Build a Neuron
By:
Build a Neuron
By:
In this activity, you will learn about how the physical structure of a neuron affects the way it functions by manipulating some of its key components.
After completing this activity, you should be able to:
This activity relates to the following principles of nervous system function:
The neuron is the basic information-processing and transmission unit of the nervous system. There are various forms and types of neurons, defined according to their functions. Most neurons contain several basic components, including the dendrites, soma (cell body), axon, and terminal buttons. These components enable the reception, processing, and transmission of neural information.
Now let's take some time to explore the major structures of a typical neuron. Select each term below to read a brief description.
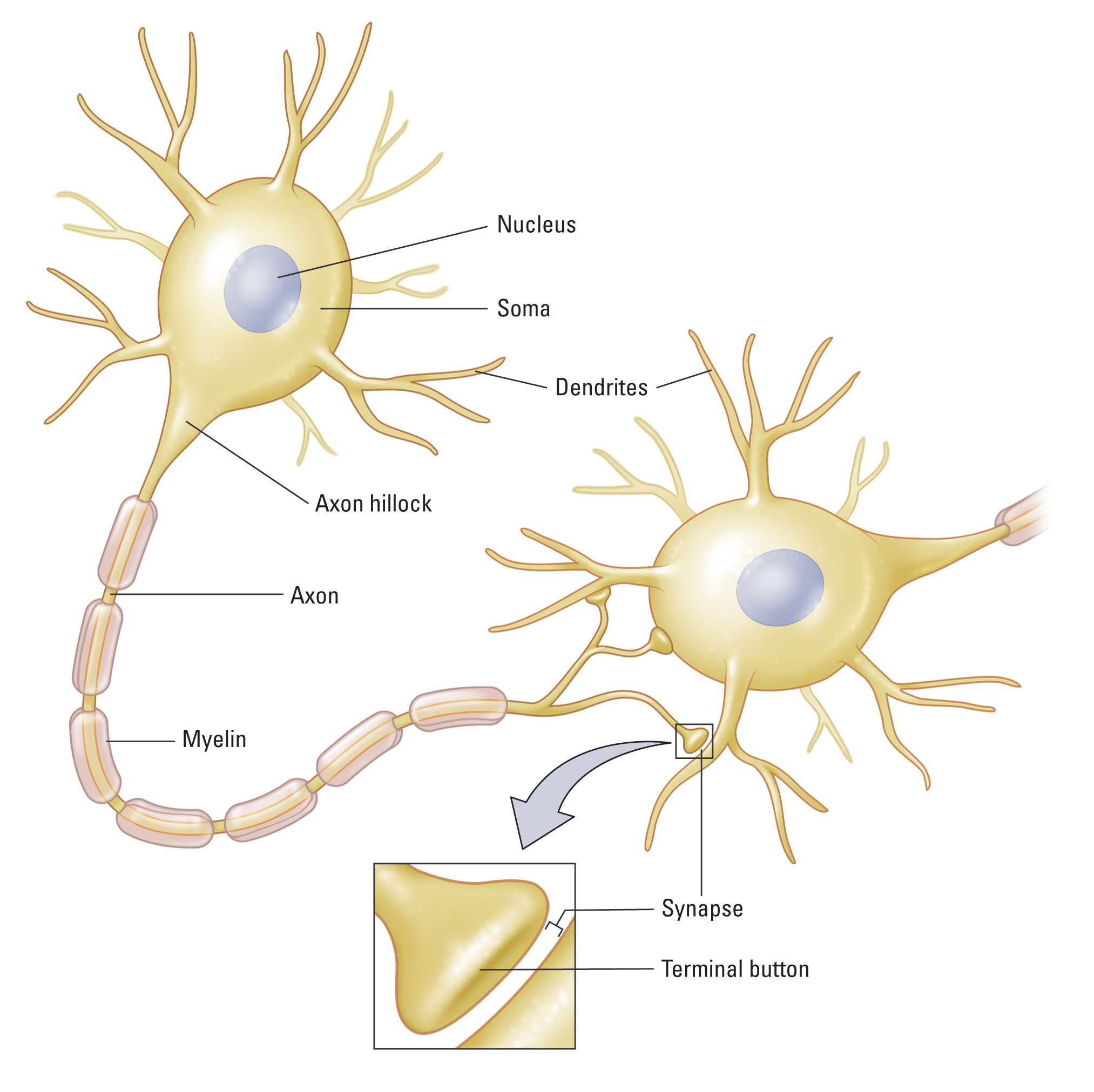
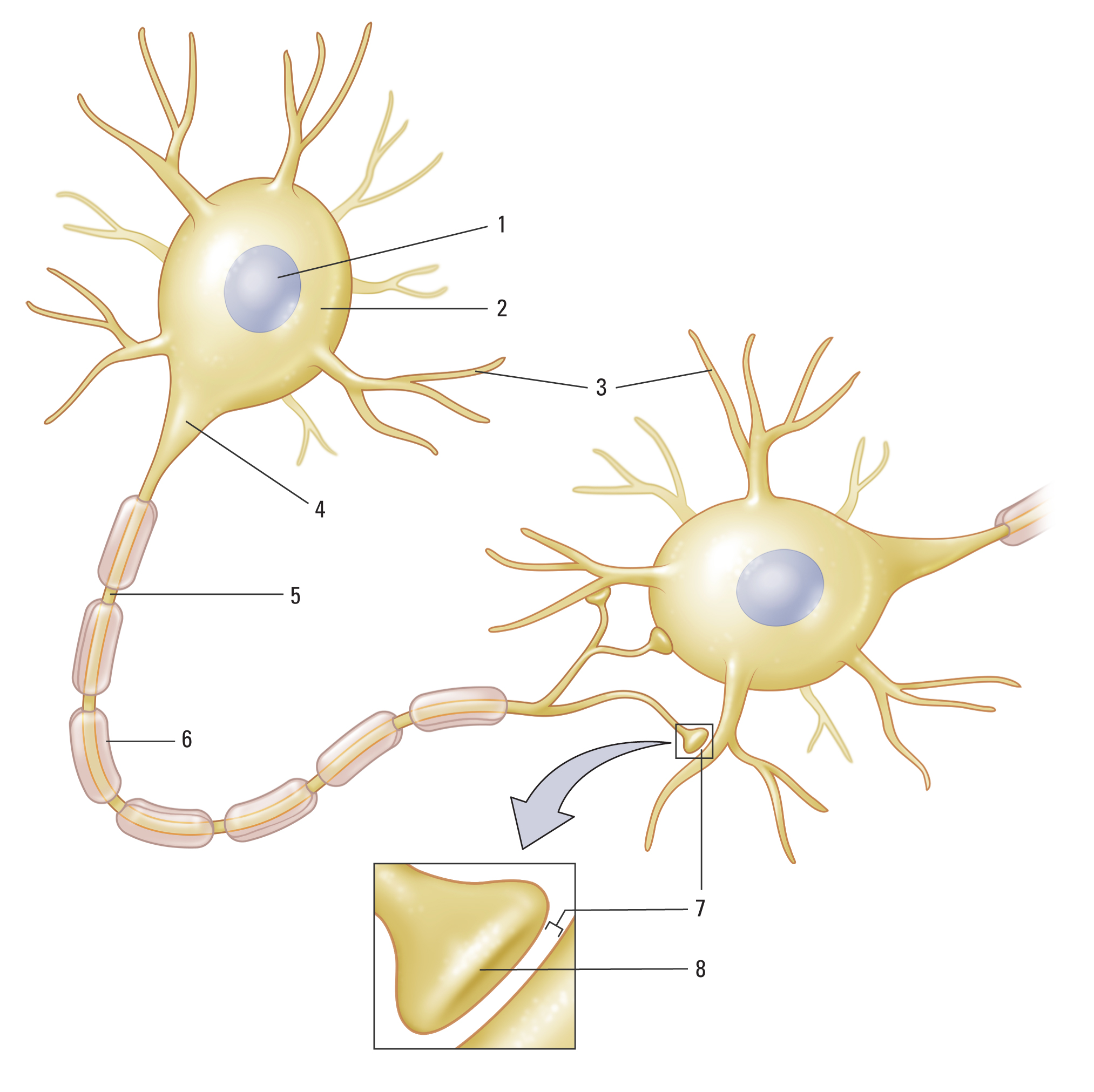
Before we explore the various types of neurons, let's review the major parts. Select the appropriate label for each part of the neuron below.
Neurons, as seen from the examples below, can look quite different from each other. A neuron’s function is closely related to its structural features, including (but not limited to) the extent of dendritic branching, number of dendritic spines, number of axon collaterals, length of the axon, and the extent of terminal branching.
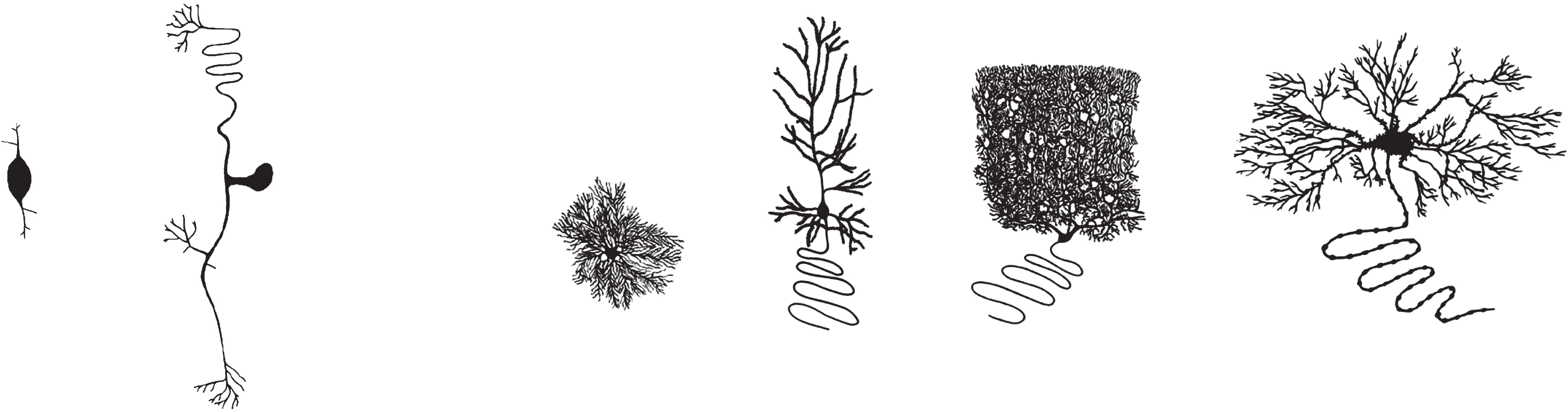

Variation in these structural features enable neurons to perform different functions:
In this activity you will get some hands-on experience with the various structural features of a neuron and how they impact its function by manipulating these features as you build your own neuron.
Sensory Neuron: A neuron that carries afferent (incoming) information from the body into the spinal cord and brain.
You have selected Sensory Neuron. Now choose the structural features from the options below that will enable your neuron to carry out its intended function. After you finish, you’ll test your neuron to see if your choices are compatible with your neuron’s functions.
Interneuron: A neuron that integrates sensory and motor information within the central nervous system.
You have selected Interneuron. Now choose the structural features from the options below that will enable your neuron to carry out its intended function. After you finish, you’ll test your neuron to see if your choices are compatible with your neuron’s functions.
Motor Neuron: A neuron that carries efferent (outgoing) information from the brain and spinal cord to muscles.
You have selected Motor Neuron. Now choose the structural features from the options below that will enable your neuron to carry out its intended function. After you finish, you’ll test your neuron to see if your choices are compatible with your neuron’s functions.
Before we test your neuron, let’s review how structural features of a neuron impact its function.
Sensory Neurons
Interneurons


Motor Neurons
| Structural Features | Your Neuron |
model.selectedNeuronType === "sensory neuron"
model.selectedNeuronType === "interneuron"
model.selectedNeuronType === "motor neuron"
|
|---|---|---|
| Number of Dendrites |
model.dendritesNumber === 1
1 
model.dendritesNumber === 10
10 
model.dendritesNumber === 20
20 
|
model.selectedNeuronType === "sensory neuron"
1 
model.selectedNeuronType === "interneuron" || model.selectedNeuronType === "motor neuron"
Can be 10 or 20 

|
| Dendritic Branching |
model.dendriticBrachningLevel === "low"
low 
model.dendriticBrachningLevel === "medium"
medium 
model.dendriticBrachningLevel === "high"
high 
|
model.selectedNeuronType === "sensory neuron"
Can be low or medium 

model.selectedNeuronType === "interneuron" || model.selectedNeuronType === "motor neuron"
Can be medium or high 

|
| Axon Length |
model.axonLength === "short"
short 
model.axonLength === "long"
long 
|
model.selectedNeuronType === "sensory neuron" || model.selectedNeuronType === "interneuron"
Can be short or long 

model.selectedNeuronType === "motor neuron"
Long 
|
| Axon Collateral |
model.axonCollateralsLevel === 0
0 
model.axonCollateralsLevel === 1
1 
|
model.selectedNeuronType === "sensory neuron"
0 
model.selectedNeuronType === "interneuron" || model.selectedNeuronType === "motor neuron"
Can be 0 or 1 

|
| Terminal Branching |
model.terminalBrachningLevel === "low"
low 
model.terminalBrachningLevel === "high"
high 
|
model.selectedNeuronType === "sensory neuron"
Low 
model.selectedNeuronType === "interneuron" || model.selectedNeuronType === "motor neuron"
Can be low or high 

|
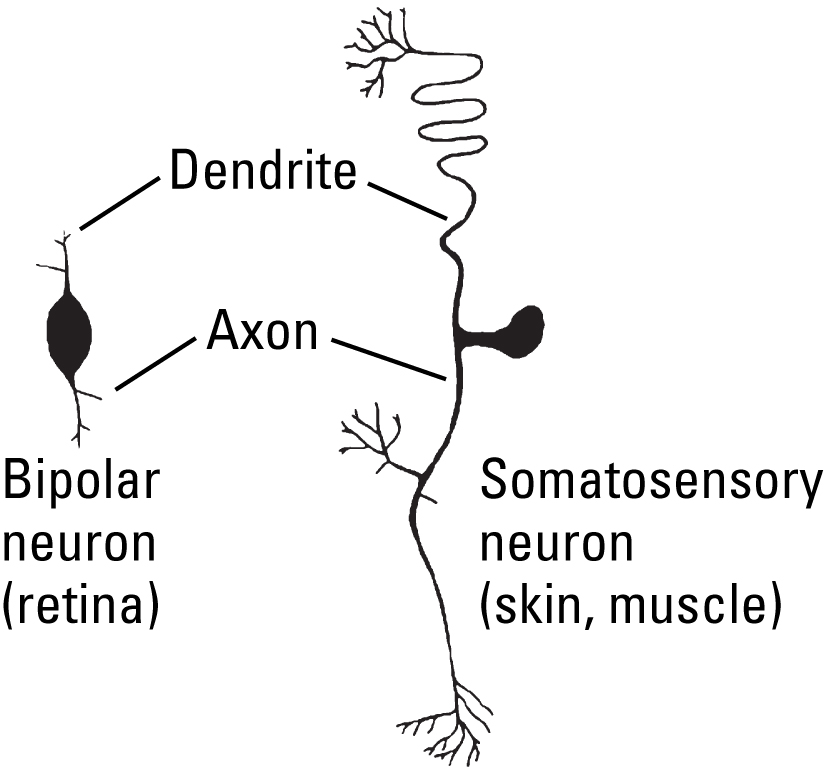
A single dendrite, with little or no branching, enables sensory neurons to carry afferent (incoming) information from specific sensory receptors to the spinal cord and brain. These neurons generally do not integrate information from multiple sources, which reduces mixing and optimizes the acuity (sharpness or clarity) of sensory input. Bipolar neurons in the retina, for example, use a single, sparsely branched dendrite to communicate highly specific light information from a distinct area of the retina to specific neurons in the visual system, resulting in high visual acuity. Somatosensory neurons have a single, sparsely branched dendrite that connects directly to a long axon, enabling it to carry touch information from specific areas of skin and muscle across relatively large distances to the spinal cord.
Sensory neurons generally do not integrate information from multiple sources or send information to multiple targets. A neuron with multiple dendrites and/or highly branched dendrites would receive and integrate information from multiple sources. A neuron with an axon that divides into multiple collaterals and/or has extensive terminal branching would send information to a variety of targets.
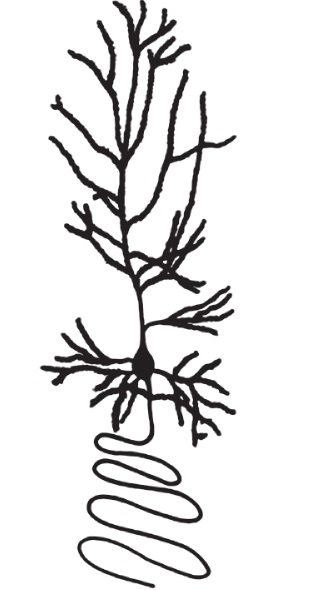
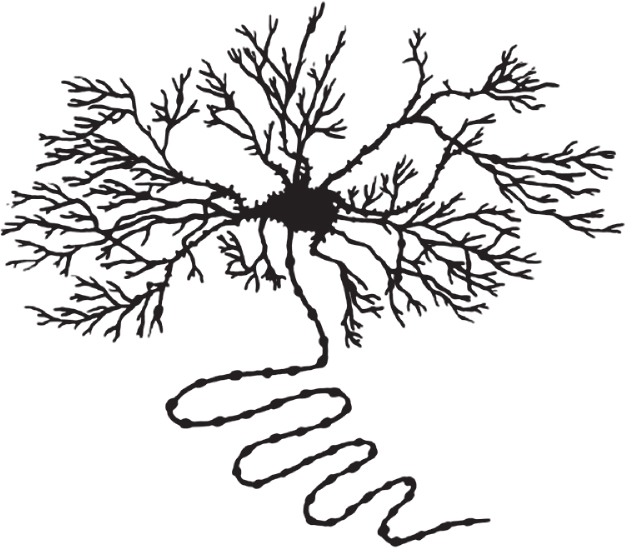
Numerous, extensively branched dendrites enable interneurons to gather and integrate sensory and motor information from a variety of sources within the central nervous system. A short axon would allow the neuron to communicate this information to other cells within the same brain area. Stellate cells, for example, are small, star-shaped interneurons with many, highly branched dendrites and a short axon, that integrate sensory information within the thalamus. A long axon would allow the neuron to communicate this information to long distance targets within the nervous system. Pyramidal cells, for example, are interneurons with a number of branched dendrites that gather and integrate information in the cortex, and a long axon which carries information over a relatively long distance, from the cortex to other parts of the brain and spinal cord.
Interneurons gather and integrate sensory and motor information and communicate that information to other cells within the same brain area or to distant areas of the nervous system. A single dendrite and/or sparsely branched dendrites would limit the ability of a neuron to receive and integrate information from multiple sources.
Numerous, extensively branched dendrites enable motor neurons to gather and integrate efferent (outgoing) neural information from many sources. A long axon allows motor neurons to send this information over great distances, such as from the lower brainstem and spinal cord to muscles.
Motor neurons gather and integrate efferent (outgoing) neural information from many sources and send this information over great distances, from the brain and spinal cord to muscles. A single dendrite and/or sparsely branched dendrites would limit the ability of a neuron to receive and integrate information from multiple sources. A short axon would not allow a neuron to send information over long distances.
If you want to keep practicing, try building a new neuron by going back to
You have seen how the various structures impact the functionality of your neuron. Here is a brief summary of how these features impact all three types of neurons.

A single dendrite, with little or no branching, enables sensory neurons to carry afferent (incoming) information from specific sensory receptors to the spinal cord and brain. These neurons generally do not integrate information from multiple sources, which reduces mixing and optimizes the acuity (sharpness or clarity) of sensory input. A bipolar neurons in the retina, for example, use a single, sparsely branched dendrite to communicate highly specific light information from a distinct area of the retina to specific neurons in the visual system, resulting in high visual acuity. Somatosensory neurons have a single, sparsely branched dendrite that connects directly to a long axon, enabling it to carry touch information from specific areas of skin and muscle across relatively large distances to the spinal cord.
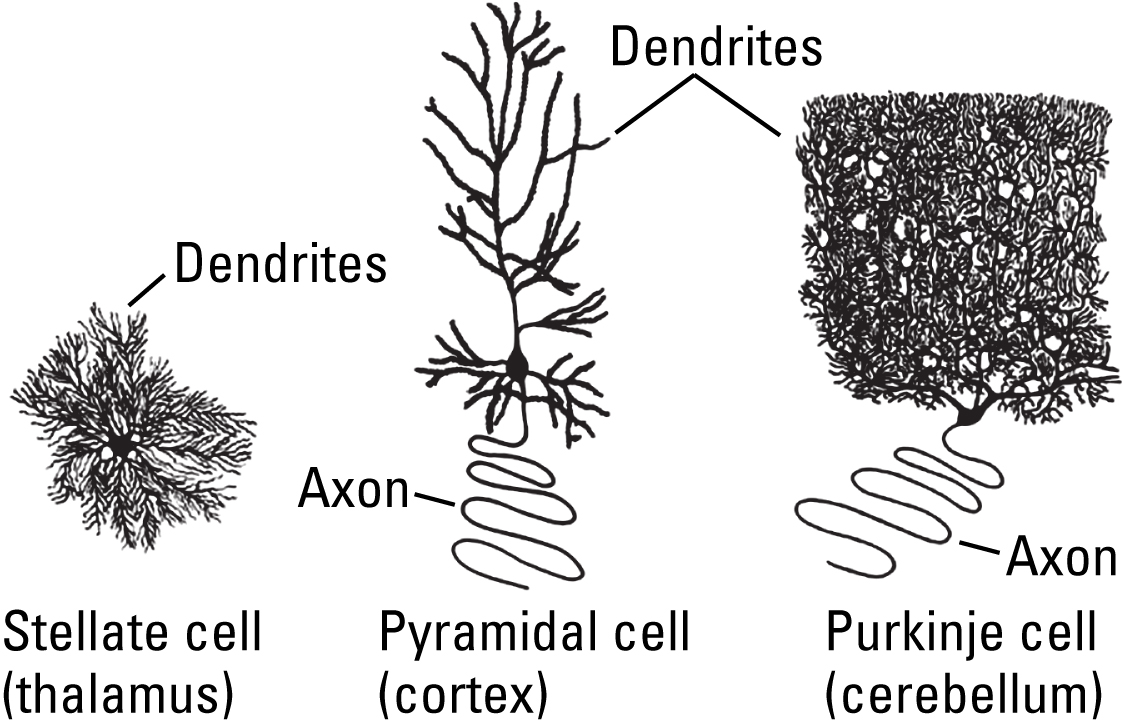
Numerous, extensively branched dendrites enable interneurons to gather and integrate sensory and motor information from a variety of sources within the central nervous system. A short axon would allow the neuron to communicate this information to other cells within the same brain area. Stellate cells, for example, are small, star-shaped interneurons with many, highly branched dendrites and a short axon, that integrate sensory information within the thalamus. A long axon would allow the neuron to communicate this information to long-distance targets within the nervous system. Pyramidal cells, for example, are interneurons with a number of branched dendrites that gather and integrate information in the cortex, and a long axon that carries information over a relatively long distance, from the cortex to other parts of the brain and spinal cord.
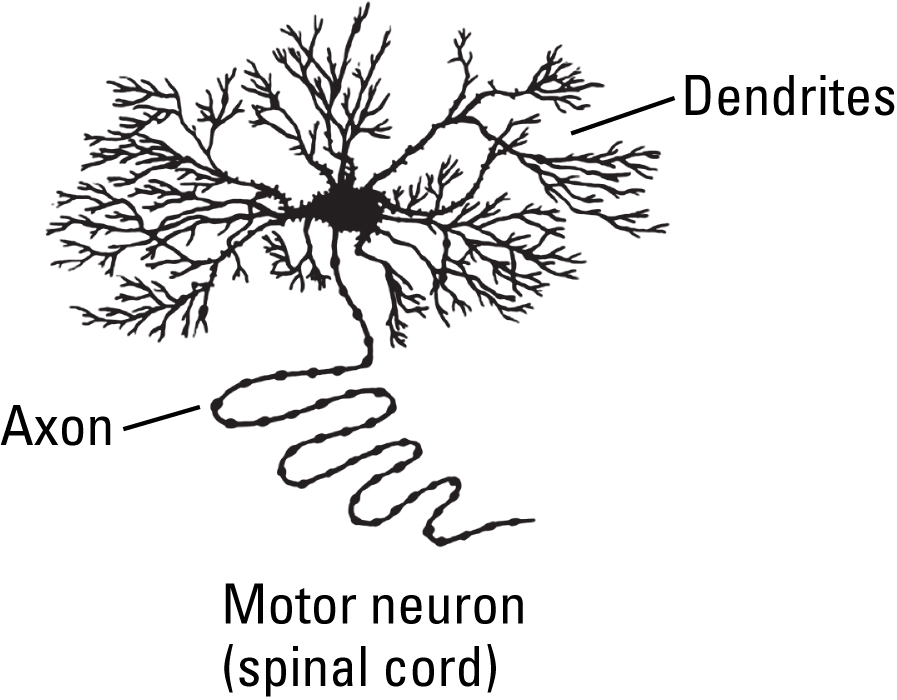
Numerous, extensively branched dendrites enable motor neurons to gather and integrate efferent (outgoing) neural information from many sources. A long axon allows motor neurons to send this information over great distances, such as from the lower brainstem and spinal cord to muscles.
Congratulations! You successfully completed the Build a Neuron activity. In this activity, you reviewed the major components of a neuron and their functions, the different types of neurons, and the way in which the physical structure of a neuron affects its function.
Your instructor may now have you take a short quiz about this activity. Good luck!