HOW DO WE KNOW?
FIG. 18.10
What is the relative importance of genes and of the environment for complex traits?
BACKGROUND Twin studies remain important for assessing the relative importance of “nature” (genotype) and “nurture” (environment) in determining variation among individuals for complex traits. The idea of using twins to distinguish nature from nurture is usually attributed to Francis Galton because of an article he wrote about twins in 1875. In fact, the modern twin study does not trace to Galton but to Curtis Merriman in the United States and Hermann Siemens in Germany, who independently hit upon the idea in 1924. In Galton’s time, it was not even known that there are genetically two kinds of twins.
EXPERIMENT The rationale of a twin study is to compare identical twins with same-
RESULTS The bar graph shows the results of typical twin studies for various traits. The concordance between twins is the fraction of twin pairs in which both twins show the trait among all those pairs in which at least one twin shows the trait. Roughly speaking, the difference in the concordance between identical twins and fraternal twins is a measure of the relative importance of genotype. In the data shown here, for example, autism and clinical depression both show strong genetic influences, whereas female alcoholism shows almost no genetic influence.
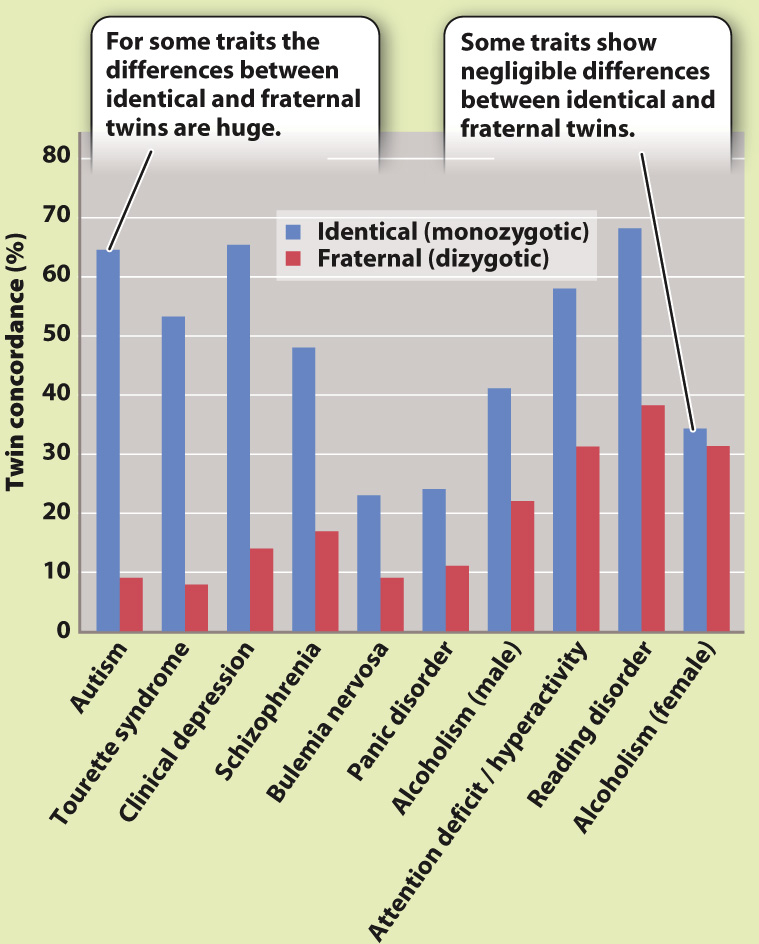
CONCLUSION The examples shown here indicate very large differences in the importance of genotype versus environment among complex traits. These results are typical of most complex traits.
FOLLOW-
SOURCES Rende, R. D., R. Plomin, and S. G. Vandenberg. 1990. “Who Discovered the Twin Method?” Behavior Genetics 20:277–