Extracellular matrix proteins influence cell shape and gene expression.
Cells continue to interact with the extracellular matrix long after they have synthesized it or moved into it, and these interactions can have profound effects on cell shape and gene expression. Some of these cellular responses are the result of interactions between the extracellular matrix and integrins on the cell surface. The integrins act as receptors that relay the signal to the interior of the cell as the first step in a signal transduction pathway, like those discussed in Chapter 9. Biologists have observed the results of these interactions in experiments conducted with cells grown in culture in the laboratory.
An example shows how the structure of the extracellular matrix can influence the shape of cells. Fibroblasts cultured on a two-
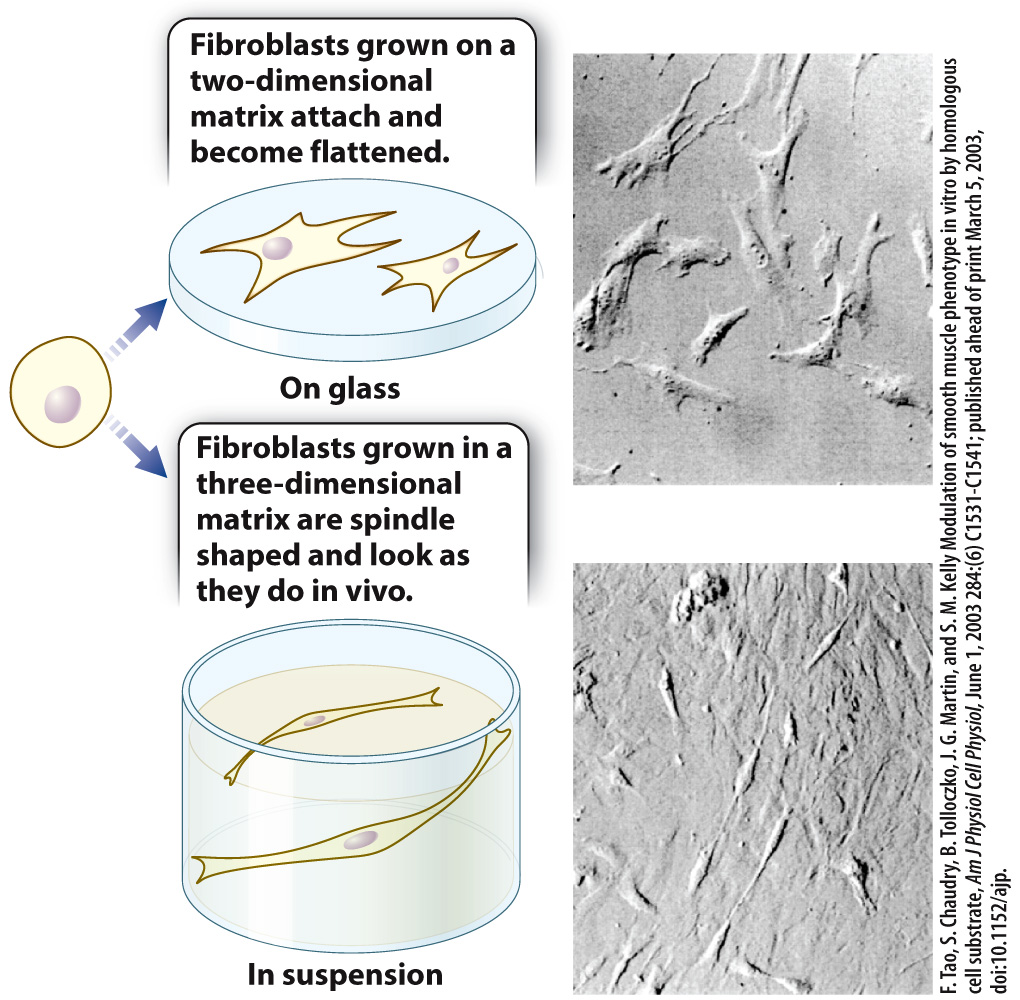
A second example shows how the composition of the extracellular matrix can influence cell shape. When nerve cells are grown in culture on a plastic surface, they attach to the surface of the dish but do not take on a neuron-
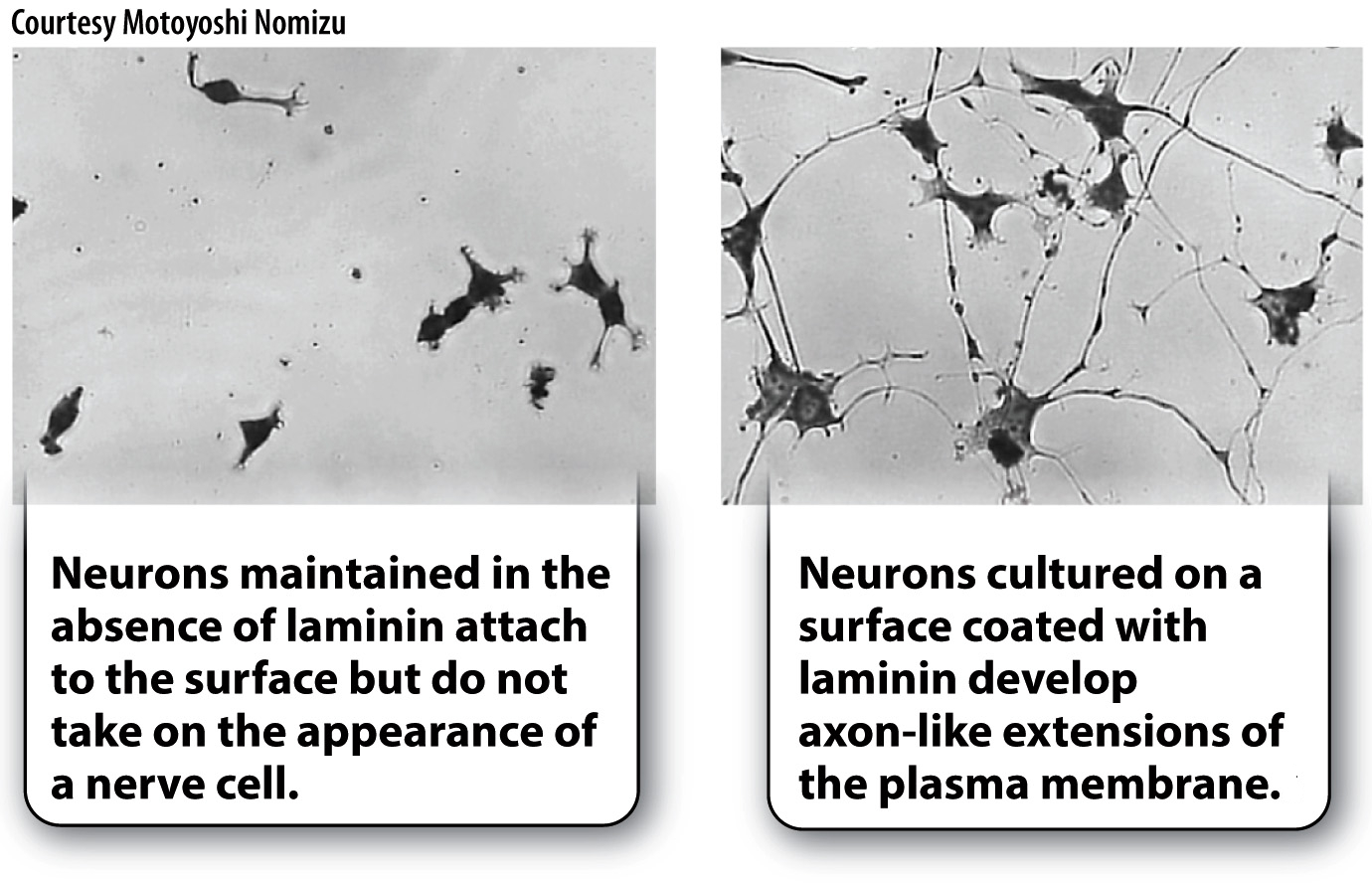
In addition to influencing cell shape, the structure and composition of the extracellular matrix can influence gene expression of the cells that are grown in it. When stimulated by the milk-
Quick Check 4 Do you think cadherins or integrins are responsible for the dependence of mammary cells on the extracellular matrix for their ability to produce milk proteins? Why?
Quick Check 4 Answer
Integrins are responsible for the production of milk proteins by mammary cells in response to the extracellular matrix because integrins bind extracellular matrix proteins. By contrast, cadherins bind to other cadherins when cells adhere to other cells.
An experiment that explores the importance of the composition of the extracellular matrix proteins in the regulation of gene expression is described in Fig. 10.22. This experiment, and the others described here, demonstrate that there is a dynamic interplay between the extracellular matrix and the cells that synthesize it.
HOW DO WE KNOW?
FIG. 10.22
Can extracellular matrix proteins influence gene expression?
BACKGROUND The adhesion of cells to the extracellular matrix is required for cell division, DNA synthesis, and proper cell shape. Research by Iranian-
HYPOTHESIS Caron hypothesized that a specific protein in the extracellular matrix is necessary for the expression of the protein albumin from hepatocytes grown in culture. Albumin is a major product of hepatocytes.
EXPERIMENT Caron cultured hepatocytes on a thin layer of type I collagen, which does not induce albumin synthesis. Next, she added a mixture of several different extracellular matrix proteins to the culture and looked for changes in albumin gene expression and protein secretion into the media. She then tested individual extracellular matrix proteins from the mixture to see which one was responsible for the increase in albumin gene expression.
RESULTS Caron found that when she cultured cells on collagen with a combination of three extracellular matrix proteins—
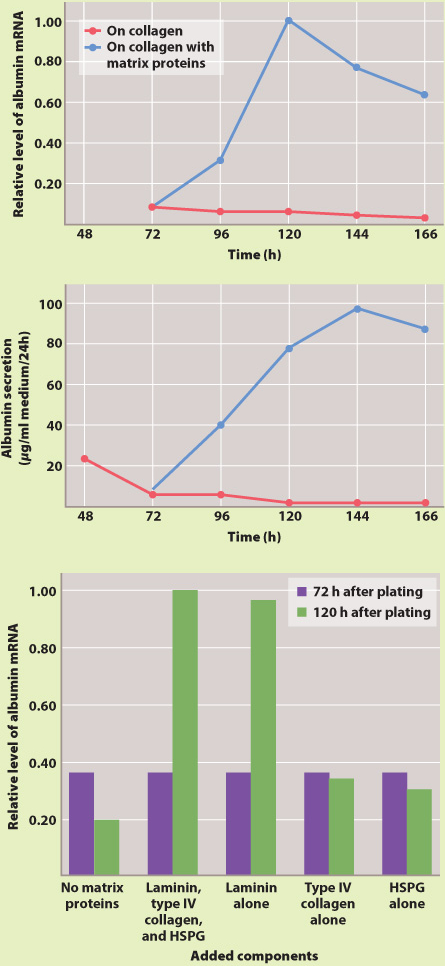
CONCLUSION Caron’s hypothesis was supported by the experiments. A specific extracellular matrix protein, laminin, influences the expression of albumin by hepatocytes.
FOLLOW-
SOURCES Lee, E. Y., et al. 1985. “Interaction of Mouse Mammary Epithelial Cells with Collagen Substrata: Regulation of Casein Gene Expression and Secretion.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 82:1419–