If you look at a mature plant cell through a microscope, one organelle, the central vacuole, usually stands out more than all the others because it is so huge and appears empty (FIGURE 3-40). Although it may look like an empty sac, the central vacuole is anything but. Surrounded by a membrane, filled with fluid, and occupying from 50% to 90% of a plant cell’s interior space, the central vacuole can play an important role in five different areas of plant life. (Vacuoles are also found in some other eukaryotes, including some protists, fungi, and animals, but they tend to be particularly prominent in plant cells.)
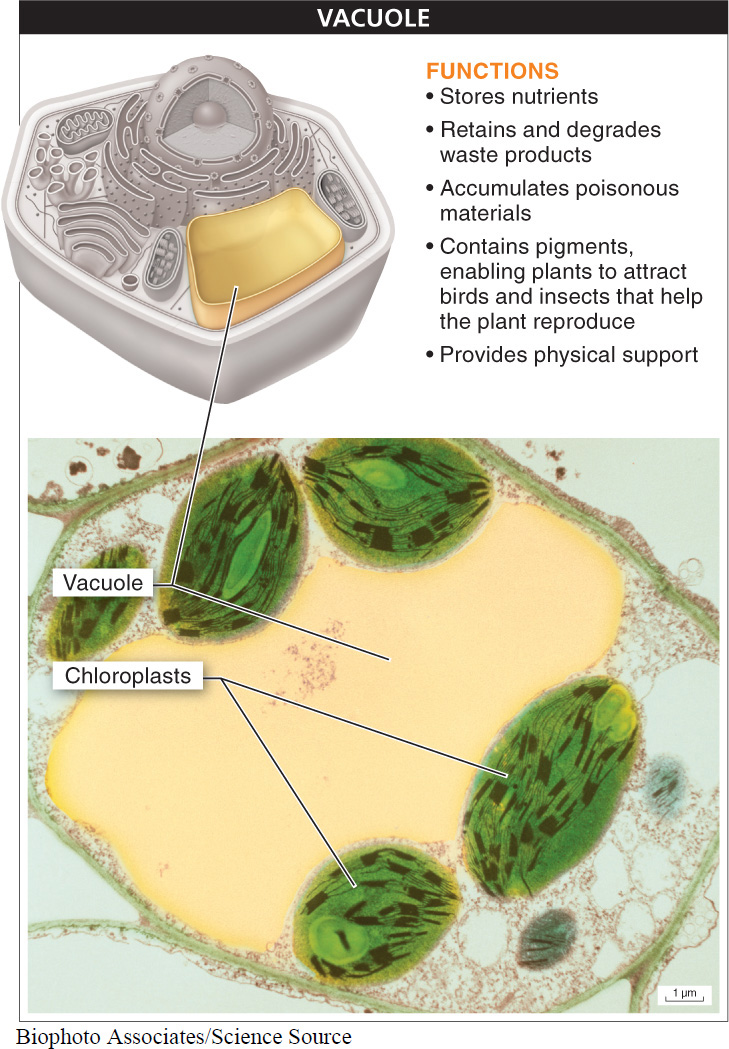
- 1. Nutrient storage. The vacuole stores hundreds of dissolved substances, including amino acids, sugars, and ions.
- 2. Waste management. The vacuole retains waste products and degrades them with digestive enzymes, much like the lysosome in animal cells.
- 3. Predator deterrence. The poisonous, nasty-
tasting materials that accumulate inside the vacuoles of some plants make a powerful deterrent to animals that might try to eat parts of the plant. - 4. Sexual reproduction. The vacuole may contain pigments that give some flowers their red, blue, purple, or other colors, enabling them to attract birds and insects that help the plant reproduce by transferring pollen.
- 5. Physical support. High concentrations of dissolved substances in the vacuole can cause water to rush into the cells through the process of osmosis. The increased fluid pressure inside the vacuole can cause the cell to enlarge a bit and push out the cell wall. This process is responsible for the pressure (called turgor pressure) that allows stems, flowers, and other plant parts to stand upright. The ability of non-
woody plants to stand upright is due primarily to turgor pressure. Wilting is the result of a loss of turgor pressure.
126
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 3.21
In plants, vacuoles can occupy most of the interior space of the cell. Vacuoles are also present in some other eukaryotic species. In plants, they function as storage spaces and play a role in nutrition, waste management, predator deterrence, reproduction, and physical support.
What are the five key functions of plant vacuoles?
Plant vacuole functions include nutrient storage, waste management, predator deterrence, sexual reproduction, and physical support.