Understanding World Societies:
Printed Page 914
Introduction for Chapter 30
30 THE GREAT DEPRESSION AND WORLD WAR II 1929–
> How did the economic suffering created by the Great Depression contribute to the outbreak of World War II? Chapter 30 examines the Great Depression and World War II. In 1929 the interconnected global economy collapsed. In the wake of the Great Depression, people everywhere looked to new leaders for relief, some democratically elected, many not. A global trend toward dictatorship produced a particularly ruthless brand of totalitarianism that reached its fullest realization in the Soviet Union, Nazi Germany, and Japan in the 1930s. Germany’s and Japan’s aggressive expansion sparked World War II. By war’s end, millions had died on the battlefields and in the bombed-
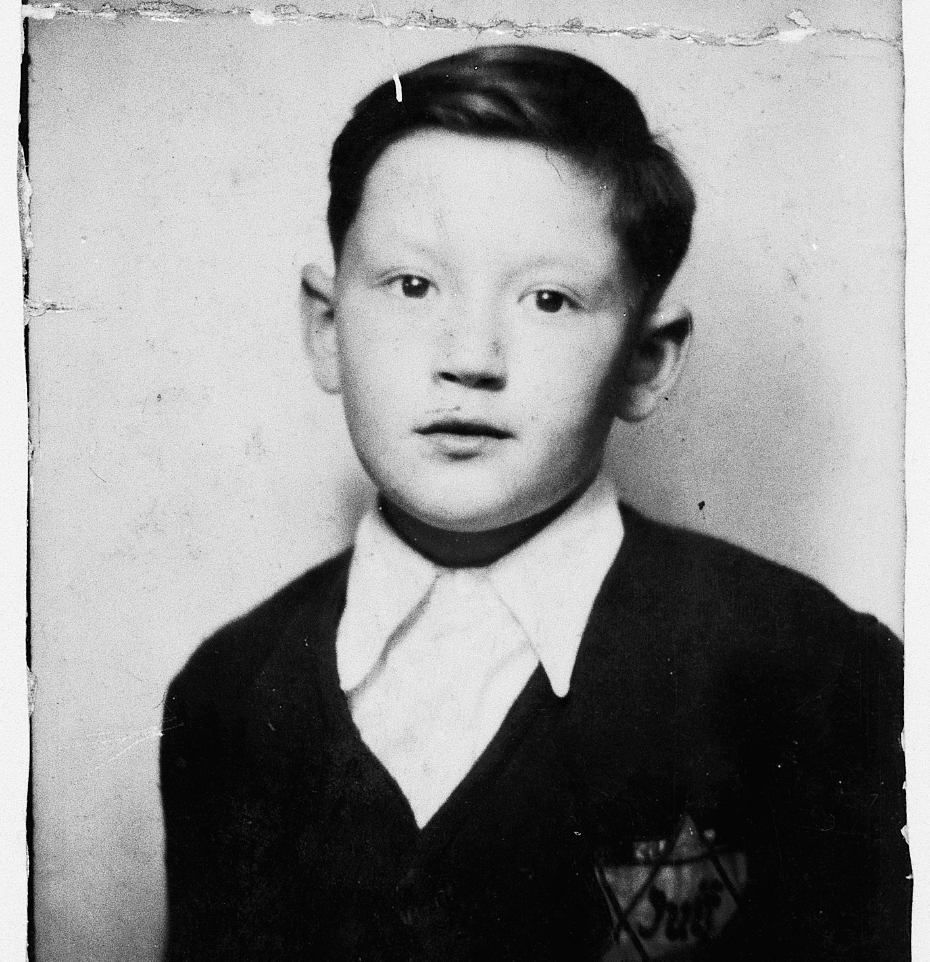
LearningCurve
After reading the chapter, use LearningCurve to retain what you’ve read.
> CHRONOLOGY
| 1921 | 1935 |
| New Economic Policy in Soviet Union | Mussolini invades Ethiopia; creation of U.S. Works Progress Administration as part of New Deal |
| 1922 | 1936 |
| Mussolini seizes power in Italy | Start of great purges under Stalin; Spanish Civil War begins |
| 1924– |
1936– |
| Buildup of Nazi Party in Germany | Popular Front government in France |
| 1925 | 1939 |
| Hitler, Mein Kampf | Germany occupies Czech lands and invades Poland; Britain and France declare war on Germany, starting World War II |
| 1927 | 1940 |
| Stalin comes to power in Soviet Union | Japan signs formal alliance with Germany and Italy; Germany defeats France; Battle of Britain |
| 1928 | 1941 |
| Stalin’s first five- |
Germany invades Soviet Union; Japan attacks Pearl Harbor; United States enters war |
| 1929 | 1941– |
| Start of collectivization in Soviet Union; Lateran Agreement | The Holocaust |
| 1929– |
1944 |
| Great Depression | Allied invasion at Normandy |
| 1931 | 1945 |
| Japan invades Manchuria | Atomic bombs dropped on Japan; World War II ends |
| 1932– |
|
| Famine in Ukraine | |
| 1933 | |
| Hitler appointed chancellor in Germany; Nazis begin control of state and society |