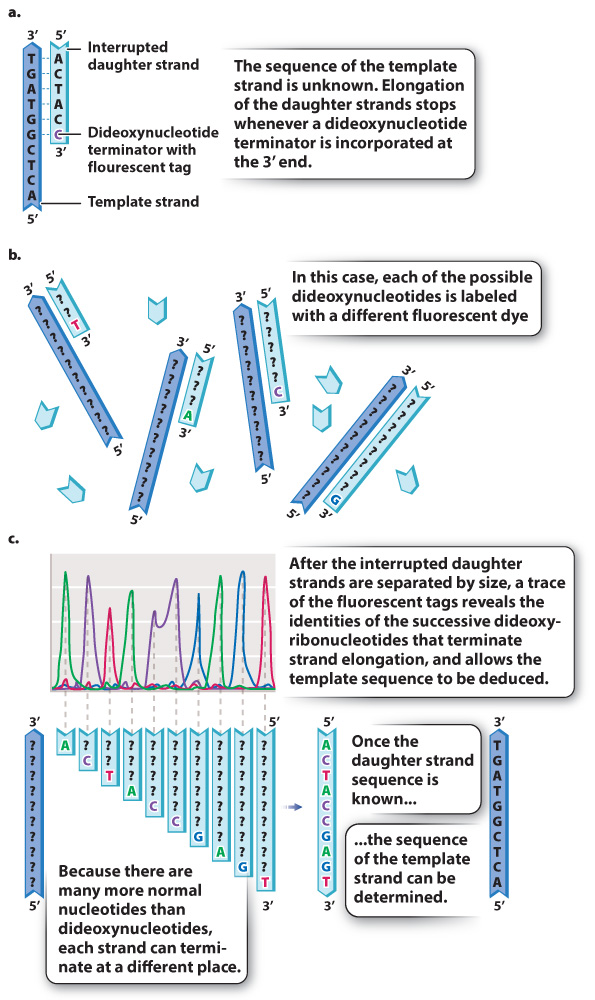
FIG. 12.18 Sanger sequencing. (a) The incorporation of an incoming dideoxynucleotide stops the elongation of a new strand. (b) Dideoxynucleotides terminate strands at different points in the template sequence. (c) Separation of interrupted daughter strands by size shows where each terminator was incorporated and hence the identity of the corresponding nucleotide in the template strand.
[Leave] [Close]