29.2 The Leaf: Acquiring CO2 While Avoiding Desiccation
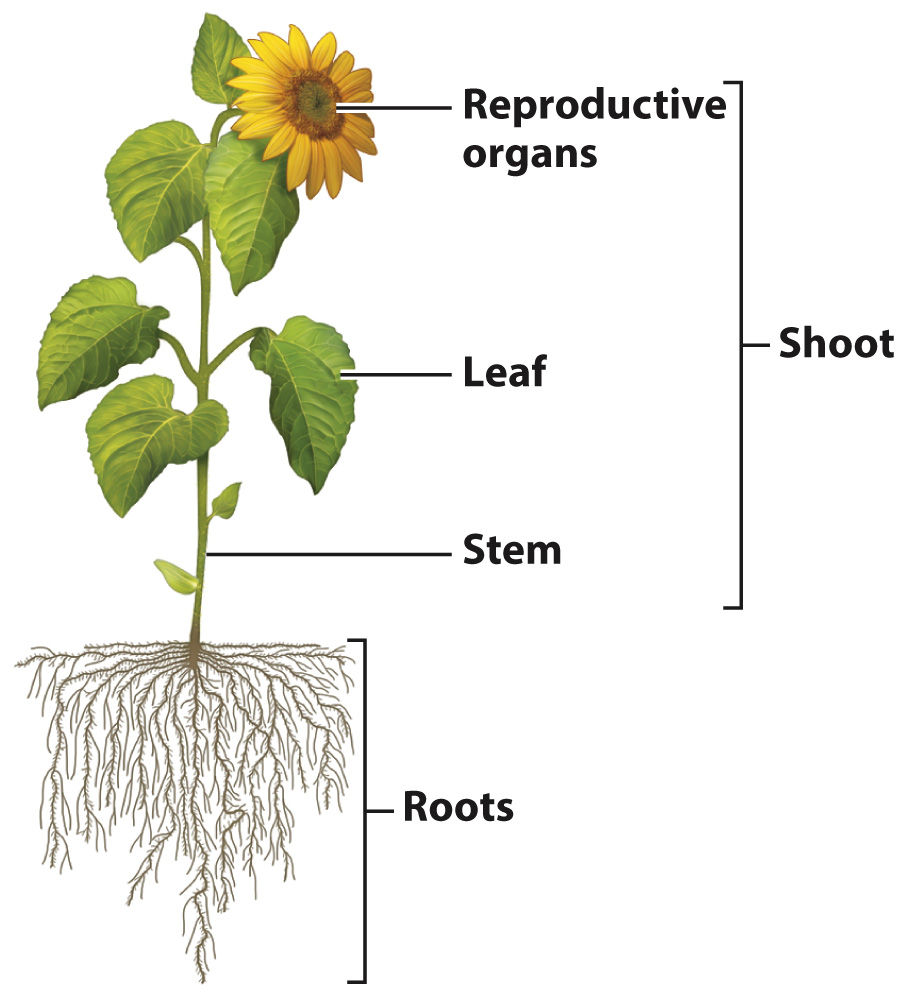
Fig. 29.3 shows the general features of a vascular plant. Aboveground, we see three major types of organ—
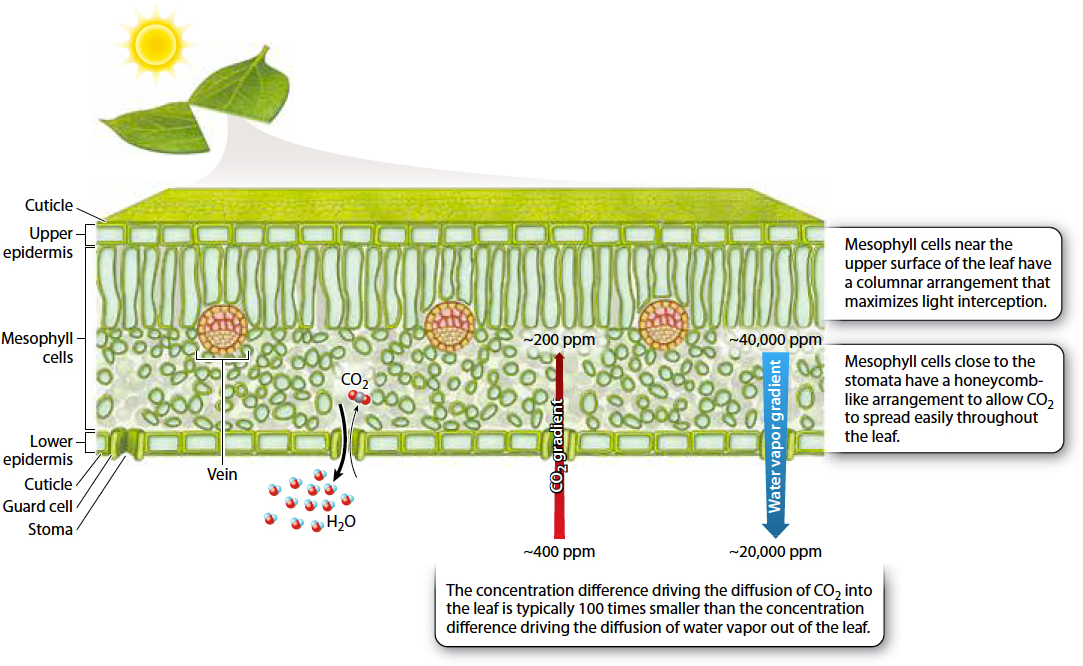
The leaf is the principal site of photosynthesis in vascular plants. A cross section shows the leaf’s three major tissues: Sheets of cells called the epidermis line the leaf’s upper and lower surfaces; loosely packed photosynthetic cells make up the mesophyll (literally, “middle leaf”); and the system of vascular conduits called veins connects the leaf to the rest of the plant (Fig. 29.4). We discuss how water and carbohydrates are transported through the vascular system in sections 29.3 and 29.4. In this section, we explore how the structure of leaves allows vascular plants to photosynthesize in air without drying out.