OSMOSIS MOVES WATER ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE
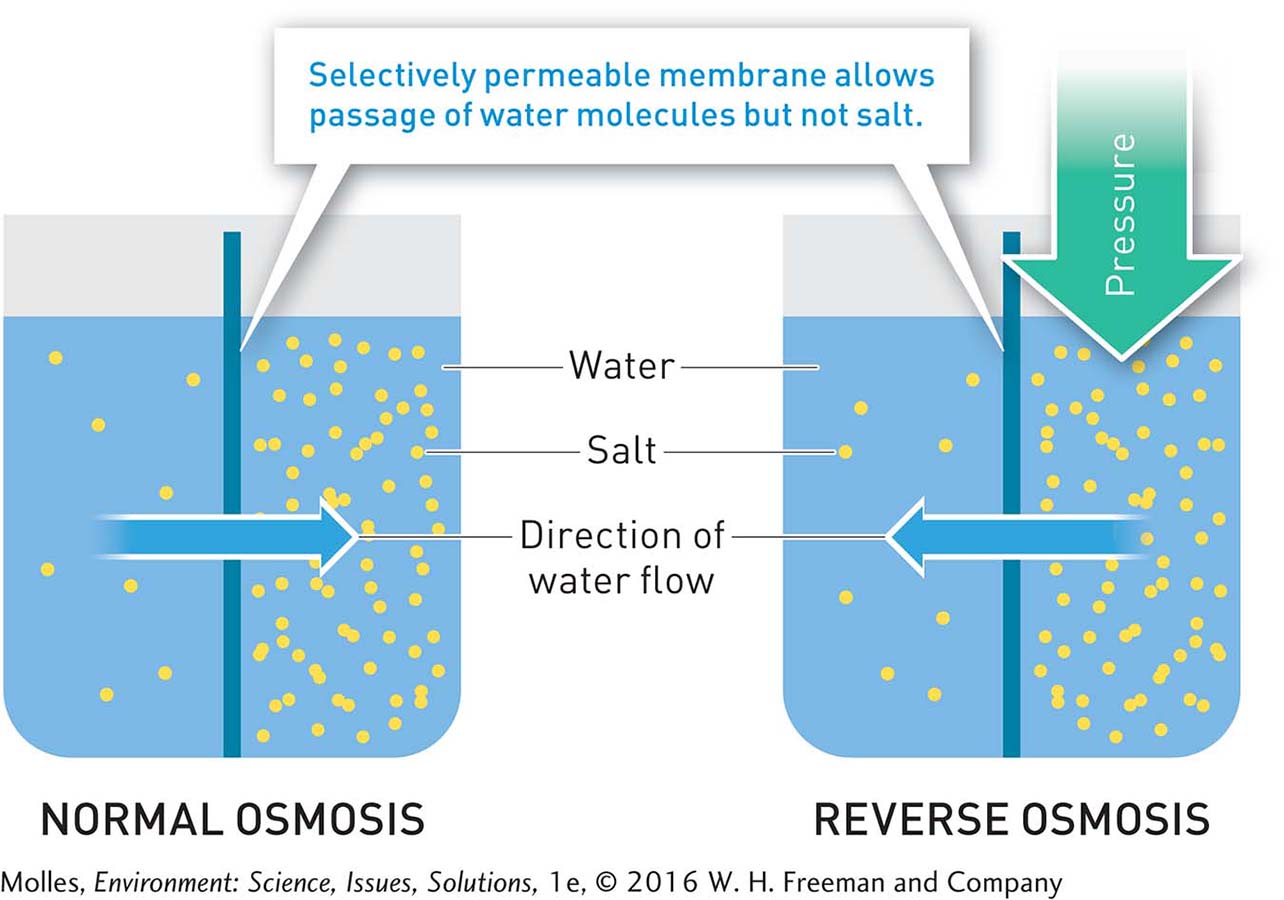
FIGURE 6.32 During the natural process of osmosis, water moves from the side of a selectively permeable membrane on which the concentration of salts is lower to the side on which the concentration of salts is higher. Reverse osmosis changes (“reverses”) this normal direction of flow by applying physical pressure to the side of the membrane with higher salt content, forcing water to move toward the side of the membrane with the lower salt content.