Enzyme activity can be influenced by inhibitors and activators.
The activity of enzymes can be influenced by inhibitors and activators. Inhibitors decrease the activity of enzymes, whereas activators increase the activity of enzymes. Enzyme inhibitors are quite common. They are synthesized naturally by many plants and animals as a defense against predators. Similarly, pesticides and herbicides often target enzymes to inactivate them. Many drugs used in medicine are enzyme inhibitors, including drugs used to treat infections as well as drugs used to treat cancer and other diseases. Given the importance of chemical reactions and the role of enzymes in metabolism, it is not surprising that enzyme inhibitors have such widespread applications.
There are two classes of inhibitors. Irreversible inhibitors usually form covalent bonds with enzymes and irreversibly inactivate them. Reversible inhibitors form weak bonds with enzymes and therefore easily dissociate from them.
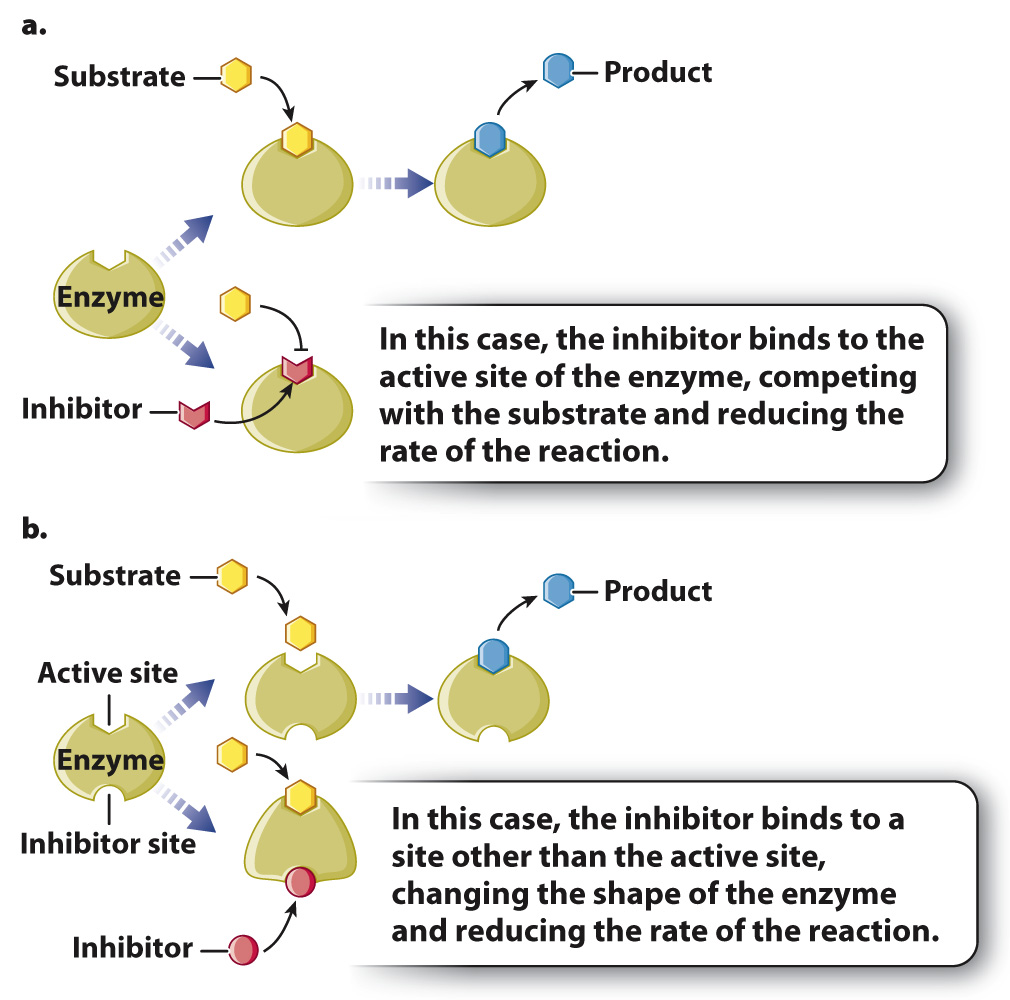
Inhibitors can act in many different ways, two of which are shown in Fig. 6.17. In some cases, an inhibitor is similar in structure to the substrate and therefore is able to bind to the active site of the enzyme (Fig. 6.17a). Binding of the inhibitor prevents the binding of the substrate. In other words, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active site of the enzyme. These types of inhibitors can often be overcome by increasing the concentration of substrate. Other inhibitors bind to a site other than the active site of the enzyme, but still inhibit the activity of the enzyme (Fig. 6.17b). In this case, binding of the inhibitor changes the shape and activity of the enzyme. This type of inhibitor usually has a structure very different from that of the substrate.
Enzymes that are regulated by molecules that bind at sites other than their active sites are called allosteric enzymes. The activity of allosteric enzymes can be influenced by both inhibitors and activators. They play a key role in metabolic pathways, as we discuss next.