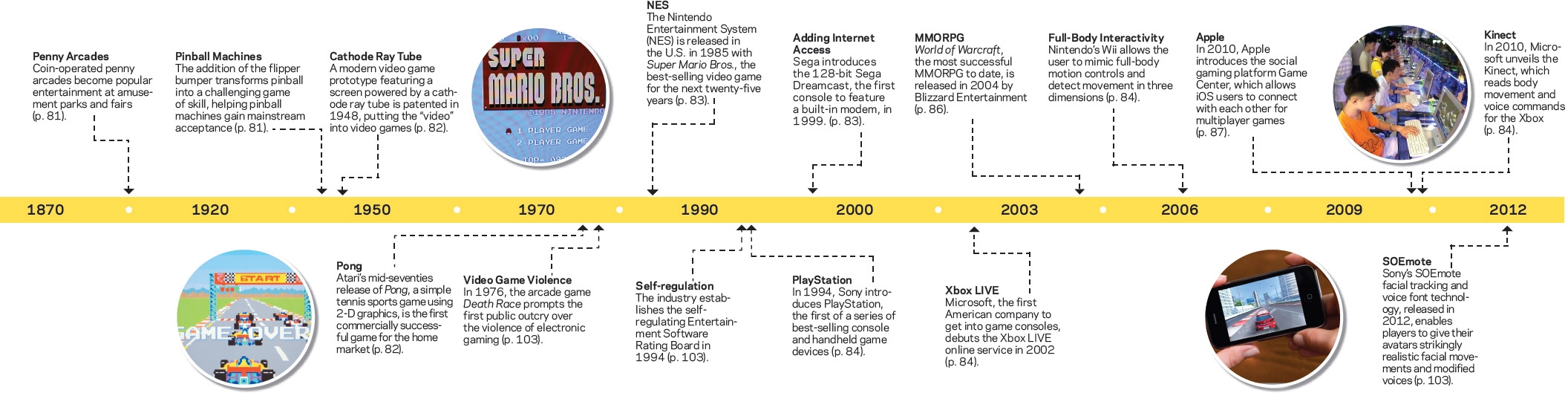
The Development of Digital Gaming
When the Industrial Revolution swept Western civilization two centuries ago, the technological advances involved weren’t simply about mass production. They also promoted mass consumption and the emergence of leisure time—both of which created money-making opportunities for media makers. By the late nineteenth century, the availability of leisure time sparked the creation of mechanical games like pinball. Technology continued to grow, and by the 1950s computer science students in the United States had developed early versions of the video games we know today.
In their most basic form, digital games involve users in an interactive computerized environment where they strive to achieve a desired outcome. These days, most digital games go beyond a simple competition like the 1975 tennis-style game of Pong: They often entail sweeping narratives and offer imaginative and exciting adventures, sophisticated problem-solving opportunities, and multiple possible outcomes.
But the boundaries were not always so varied. Digital games evolved from their simplest forms in the arcade into four major formats: television, handheld devices, computers, and the Internet. As these formats evolved and graphics advanced, distinctive types of games emerged and became popular. These included action games, sports games, shooter games, family entertainment games, role-playing games, adventure games, racing games, strategy games, fighting games, simulation games, computerized versions of card games, fantasy sports leagues, and virtual social environments. Together, these varied formats constitute an industry that analysts predict will reach $91 billion in annual revenues worldwide by 2015—and one that has become a socially driven mass medium.3
Digital Gaming and the Media Playground