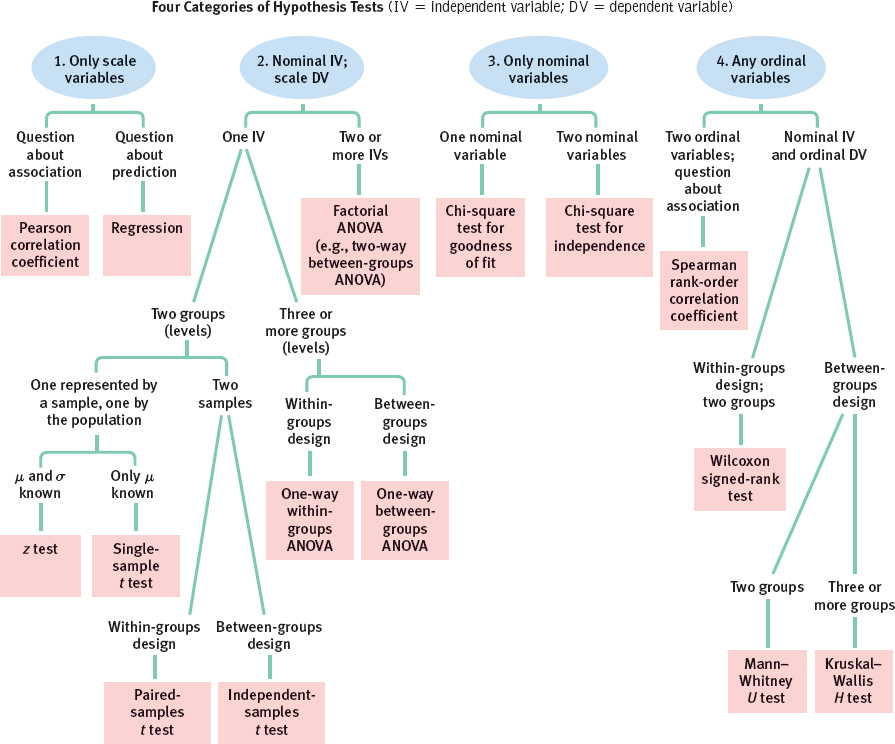
Category 4: At Least One Ordinal Variable
If we have a design with even one ordinal variable or a design in which it makes sense to convert the data from scale to ordinal, then we have several choices, as seen in Table E-4. All these choices have parallel parametric hypothesis tests, as seen in Table E-5. For situations in which we want to investigate the relation between two ordinal variables, we use the Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient. For situations in which we have a within-groups research design and two groups, we use the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. When we have a between-groups design with two groups, we use a Mann–Whitney U test. And when we have a between-groups design with more than two groups, we use a Kruskal–Wallis H test.
Table : TABLE E.4 Category 4 Statistics When at least one variable is ordinal, we have several choices. If both variables are ordinal, or can be converted to ordinal, and we are interested in quantifying the relation between them, we use the Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient. If the independent variable is nominal and the dependent variable is ordinal, we choose the correct nonparametric test based on the research design and the number of levels of the independent variable.
| Type of Independent Variable (And Number of Levels, If Applicable) |
Research Design |
Question to Be Answered |
Hypothesis Test |
| Ordinal |
Not applicable |
Are two variables related? |
Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient |
| Nominal (two levels) |
Within-groups |
Are two groups different? |
Wilcoxon signed-rank test |
| Nominal (two levels) |
Between-groups |
Are two groups different? |
Mann–Whitney U test |
| Nominal (three or more levels) |
Between-groups |
Are three or more groups different? |
Kruskal–Wallis H test |
Table : TABLE E.5 Nonparametric Statistics and Their Parametric Counterparts Every parametric hypothesis test has at least one nonparametric counterpart. If the data are far from meeting the assumptions for a parametric test or at least one variable is ordinal, we should use the appropriate nonparametric test instead of a parametric test.
| Design |
Parametric Test |
Nonparametric Test |
| Association between two variables |
Pearson correlation coefficient |
Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient |
| Two groups; within-groups design |
Paired-samples t test |
Wilcoxon signed-rank test |
| Two groups; between-groups design |
Independent-samples t test |
Mann–Whitney U test |
| More than two groups; between-groups design |
One-way between-groups ANOVA |
Kruskal–Wallis H test |
The decisions we’ve outlined are summarized in Figure E-1.