Neural Integration: Sending Signals
By:
Neural Integration: Sending Signals
By:
In this activity, you will explore the process of neural integration, the way that signals are passed from one neuron to another. Many neurons have extensive dendritic trees covered in spines that are ready to receive inputs from other neurons. The neural cell body (the soma) can also receive multiple inputs. Inputs create either excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and are summed in the neural cell body. This summation process may or may not lead to an action potential in the receiving neuron.
After completing this activity, you should be able to:
This activity relates to the following principles of nervous system function:
Inputs to a neuron produce graded potentials that are classified as excitatory or inhibitory. An excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a brief depolarization of the receiving neuron that makes the neuron more likely to produce an action potential. An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is a brief hyperpolarization of the receiving neuron that makes the neuron less likely to produce an action potential.
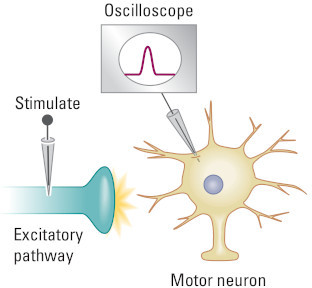
The two oscilloscope screens below show potential membrane changes. Select the oscilloscope that represents the graded membrane potential change in a neuron receiving an excitatory input.
Note: you must choose an answer before proceeding.
Here is a simplified illustration of two different neurons, each with two inputs (S1 and S2). In which of these two neurons would spatial summation occur and produce a larger effect at the recording electrode (R1)?
Excitatory and inhibitory inputs to a neuron can occur at different points in time and at different locations on the neuron (either on the dendrite or cell body). If two inputs are widely spaced in time, each will produce an independent graded potential. However, if the inputs occur close together in time, the second input will summate (combine) with the first input. This effect is called temporal summation.
To illustrate this process, assume that the neuron has already received one excitatory input (S1). Manipulate the timing of a second excitatory input (S2) by using the arrows below. At what point will the two inputs summate?
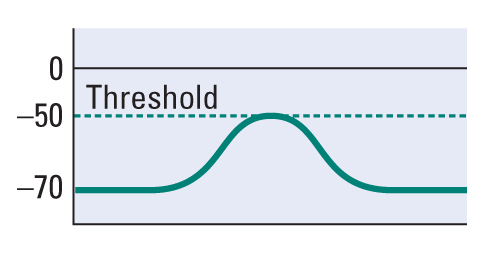
When two excitatory inputs occur closely together in time, they produce temporal summation, and if they are sufficient to reach threshold at the initial segment of the axon, an action potential is generated.
Temporal summation can occur with either excitatory or inhibitory inputs. Let’s look at how this summation works with three inputs: two excitatory inputs (S1 and S2) and one inhibitory input (S3). Manipulate the timing of the inputs to see the resulting changes in membrane potential.
Two excitatory inputs (S1 and S2) paired closely together in time produce temporal summation. When threshold is reached at the initial segment of the axon hillock, an action potential would be generated. Temporal summation with at least one excitatory input close in time to one inhibitory input (S3) will balance the resulting graded potential change. Adding at least one inhibitory input close to an excitatory input will make it difficult to reach threshold and produce an action potential.
Now let’s consider what happens when inputs occur at different locations on the neuron (either on the dendrites or cell body). If the two inputs are far enough apart on the neuron, each will produce an independent graded potential. However, if the inputs occur close together on the neuron, the two inputs will summate and produce a larger EPSP or IPSP. This effect is called spatial summation.
Each neuron can have several inputs, and each input can produce either an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) or an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP), which can summate if they are close together in time or space with another input. The cell body indicates the summed influence of multiple temporal and spatial inputs.
Select the two inputs that would be most likely to spatially summate to produce an action potential. You have three attempts to choose the correct inputs.
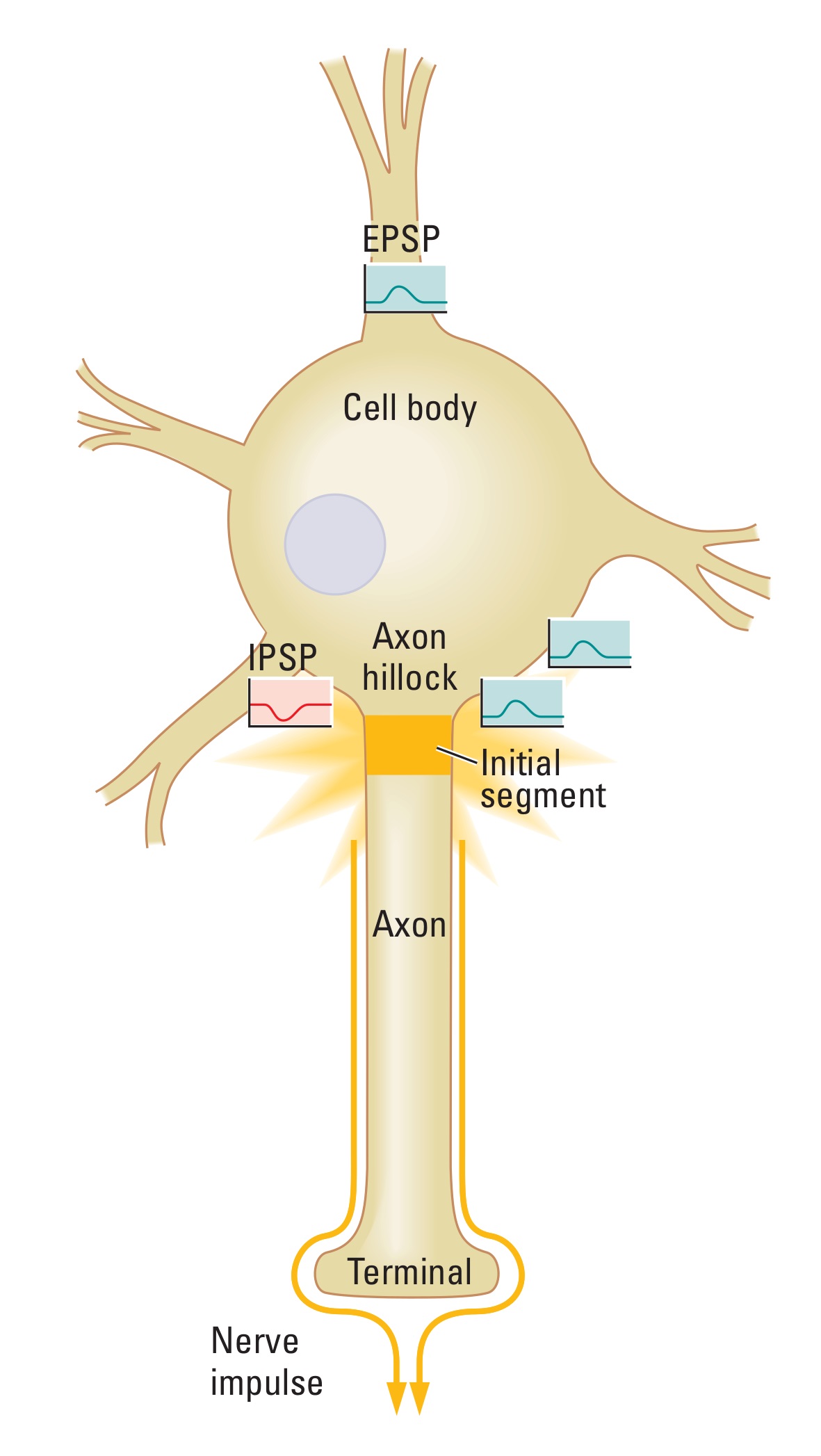
Two EPSPs that are in close proximity would spatially sum and likely produce a large enough EPSP to reach threshold and produce an action potential at the initial segment of the axon. Although an EPSP and IPSP would sum spatially, the IPSP hyperpolarizes the neuron, and the EPSP depolarizes the neuron. Therefore, the IPSP would cancel the effect of the EPSP, and no action potential would be produced.
Congratulations! You have successfully completed the activity. In this activity, you reviewed excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs), inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), temporal summation, spatial summation, and how multiple inputs summate at the initial segment of the axon to produce an action potential.
Your instructor may now have you take a short quiz about this activity. Good luck!