Moving farther outward from the nucleus, we encounter another organelle within the endomembrane system: the Golgi (GOHL-jee) apparatus (FIGURE 3-37). The Golgi apparatus processes molecules synthesized in the cell—
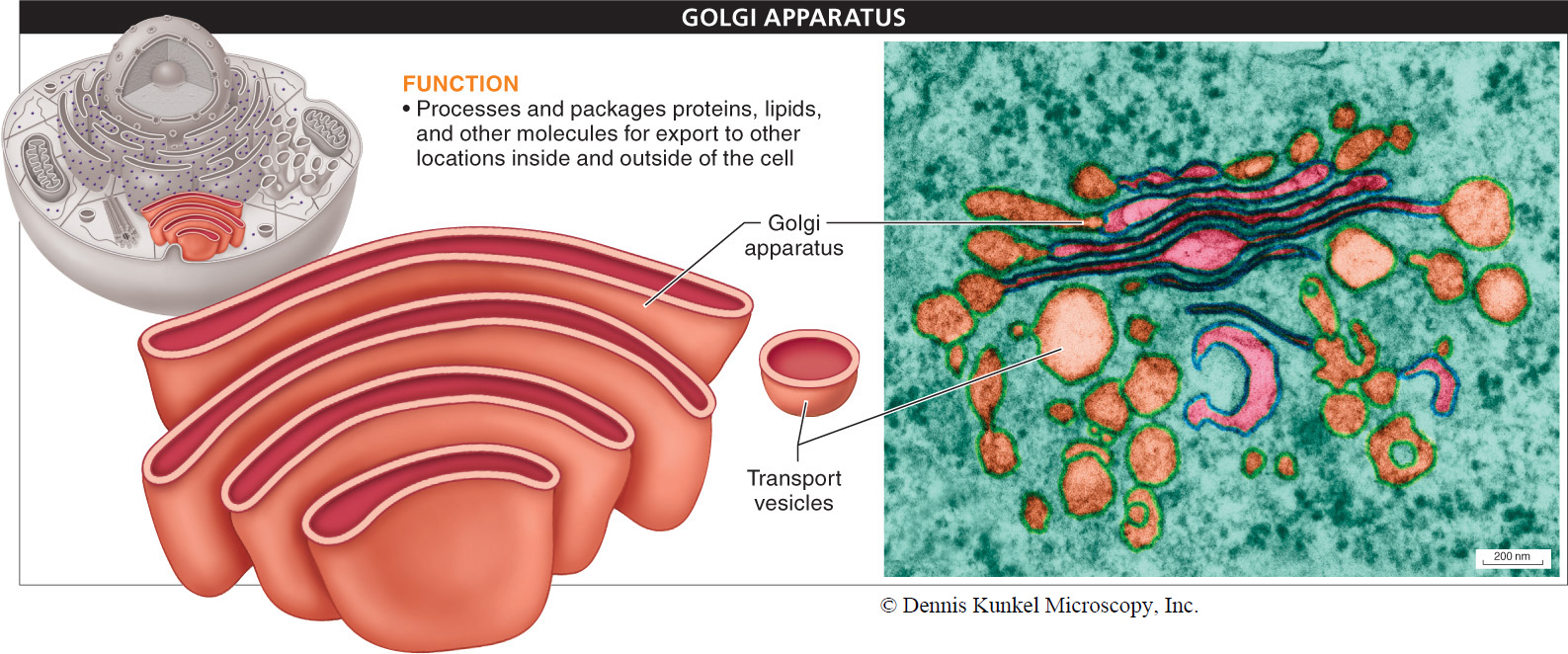
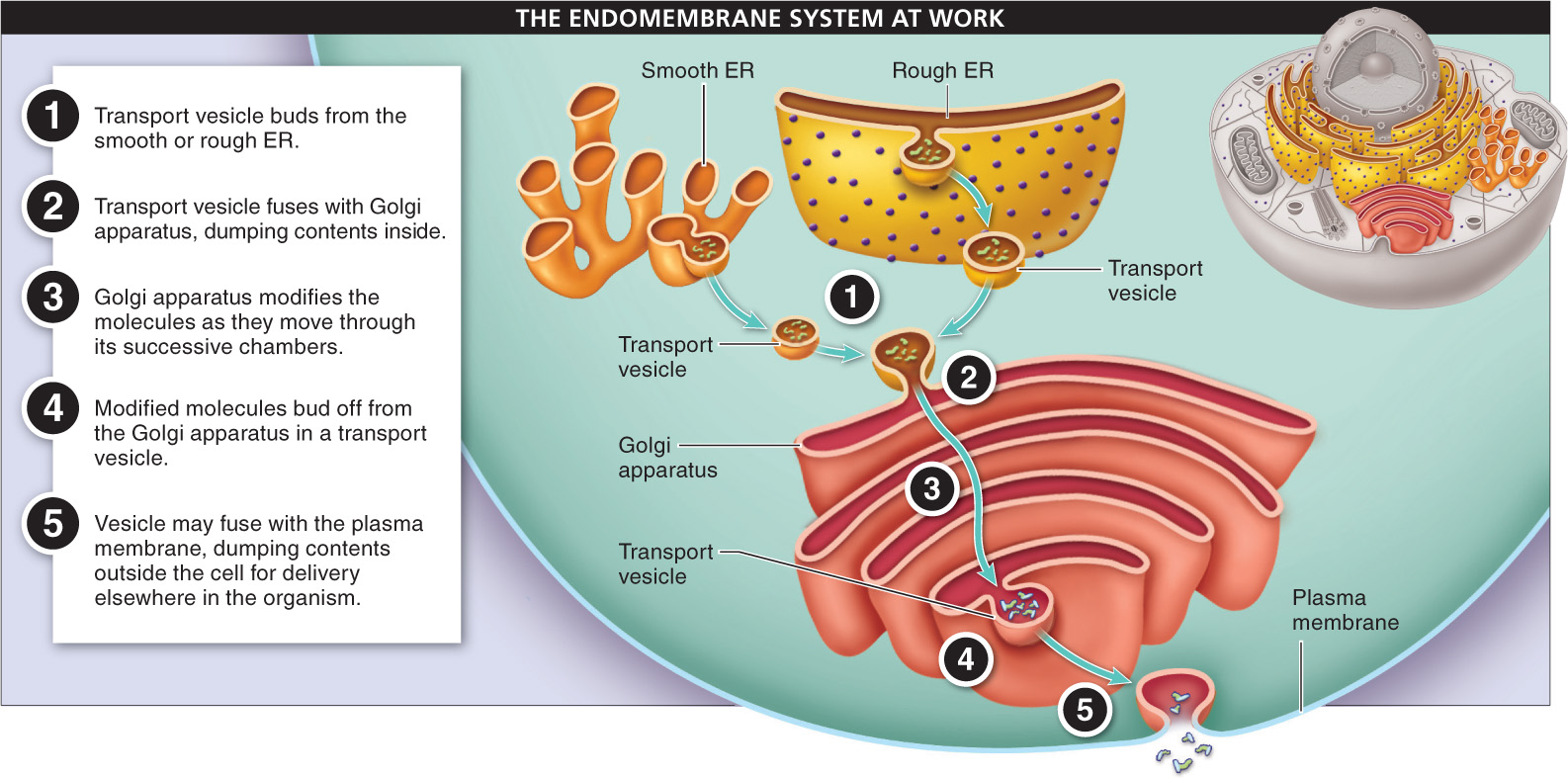
After transport vesicles bud from the endoplasmic reticulum, they move through the cytoplasm until they reach the Golgi apparatus. Here, the vesicles fuse with the Golgi apparatus membrane and dump their contents into a Golgi body. The molecules pass through about four successive Golgi body chambers. In each Golgi body, enzymes make slight modifications to the molecules (such as the addition or removal of phosphate groups or sugars). The processing that occurs in the Golgi apparatus often involves tagging molecules (much like adding a postal address or tracking number) to direct them to some other part of the organism. After they are processed, the molecules bud off from the Golgi apparatus in a vesicle, which then moves into the cytosol. If the molecules are destined for delivery and use elsewhere in the body, the transport vesicle eventually fuses with the cell’s plasma membrane and dumps the molecules into the bloodstream via exocytosis.
123
FIGURE 3-38 shows how the various parts of the endomembrane system work to produce, modify, and package molecules within a cell.
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 3.19
The Golgi apparatus—
Give two examples of ways in which proteins are modified within the Golgi apparatus.
A protein may be modified within the Golgi apparatus by the addition or removal of a phosphate group or a sugar group.
124