FIGURE 12-2
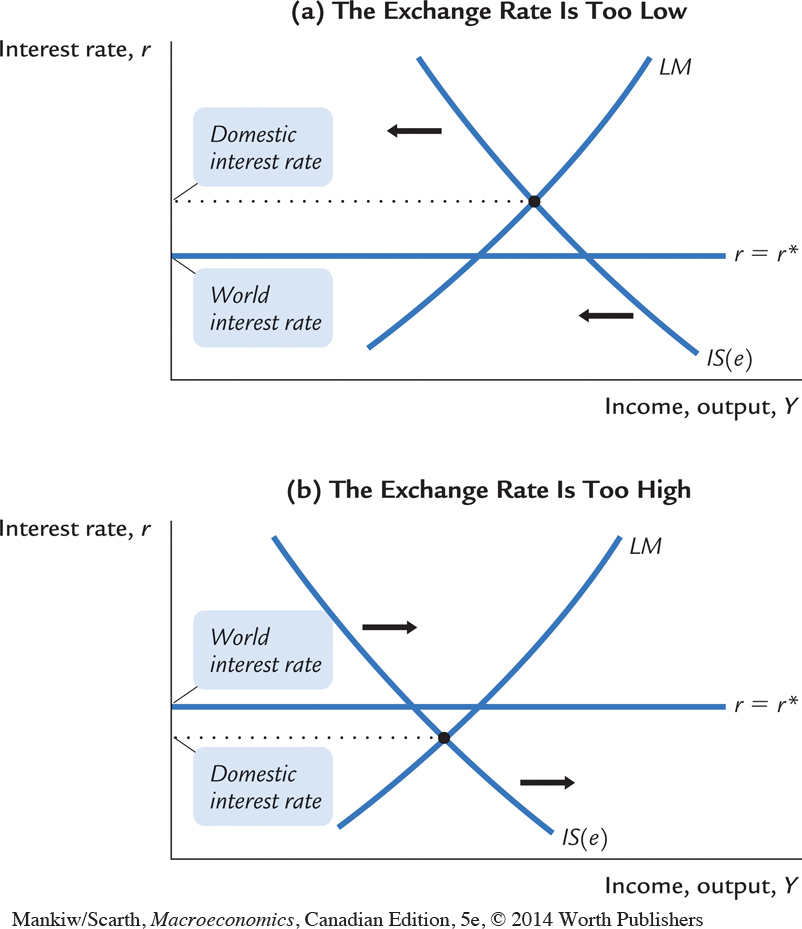 The Mundell–Fleming Model with the Exchange Rate at the Wrong Level This figure shows why the IS curve must intersect at the point at which the LM curve and the r = r* line cross. In panel (a), because the three curves do not cross at the same point, the domestic interest rate would exceed the world interest rate. Foreign investors would try to invest their funds in Canada. In the process, they would bid up the Canadian dollar and shift the IS curve downward. In panel (b), the domestic interest rate would be less than the world interest rate. Investors would try to invest their funds abroad. In the process, they would sell Canadian dollars, depressing its value. This shifts the IS curve upward.
The Mundell–Fleming Model with the Exchange Rate at the Wrong Level This figure shows why the IS curve must intersect at the point at which the LM curve and the r = r* line cross. In panel (a), because the three curves do not cross at the same point, the domestic interest rate would exceed the world interest rate. Foreign investors would try to invest their funds in Canada. In the process, they would bid up the Canadian dollar and shift the IS curve downward. In panel (b), the domestic interest rate would be less than the world interest rate. Investors would try to invest their funds abroad. In the process, they would sell Canadian dollars, depressing its value. This shifts the IS curve upward.