4
Energy
FROM THE SUN TO YOU IN JUST TWO STEPS
134
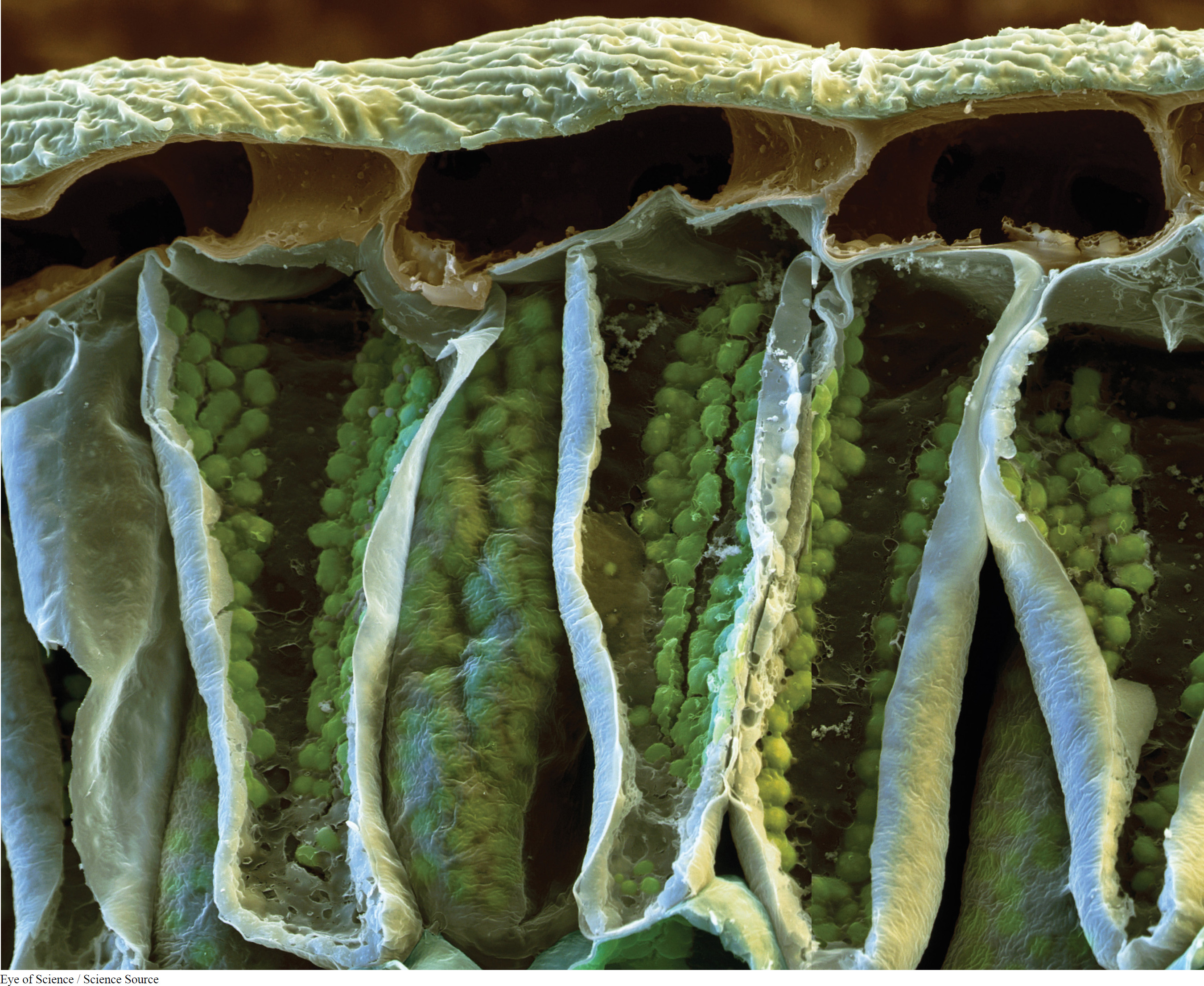
135
Energy flows from the sun and through all life on earth.
- 4.1 Cars that run on french fry oil? Organisms and machines need energy to work.
- 4.2 Energy has two forms: kinetic and potential.
- 4.3 As energy is captured and converted, the amount of energy available to do work decreases.
- 4.4 ATP molecules are like free-
floating rechargeable batteries in all living cells.
Photosynthesis uses energy from sunlight to make food.
- 4.5 Where does plant matter come from? Photosynthesis: the big picture.
- 4.6 Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts.
- 4.7 Light energy travels in waves: plant pigments absorb specific wavelengths.
- 4.8 Photons cause electrons in chlorophyll to enter an excited state.
- 4.9 Photosynthesis in detail: the energy of sunlight is captured as chemical energy.
- 4.10 Photosynthesis in detail: the captured energy of sunlight is used to make food.
- 4.11 The battle against world hunger can use plants adapted to water scarcity.
Cellular respiration converts food molecules into ATP, a universal source of energy for living organisms.
- 4.12 How do living organisms fuel their actions? Cellular respiration: the big picture.
- 4.13 The first step of cellular respiration: glycolysis is the universal energy-
releasing pathway. - 4.14 The second step of cellular respiration: the Krebs cycle extracts energy from sugar.
- 4.15 The third step of cellular respiration: ATP is built in the electron transport chain
- 4.16 This is how we do it: Can we combat the fatigue and reduced cognitive functioning of jet lag with NADH pills?
There are alternative pathways to energy acquisition.
- 4.17 Beer, wine, and spirits are by-
products of cellular metabolism in the absence of oxygen. - 4.18 Eating a complete diet: cells can run on protein and fat as well as on glucose.
136