Excess light energy can cause damage.
Photosynthesis is an inherently dangerous enterprise. Unless the photosynthetic reactions are carefully controlled, molecules will be formed that can damage cells through the indiscriminate oxidization of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (Fig. 8.16).
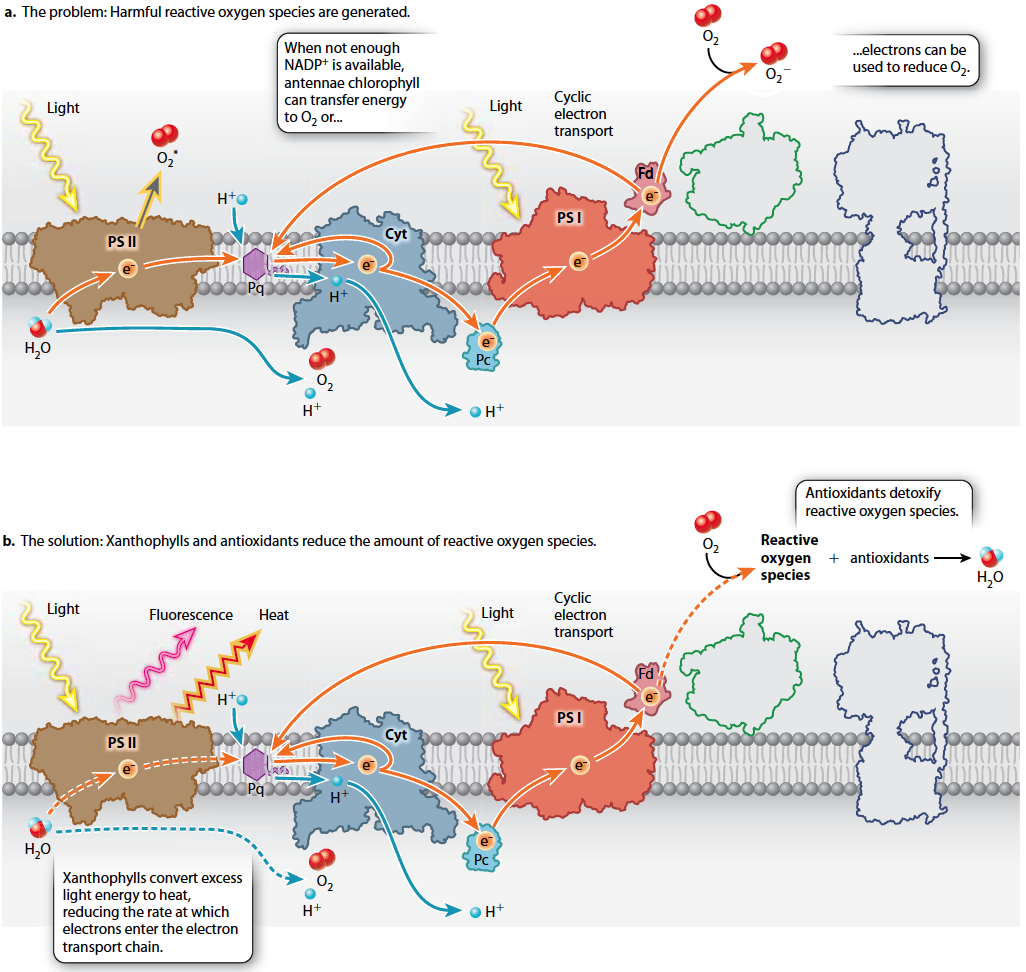
Under normal conditions, the photosynthetic electron transport chain proceeds in an orderly fashion from the absorption of light to the formation of NADPH. However, when NADP+ is in short supply, the electron transport chain “backs up,” greatly increasing the probability of creating highly reactive forms of oxygen known collectively as reactive oxygen species (Fig. 8.16a). These highly reactive molecules can be formed either by the transfer of absorbed light energy from antenna chlorophyll directly to O2 or by the transfer of an electron, forming O2−. Both forms of O2 can cause substantial damage to the cell.
NADP+ is returned to the photosynthetic electron transport chain by the Calvin cycle’s use of NADPH. Thus, any factor that causes the rate of NADPH use to fall behind the rate of light-
The rate at which the Calvin cycle can make use of NADPH is also influenced by a number of factors that are independent of light intensity. For example, cold temperatures cause the enzymes of the Calvin cycle to function more slowly, but they have little impact on the absorption of light energy. On a cold, sunny day, more light energy is absorbed than can be used by the Calvin cycle.
Photosynthetic organisms employ two major lines of defense to avoid the stresses that occur when the Calvin cycle cannot keep up with light harvesting (Fig. 8.16b). First among these are chemicals that detoxify reactive oxygen species. Ascorbate (vitamin C), β-(beta-)carotene, and other antioxidants are able to neutralize reactive oxygen species. These compounds exist in high concentration in chloroplasts. Some of these antioxidant molecules are brightly colored, like the red pigments found in algae that live on snow shown in Fig. 8.1c. The presence of antioxidant compounds is one of the many reasons that eating green, leafy vegetables is good for your health.
A second line of defense is to prevent reactive oxygen species from forming in the first place. Xanthophylls are yellow-
Converting absorbed light energy into heat is beneficial at high light levels, but at low light levels it would decrease the production of carbohydrates. Therefore, this capability is switched on only when the photosynthetic electron transport chain is working at high capacity.