11.5 Misuse and overuse have promoted resistance to antibiotics and insecticides
antibiotics Substances that suppress bacterial growth or attack and that are used in modern medicine in the treatment of bacterial diseases.
In March 2013 the director of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC), Tom Frieden, held a press conference to discuss a “nightmare bacteria” killing patients in long-
Furthermore, it appears that CRE are spreading. In the first half of 2012 alone, nearly 200 medical facilities treated at least one patient who was infected with these bacteria. Scientists at the CDC have tracked CRE from a single health-
MRSA (methicillin-
Why is the spread of CRE an environmental issue? If it were a single deadly case, it would be a tragedy for the patient and the patient’s family, but it is an environmental issue because antibiotic resistant bacteria do not remain isolated. For example, penicillin, the first antibiotic to be discovered, became available for clinical use in 1944 and in 1945 the first penicillin-
mutation A change in the structure of an organism’s DNA, i.e., in its genes.
Though drug resistance evolves as bacteria adapt through mutation and natural selection, human behavior is also implicated. Failure to take antibiotics as prescribed, as well as overuse of antibiotics, leads to increased prevalence of antibiotic resistance in bacterial populations. Health providers sometimes prescribe antibiotics for patients who ask for them, even when there is no medical necessity. Antibiotics will not cure a cold, for instance, because viruses cause colds and antibiotics have no effect on viruses. Regardless, many people demand them from their doctors or get them from friends in the belief that antibiotics can cure anything.
The overuse of these drugs can speed up the natural selection process for antibiotic resistance. This is because one mode of competition among microorganisms is the production and release of antibiotics. Thus, bacteria were coping with naturally occurring antibiotics billions of years before humans started to use antibiotics to treat bacterial infections. Penicillin is produced by the mold Penicillium crysogenum, and most antibiotics used in medicine are still derived from microorganisms. Thus, exposure to antibiotics and the evolution of antibiotic resistance have been part of bacterial biology throughout their evolutionary history. What is new is the use of antibiotics to treat infections, the high frequency of antibiotic resistance found in bacteria in some settings, and the increasing occurrence of bacteria that are resistant to multiple antibiotics (Figure 11.12). The consequences of these new factors have enormous significance for human health.
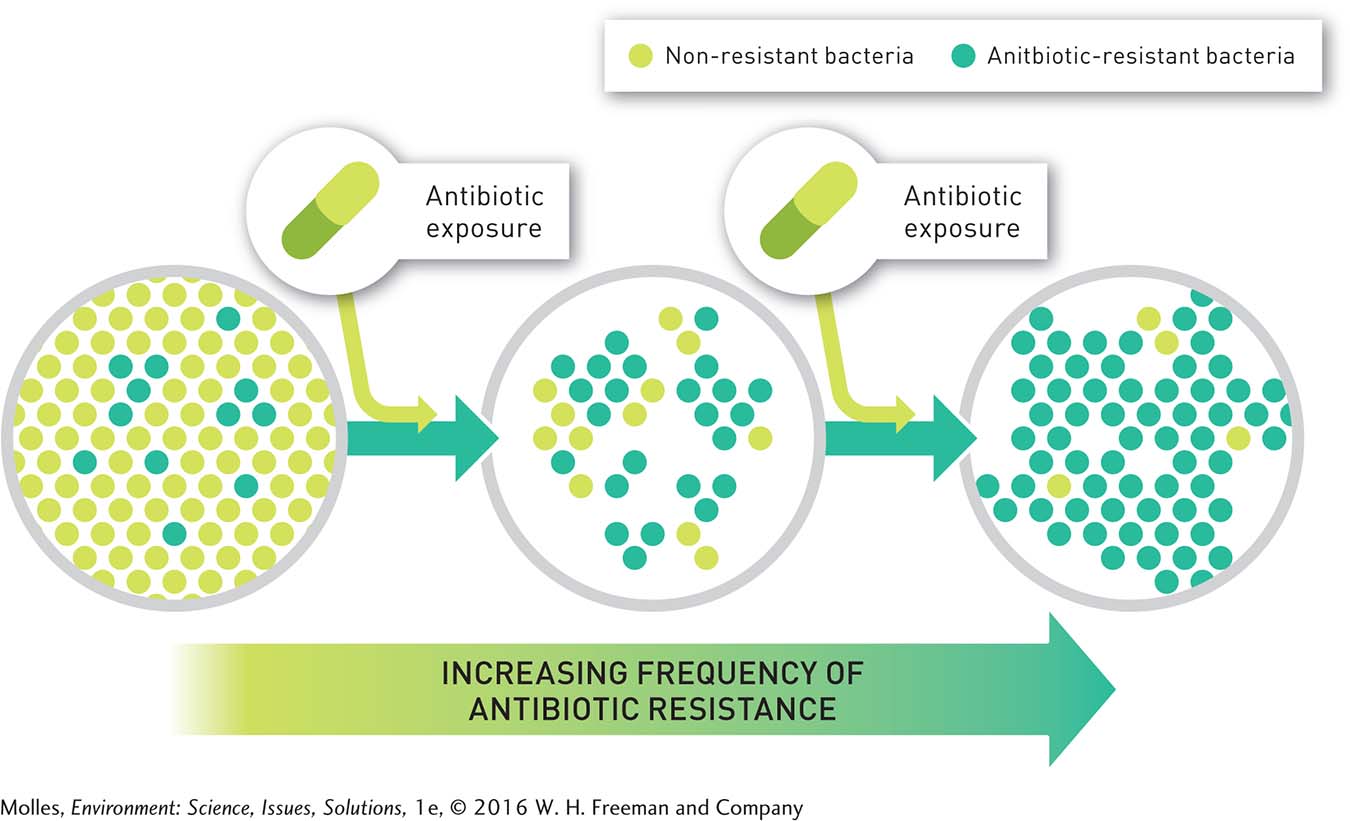
Industrial Meat Production and Antibiotic Resistance
Medical misuse and overuse of antibiotics are important issues, but the use of antibiotics as growth promoters in agriculture overshadows them. Antibiotics—
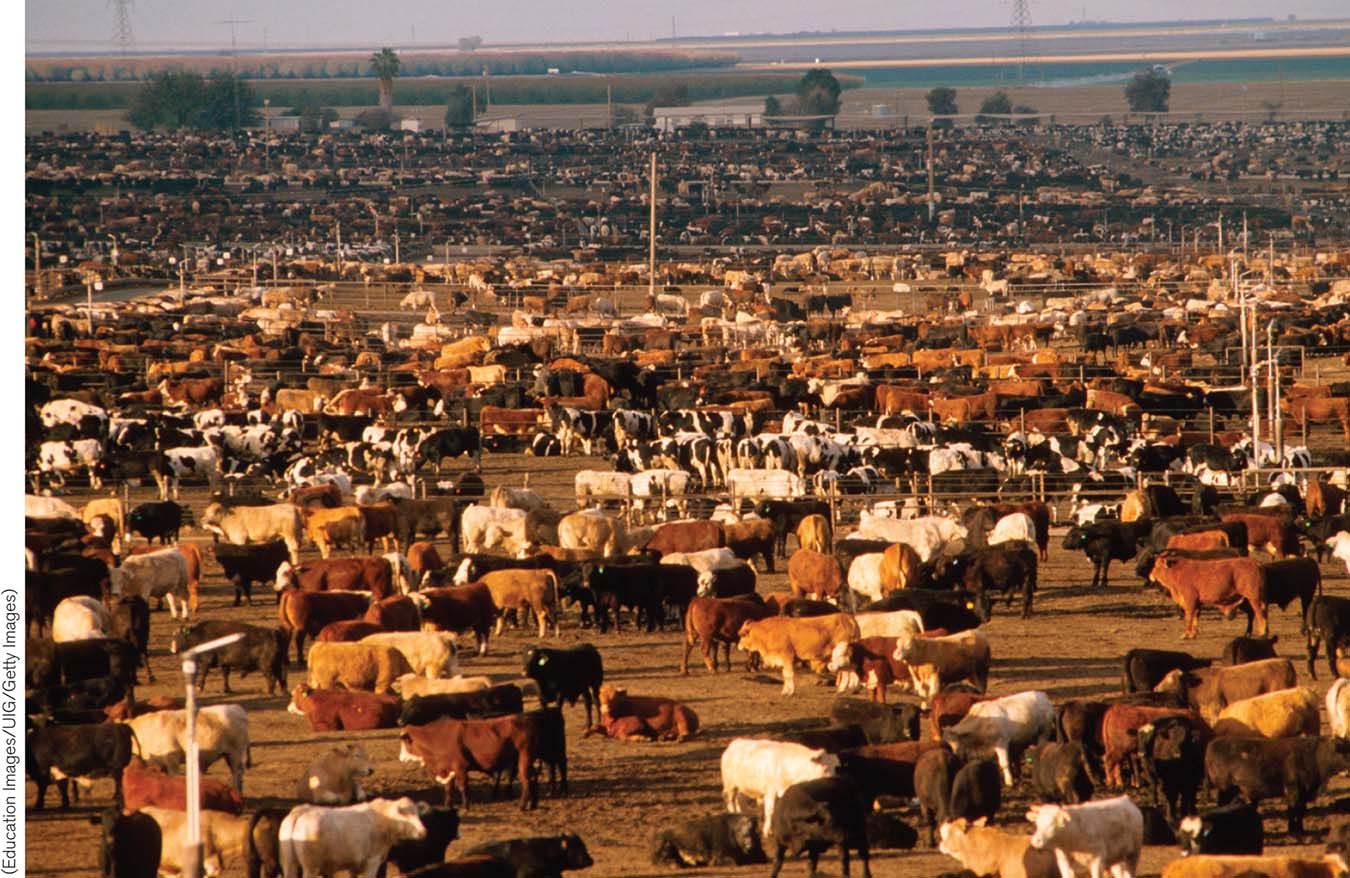

Meat producers in the United States administer more antibiotics per kilogram of meat produced than in any other country. A study by the Pew Charitable Trusts estimated that in 2011, 13.6 million kilograms (30 million pounds) of antibiotics were used in the production of food-

Do individuals have an ethical obligation to the larger community to avoid misusing antibiotics?
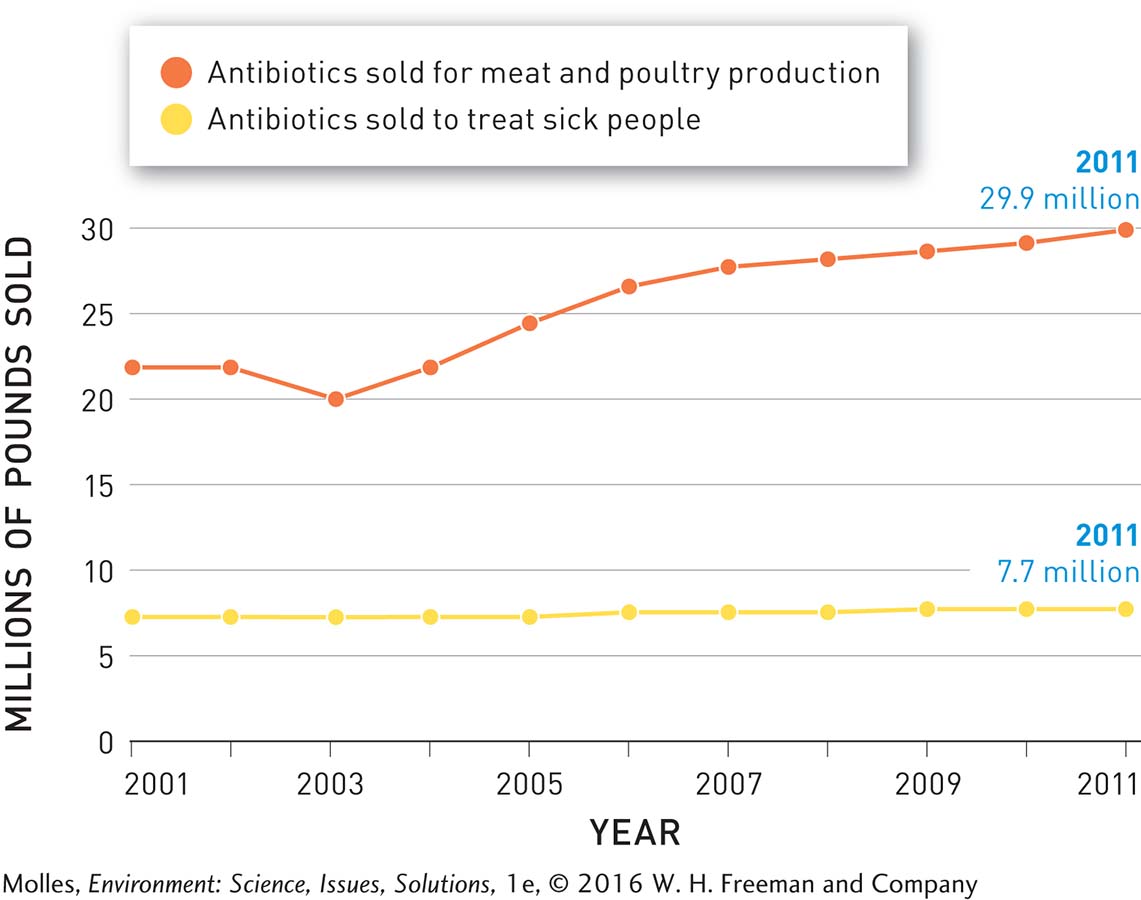
It is hard to imagine a more effective method of selecting for antibiotic resistance than to expose bacteria in the guts of livestock to constant low levels of antibiotics. Resistant bacteria that originated in livestock have been found in soil, ponds, and groundwater near sites where large numbers of animals are being reared. Furthermore, the transfer of antibiotic-

Might livestock farmers be able to develop a profitable market for meat produced without the overuse of antibiotics?
Antibiotic-
Think About It
What drives antibiotic resistance?
How do the large population sizes and short generation time of pathogenic bacteria add to the challenge of controlling them?
Is antibiotic resistance just about the misuse of antibiotics?