Creating APA in-text citations
An in-text citation in APA style always indicates which source on the references page the writer is referring to, and it explains in what year the material was published; for quoted material, the in-text citation also indicates where in the source the quotation can be found.
Note that APA style generally calls for using the past tense or present perfect tense for signal verbs: Baker (2003) showed or Baker (2003) has shown. Use the present tense only to discuss results (the experiment demonstrates) or widely accepted information (researchers agree).
1. Basic format for a quotation Generally, use the author’s name in a signal phrase to introduce the cited material, and place the date, in parentheses, immediately after the author’s name. The page number, preceded by p., appears in parentheses after the quotation.
Gitlin (2001) pointed out that “political critics, convinced that the media are rigged against them, are often blind to other substantial reasons why their causes are unpersuasive” (p. 141).
If the author is not named in a signal phrase, place the author’s name, the year, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation: (Gitlin, 2001, p. 141). For a long, set-off quotation (more than forty words), place the page reference in parentheses one space after the final quotation.
For quotations from works without page numbers, you may use paragraph numbers, if the source includes them, preceded by the abbreviation para.
Driver (2007) has noticed “an increasing focus on the role of land” in policy debates over the past decade (para. 1).
2. Basic format for a paraphrase or summary Include the author’s last name and the year as in model 1, but omit the page or paragraph number unless the reader will need it to find the material in a long work.
Gitlin (2001) has argued that critics sometimes overestimate the influence of the media on modern life.
3. Two authors Use both names in all citations. Use and in a signal phrase, but use an ampersand (&) in parentheses.
Babcock and Laschever (2003) have suggested that many women do not negotiate their salaries and pay raises as vigorously as their male counterparts do.
A recent study has suggested that many women do not negotiate their salaries and pay raises as vigorously as their male counterparts do (Babcock & Laschever, 2003).
4. Three to five authors List all the authors’ names for the first reference.
Safer, Voccola, Hurd, and Goodwin (2003) reached somewhat different conclusions by designing a study that was less dependent on subjective judgment than were previous studies.
In subsequent references, use just the first author’s name followed by et al.
Based on the results, Safer et al. (2003) determined that the apes took significant steps toward self-expression.
5. Six or more authors Use only the first author’s name and et al. in every citation.
As Soleim et al. (2002) demonstrated, advertising holds the potential for manipulating “free-willed” consumers.
6. Corporate or group author If the name of the organization or corporation is long, spell it out the first time you use it, followed by an abbreviation in brackets. In later references, use the abbreviation only.
| FIRST CITATION | (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2006) |
| LATER CITATIONS | (CDC, 2006) |
7. Unknown author Use the title or its first few words in a signal phrase or in parentheses. A book’s title is italicized, as in the following example; an article’s title is placed in quotation marks.
The employment profiles for this time period substantiated this trend (Federal Employment, 2001).
8. Two or more authors with the same last name Include the authors’ initials in each citation.
S. Bartolomeo (2000) conducted the groundbreaking study on teenage childbearing.
9. Two or more works by an author in a single year Assign lowercase letters (a, b, and so on) alphabetically by title, and include the letters after the year.
Gordon (2004b) examined this trend in more detail.
10. Two or more sources in one parenthetical reference List any sources by different authors in alphabetical order by the authors’ last names, separated by semicolons: (Cardone, 1998; Lai, 2002). List works by the same author in chronological order, separated by commas: (Lai, 2000, 2002).
11. Source reported in another source Use the phrase as cited in to indicate that you are reporting information from a secondary source. Name the original source in a signal phrase, but list the secondary source in your list of references.
Amartya Sen developed the influential concept that land reform was necessary for “promoting opportunity” among the poor (as cited in Driver, 2007, para. 2).
12. Personal communication Cite personal letters, email messages, electronic postings, telephone conversations, or interviews as shown. Do not include personal communications in the reference list.
R. Tobin (personal communication, November 4, 2006) supported his claims about music therapy with new evidence.
13. Digital source Cite a Web or electronic document as you would a print source, using the author’s name and date.
Link and Phelan (2005) argued for broader interventions in public health that would be accessible to anyone, regardless of individual wealth.
The APA recommends the following for electronic sources without names, dates, or page numbers:
AUTHOR UNKNOWN
Use a shortened form of the title in a signal phrase or in parentheses (see model 7). If an organization is the author, see model 6.
DATE UNKNOWN
Use the abbreviation n.d. (for “no date”) in place of the year: (Hopkins, n.d.).
NO PAGE NUMBERS
Many works found online or in electronic databases lack stable page numbers. (Use the page numbers for an electronic work in a format, such as PDF, that has stable pagination.) If paragraph numbers are included in such a source, use the abbreviation para.: (Giambetti, 2014, para. 7). If no paragraph numbers are included but the source includes headings, give the heading and identify the paragraph in the section:
Jacobs and Johnson (2007) have argued that “the South African media is still highly concentrated and not very diverse in terms of race and class” (South African Media after Apartheid, para. 3).
14. Entire Web site If you are citing an entire Web site, not simply a page or document from a site, list the URL in parentheses in the text of your writing project. Do not include it in the list of references.
15. Table or figure reproduced in the text Number figures (illustrations, graphs, charts, and photographs) and tables separately.
For a table, place the label (Table 1) and an informative heading (Hartman’s Key Personality Traits) above the table; below, provide information about its source.
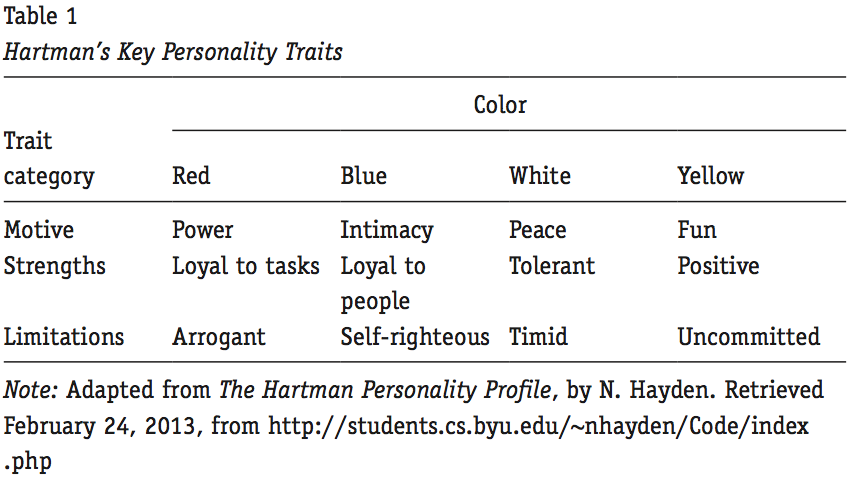
For a figure, place the label (Figure 3) and a caption indicating the source below the image. If you do not cite the source of the table or figure elsewhere in your text, you do not need to include the source on your list of references.