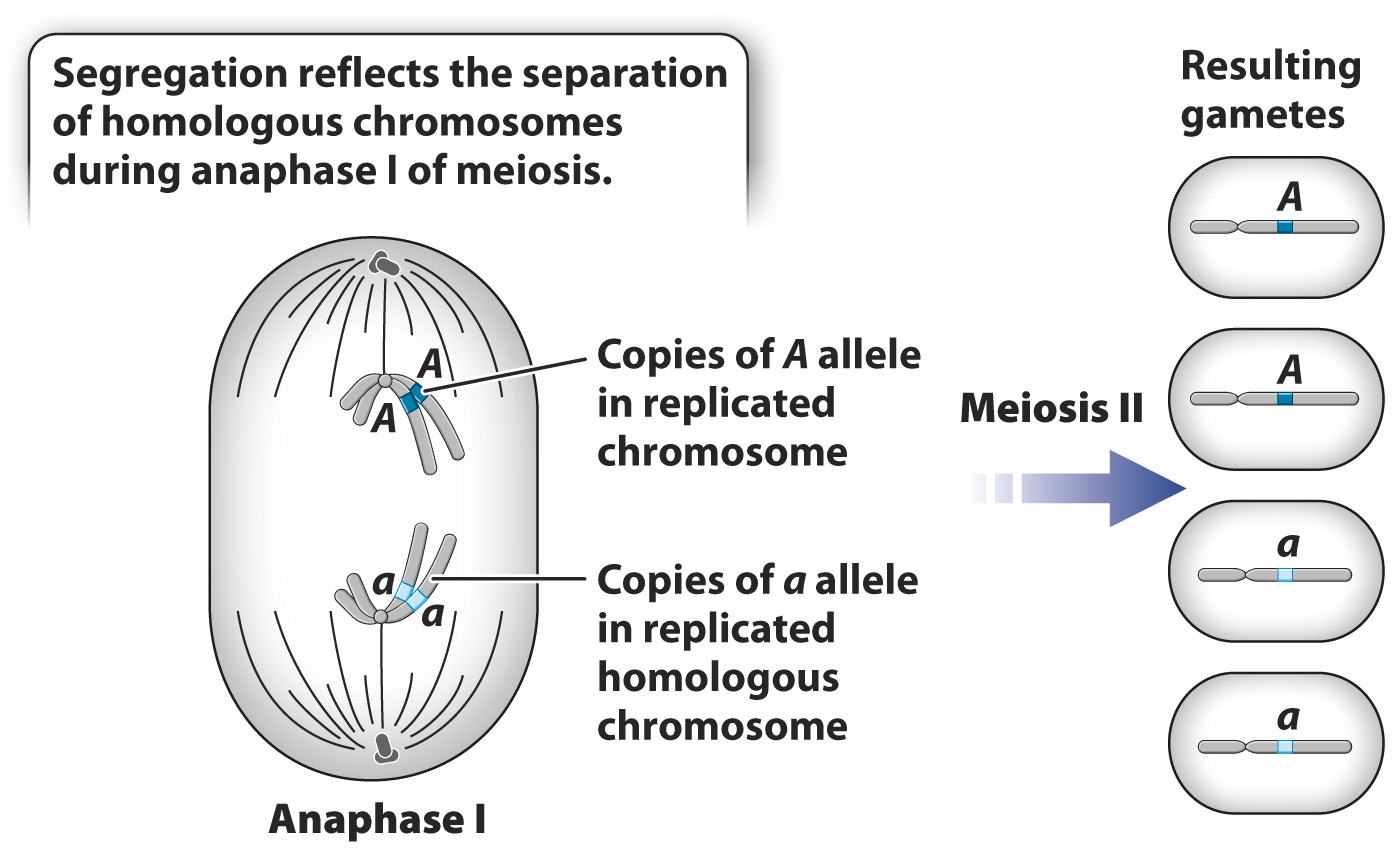
Segregation of alleles reflects the separation of chromosomes in meiosis.
The principles of transmission genetics have a physical basis in the process of meiosis (Chapter 11). During meiosis I, maternal and paternal chromosomes (homologous chromosomes) align on the metaphase plate. Then, during anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate, and each chromosome goes to a different pole. Because gene pairs are carried on homologous chromosomes, the segregation of alleles observed by Mendel corresponds to the separation of chromosomes that takes place in anaphase I.
Fig. 16.9 illustrates the separation of a pair of homologous chromosomes in anaphase I. In the configuration shown, the copies of the A allele (dark blue) separate from the copies of the a allele (light blue) in anaphase I. The separation of chromosomes is the physical basis of the segregation of alleles.