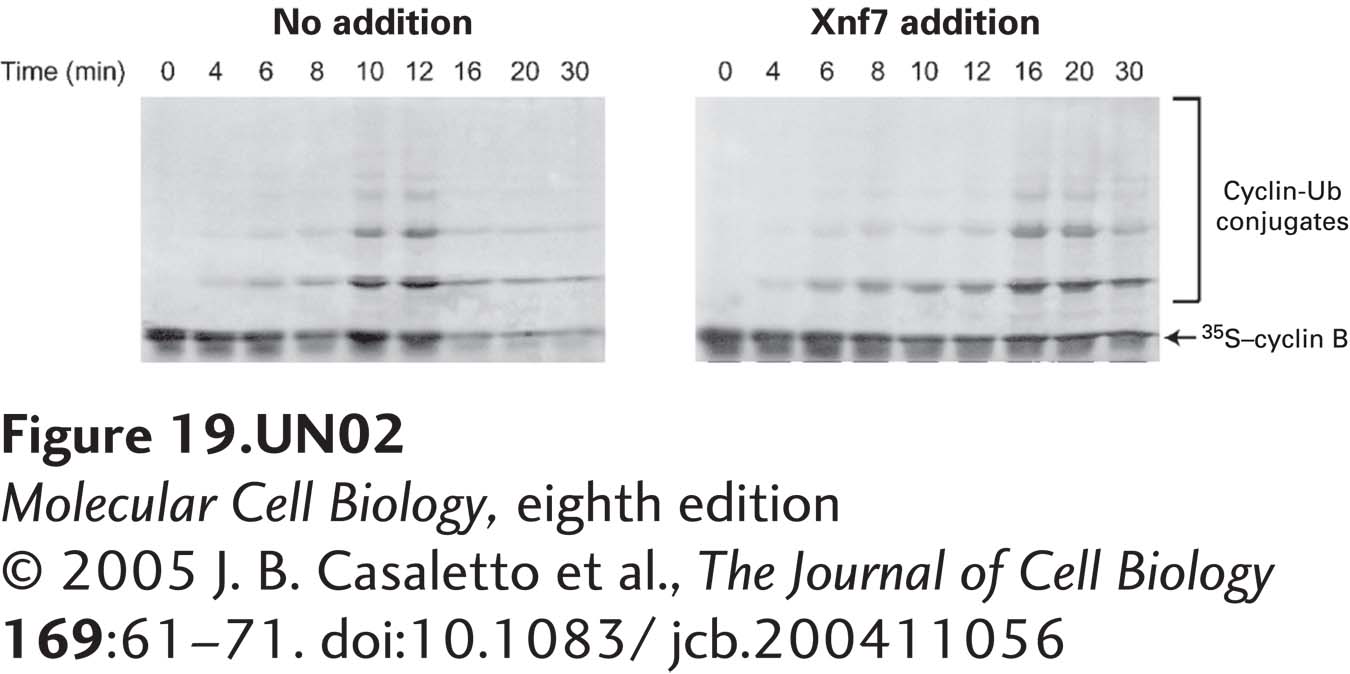
In untreated extracts, cyclin B is polyubiquitinylated 10 minutes after release from metaphase arrest, whereas addition of exogenous Xnf7 delays the onset of cyclin polyubiqutination to 16 minutes. These data reinforce those in (a), suggesting that the presence or absence of Xnf7 affects the timing of cyclin B ubiquitinylation and subsequent destruction. These data suggest that Xnf7 affects the activity APC/C, the ligase responsible for ubiquitinylating cyclin B.
c. The spindle assembly checkpoint pathway prevents cells with unattached kinetochores from proceeding to anaphase. Thus cells in which this checkpoint pathway has been activated do not enter anaphase and do not degrade mitotic cyclin. Nocodazole, a drug that prevents microtubule assembly, can be used to activate the spindle assembly checkpoint pathway. Cells treated with nocodazole become arrested in early mitosis because they cannot form a spindle, and so all kinetochores remain unattached. To determine if Xnf7 is required for a functional spindle assembly checkpoint pathway, Xenopus egg extracts, arrested in metaphase, were subjected to various protocols (see the following figure): untreated (no nocodazole) or treated with nocodazole and either mock depleted (preimmune) or immunodepleted of Xnf7 (α-Xnf7). The extracts were then treated with Ca2+ to overcome arrest, and aliquots of the extracts were assessed at various times for mitotic cyclin. The results are shown on the Western blot below. What can you conclude about Xnf7 from these data?

Cells proceeding normally through mitosis (see text figure on page 921, top panel ) degrade cyclin at 40 minutes after addition of Ca2+. When the spindle checkpoint is activated, as in the presence of nocodazole (middle panel), cells are checked and cyclin B is not degraded as it is in control cells (top panel). However, if the extracts are depleted of Xnf7 (bottom panel), then cyclin B is degraded even though the cells are in nocodazole and should be checked at a stage prior to cyclin degradation. These data suggest that Xnf7 is required for maintenance of the spindle checkpoint.
Activity results are being submitted...