THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
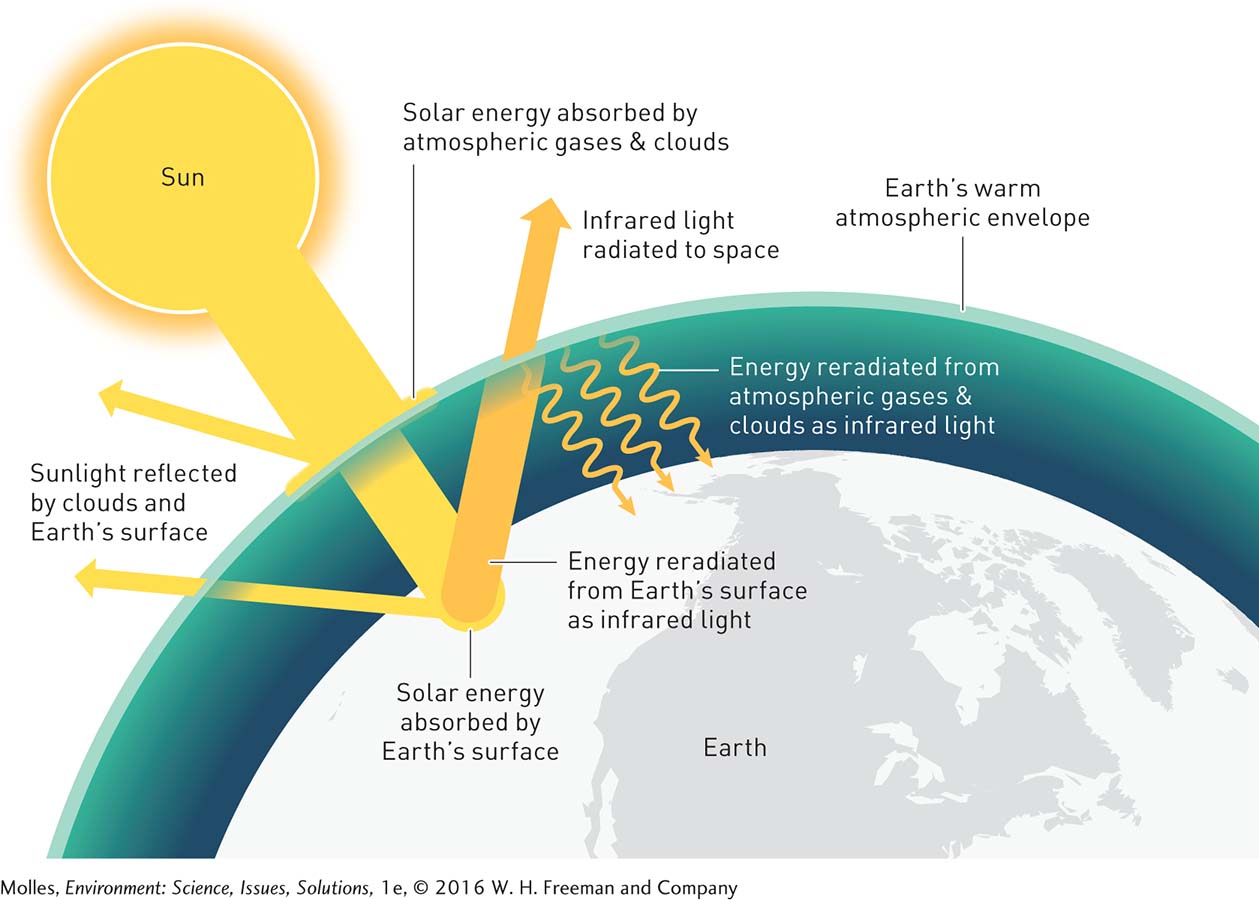
FIGURE 14.4 Earth’s atmosphere is relatively transparent to incoming sunlight, absorbing mainly in the infrared and ultraviolet ranges. Sunlight not reflected is absorbed by atmospheric gases, clouds, and Earth’s surface. Solar energy absorbed by Earth’s surface, clouds, or atmospheric gases is radiated as infrared light, heating Earth’s surface and atmosphere in the process.