A chemical reaction involves breaking and forming chemical bonds.
The chemical bonds that link atoms in molecules can change in a chemical reaction, a process by which atoms or molecules, called reactants, are transformed into different molecules, called products. During a chemical reaction, atoms keep their identity but change which atoms they are bonded to.
For example, two molecules of hydrogen gas (2H2) and one molecule of oxygen gas (O2) can react to form two molecules of water (2H2O), as shown in Fig. 2.9. In this reaction, the numbers of each type of atom are conserved, but their arrangement is different in the reactants and the products. Specifically, the H–
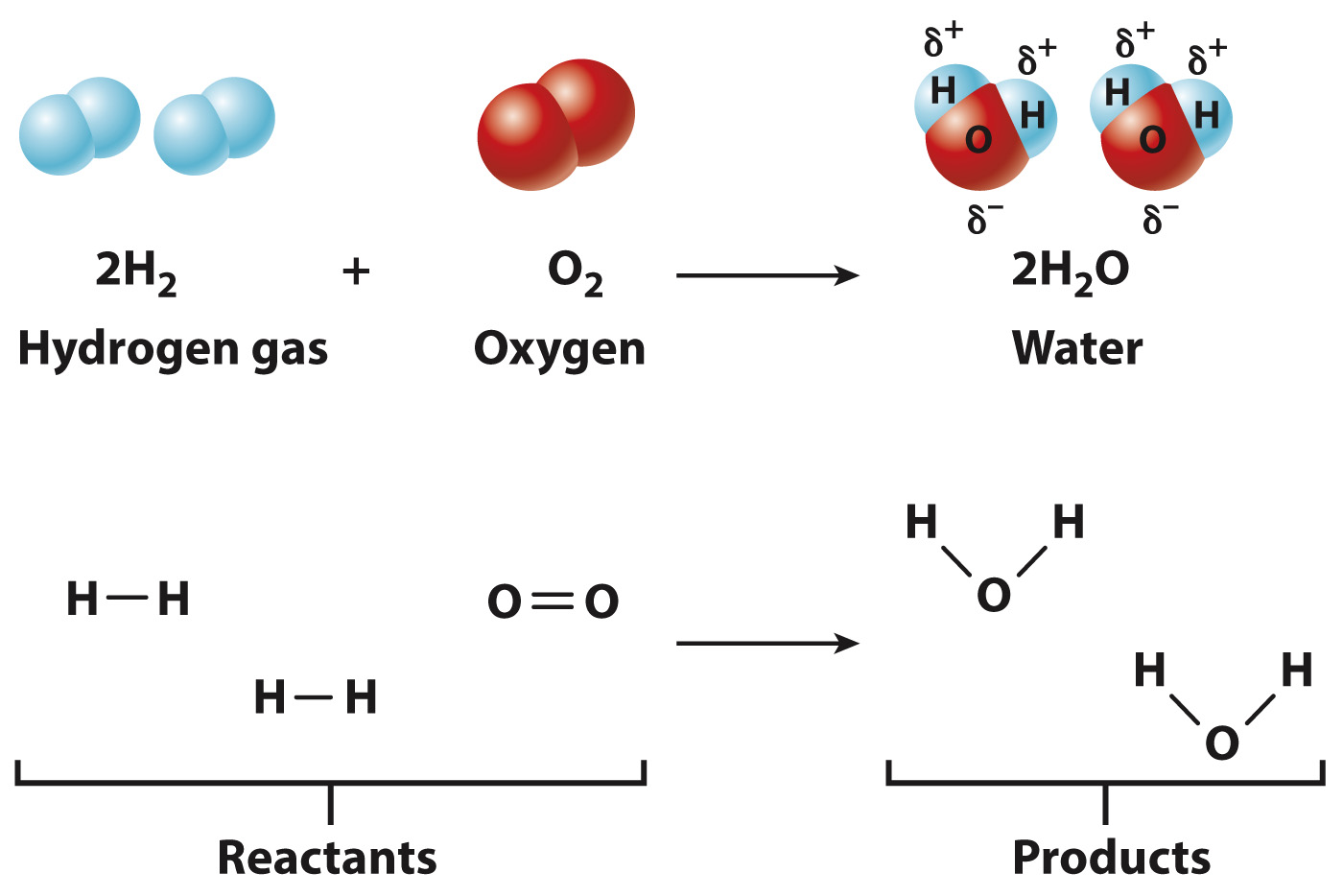
In biological systems, chemical reactions provide a way to build and break down molecules for use by the cell, as well as to harness energy, which can be held in chemical bonds (Chapter 6).