The parent cell divides into two daughter cells by cytokinesis.
Usually, as mitosis is nearing its end, cytokinesis begins and the parent cell divides into two daughter cells (Fig. 11.7). In animal cells, this stage begins when a ring of actin filaments, called the contractile ring, forms against the inner face of the cell membrane at the equator of the cell perpendicular to the axis of what was the spindle (Fig. 11.7a). As if pulled by a drawstring, the ring contracts, pinching the cytoplasm of the cell and dividing it in two. This process is similar to what occurs in binary fission, though in the case of binary fission, the process is driven by FtsZ protein, a homolog of tubulin, not by actin. The constriction of the contractile ring is driven by motor proteins that slide bundles of actin filaments in opposite directions. Successful division results in two daughter cells, each with its own nucleus. The daughter cells are now free to enter G1 phase and start the process anew.
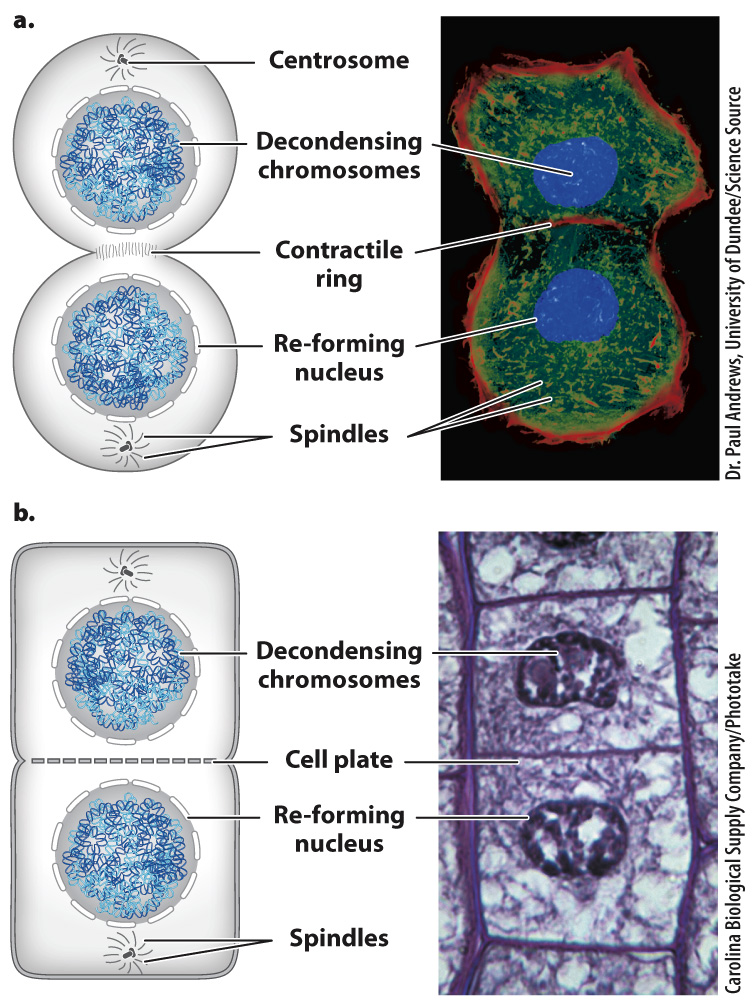
For the most part, mitosis is similar in animal and in plant cells, but cytokinesis is different (Fig. 11.7b). Since plant cells have a cell wall, the division of the cell is achieved by constructing a new cell wall. During telophase, dividing plant cells form a structure called the phragmoplast in the middle of the cell. The phragmoplast consists of overlapping microtubules that guide vesicles containing cell wall components to the middle of the cell. During late anaphase and telophase, these vesicles fuse to form a new cell wall, called the cell plate, in the middle of the dividing cell. Once this developing cell wall is large enough, it fuses with the original cell wall at the perimeter of the cell. Cytokinesis is then complete and the plant cell has divided into two daughter cells.
Quick Check 3 What would be the consequence if a cell underwent mitosis but not cytokinesis?
Quick Check 3 Answer
A cell that undergoes mitosis but not cytokinesis will become a single cell with two nuclei (and therefore with twice the normal amount of DNA); this type of cell is called a multinucleate cell.