A.2 Symbols and Notation: Arithmetic Operations
Symbols And Notation
The basic mathematical symbols used throughout this book are located in Table A.1. These include the most common arithmetic operations, and most of you will find that you are familiar with them. However, it is worth your time to review the reference table and material that outline the operations using positive and negative numbers. For those of you who have spent little time solving math equations recently, familiarizing yourselves with this material can help you avoid making common mistakes.
Table : TABLE A.1 Symbols and Notations
| + | Addition | 8 + 3 = 11 |
| − | Subtraction | 14 − 6 = 8 |
| ×, ( ) | Multiplication | 4 × 3 = 12, 4(3) = 12 |
| ÷, / | Division | 12 ÷ 6 = 2, 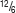 = 2
= 2 |
| > | Greater than | 7 > 5 |
| < | Less than | 4 < 9 |
| ≥ | Greater than or equal to | 7 ≥ 5, 4 ≥ 4 |
| ≤ | Less than or equal to | 5 ≤ 9, 6 ≤ 6 |
| ≠ | Not equal to | 5 ≠ 3 |
Arithmetic Operations: Worked Examples
Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Dividing with Positive and Negative Numbers
- Adding with positive numbers: Add the two (or series of) numbers to produce a sum.
- 4 + 7 = 11
- 7 + 4 + 9 = 20
- 4 + 6 + 7 + 2 = 19
- Adding with negative numbers: Sum the absolute values of each number and place a negative sign in front of the sum.
(Hint: When a positive sign directly precedes a negative sign, change both signs to a single negative sign.)- −6 + (−4) = −10
−6 − 4 = −10 - −3 + (−2) = −5
−3 − 2 = −5
- −6 + (−4) = −10
- Adding two numbers with opposite signs: Find the difference between the two numbers and assign the sign (positive or negative) of the larger number to the answer.
- 17 + (−9) = 8
- −16 + 10 = −6
- Subtracting one number from another number. (Hint: When subtracting a negative number from another number, two negative signs come in sequence, as in part (a). To solve the equations, change the two sequential negative signs into a single positive sign.)
- 5 − (−4) = 9
5 + 4 = 9 - 5 − 8 = −3
- −6 − 3 = −9
- 5 − (−4) = 9
- Multiplying two positive numbers produces a positive result.
- 6 × 9 = 54
- 6(9) = 54
- 4 × 3 = 12
- 4(3) = 12
- Multiplying two negative numbers produces a positive result.
- −3 × −9 = 27
- −3(−9) = 27
- −4 × (−3) = 12
- −4(−3) = 12
- Multiplying one positive and one negative number produces a negative result.
- −3 × 9 = −27
- −3(9) = −27
- 4 × (−3) = −12
- 4(−3) = −12
- Dividing two positive numbers produces a positive result.
- 12 ÷ 4 = 3
- 12/4 = 3
- 16 ÷ 8 = 2
- 16/8 = 2
- Dividing two negative numbers produces a positive result.
- −12 ÷ −4 = 3
- −12/−4 = 3
- −16 ÷ (−8) = 2
- −16/(−8) = 2
- Dividing a positive number by a negative number (or dividing a negative number by a positive number) produces a negative result.
- −12 ÷ 4 = −3
- −12/4 = −3
- 16 ÷ (−8) = −2
- 16/(−8) = −2
A-
Self-Quiz #1: Symbols and Notation: Arithmetic Operations
(Answers to this quiz can be found in section A-6.)
- 4 × 7 =
- 6 + 3 + 9 =
- −6 − 3 =
- −27/3 =
- 4(9) =
- 12 + (−5) =
- 16(−3) =
- −24/−3 =
- 75 ÷ 5 =
- −7(−4) =