Local chemical signals regulate neighboring target cells.
Whereas hormones enter the bloodstream to be transmitted to more distant target cells (Fig. 38.13a), other chemical compounds act locally on neighboring cells (Fig. 38.13b). In order to take up the chemical signal, these cells must have receptors for the compound to bind to before it degrades or diffuses into the bloodstream.
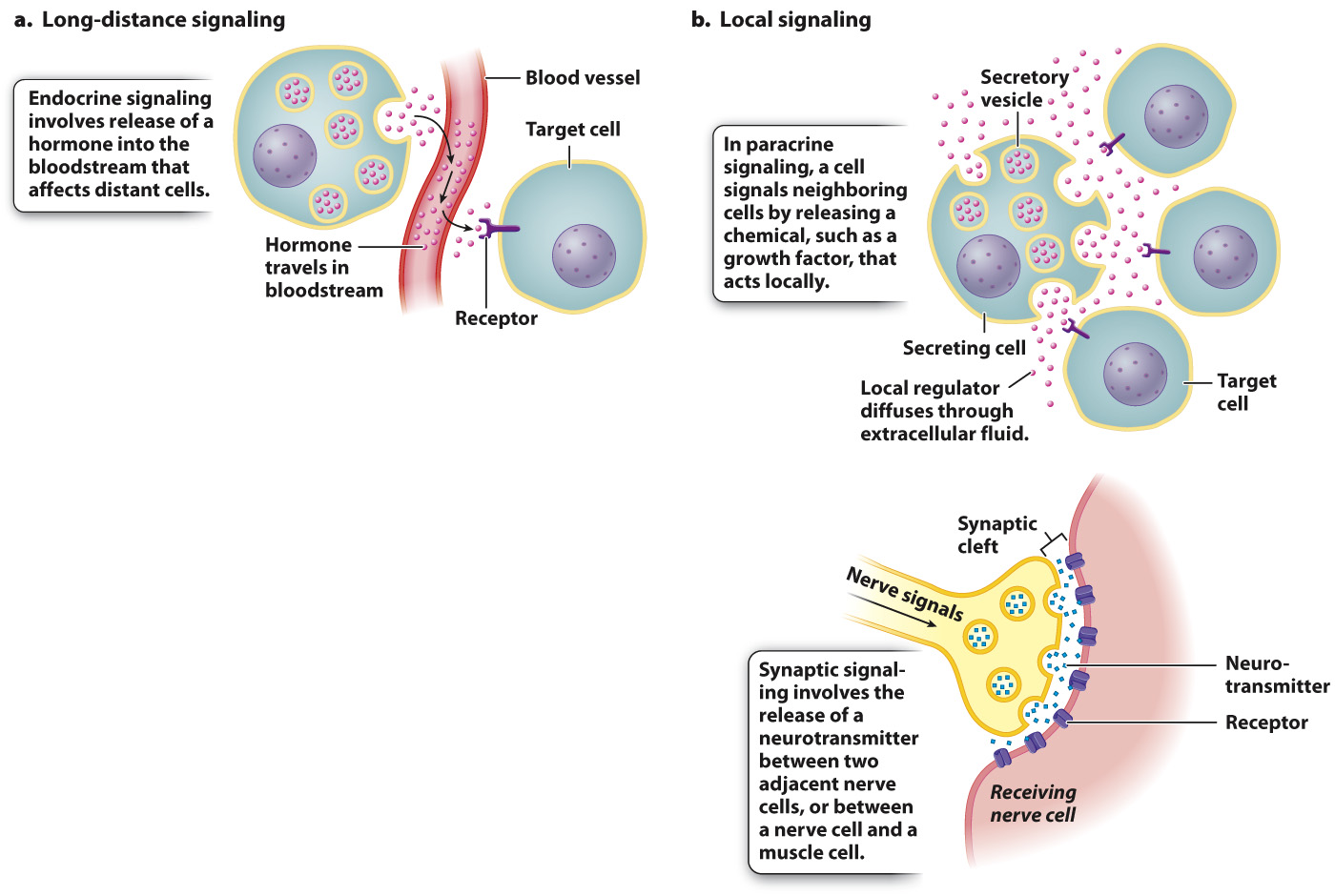
Chemical compounds that act locally are said to have paracrine function (Fig. 38.13b). If the compounds act on the secreting cell itself, they are said to have autocrine function—
Growth factors (Chapter 9) enhance the differentiation and growth of particular kinds of tissue. For example, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) promote the formation of bone in skeletal growth, and fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) stimulate the formation of connective tissue. Similarly, nerve growth factors (NGFs) promote the survival and growth of nerve cells. When tissues are damaged, specialized cells nearby release histamine. This chemical signal triggers the dilation of blood vessels, allowing blood proteins and white blood cells to move into the region to fight infection and induce repair (Chapter 43). The release of histamine causes the swelling, redness, and warmth that commonly surround a wound.
Another form of short-