14.10 Reducing greenhouse gas emissions provides new economic opportunities
In order to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by implementing new technologies, for example, some industries that depend heavily on fossil fuels will have to spend more money to maintain their businesses at the same level as they have in the past. However, considering only the new costs incurred by an existing company is but one part of the equation. When a company is forced to spend money, another company earns money by selling goods and services. If we lose one job in the fossil fuel industry, we may gain a job in the green energy sector. That’s exactly what has happened with solar energy in the United States, which gained 14,000 jobs between 2010 and 2012, while fossil fuel lost 4,000 jobs. If you look around, you’ll see that innovative new businesses are already emerging to capitalize on solutions to the climate change problem.
Repowering Transportation
You may have seen pictures of the Tesla roadster, a high-
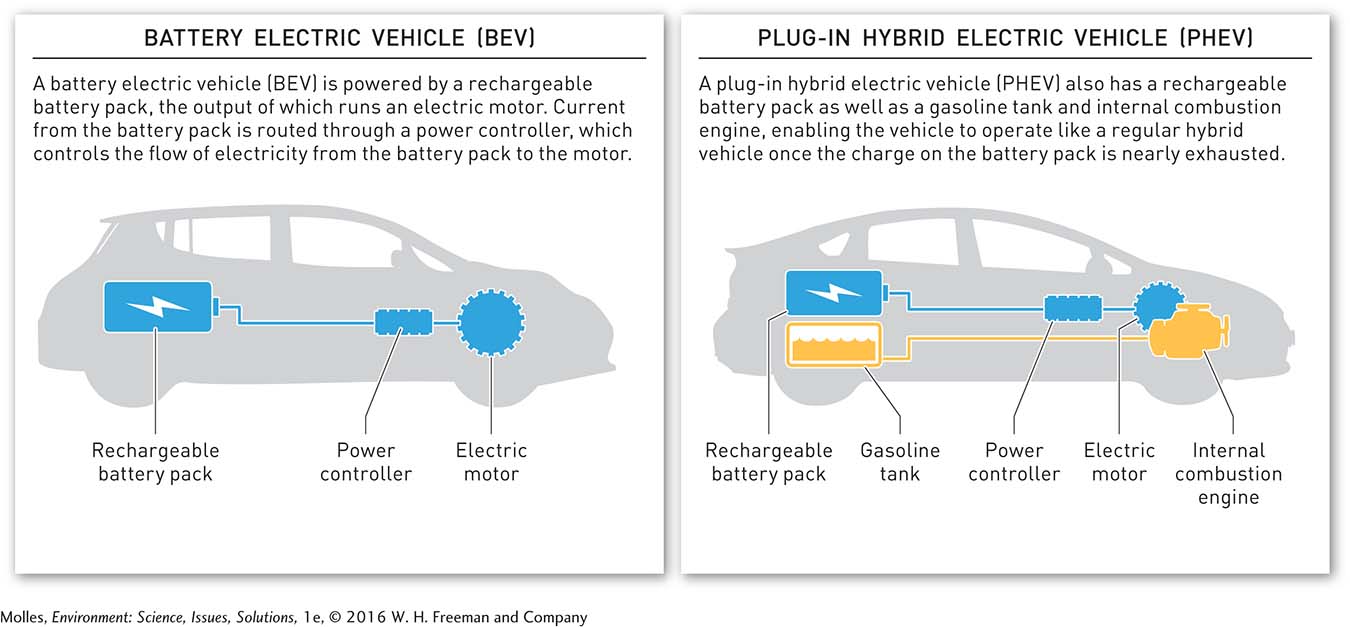
The two major types of electric vehicles on the road today include the battery electric vehicle, or BEV, and the plug-
Biofuels, including ethanol produced from corn and plant matter or biodiesel produced from cooking grease or algae, are also a promising strategy to reduce the use of fossil fuels in transportation, and a variety of companies have emerged to do just that. In theory, biofuel crops will reabsorb a fraction of the greenhouse gas emissions released from the previous year. However, technologies for efficiently producing a gasoline replacement from terrestrial crops or algae are in their infancy (see Chapter 10).
Green Building Saves Money and Creates Jobs
One of the biggest incentives for companies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is that it can save them money. When researchers at Architecture 2030—

Many states, cities, and individuals have committed themselves to more efficient construction. One of the highest profile examples is that of New York City, where former Mayor Michael Bloomberg approved a plan to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 30%. It turns out that nearly 75% of the energy consumed in New York is used to run its 1 million buildings, which is well above the national average.
Bloomberg commissioned a study that found some buildings used 3 to 5 times the amount of energy per unit area, compared with other buildings with similar uses. As a result of such discoveries, efforts to improve energy efficiency in the city could focus on those buildings where efforts will produce the greatest results. One of the main targets is to install more efficient lighting when it is lacking. Another is to “retro-
Cleaner Technologies Reduce Soot
The developing world has its own particular set of energy problems to deal with. The wood stoves and dirty coal generators used in countries like India and China do not completely burn their fuel, and they release soot in addition to greenhouse gases. Soot is a dark, powdery form of carbon that is particularly potent when it comes to heating up the atmosphere because it directly absorbs sunlight while it is floating in the air or after it lands and darkens reflective surfaces such as snow. One recent study in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres concluded that soot was more important than methane and was second only to carbon dioxide in contributing to climate change.
The good news is that soot only stays in the atmosphere for a few weeks and is washed away by rain or covered up by new snowfall. Because soot causes health problems, such as lung cancer, a transition to cleaner forms of cooking and power generation would be good for the climate and for human health. The Indian startup Prakti is already trying to profit from this transition, developing cleaner-
Think About It
How do you think the “cost” of staving off climate change will impact a country’s gross domestic product?
Can you think of industries affected by technological shifts to cleaner energy that no longer employ as many people as they once did?
If you were an entrepreneur, what company would you start to capitalize on the green economy?