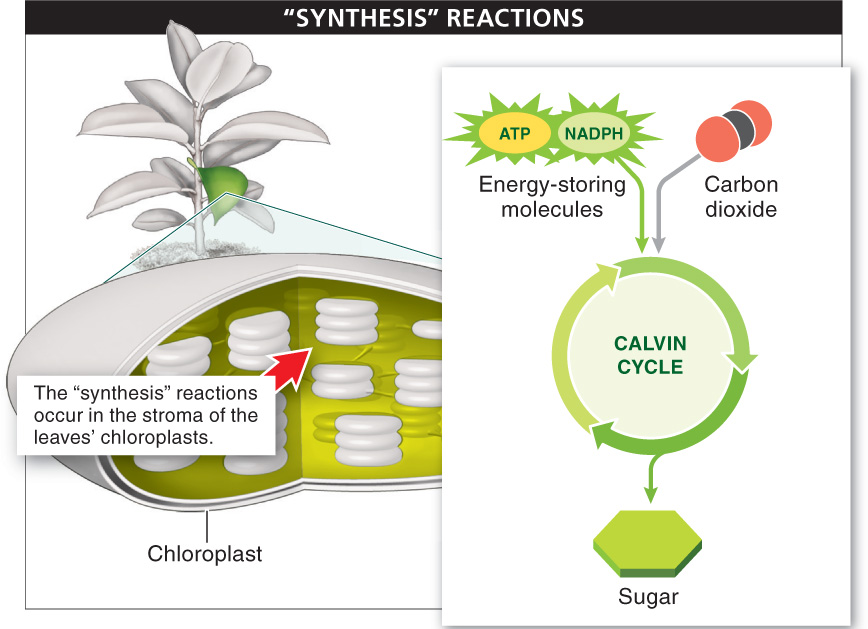
The “synthesis” part of photosynthesis takes place in a series of chemical reactions called the Calvin cycle. All the Calvin cycle reactions occur in the stroma of the leaves’ chloroplasts, outside the thylakoids. Plants carry out these reactions using the energy stored in the ATP and NADPH molecules that are built in the “photo” portion of photosynthesis. This dependency links the light-
If there is any part of photosynthesis that appears magical, it is the Calvin cycle. Just as a magician seems to make a rabbit appear from thin air, the Calvin cycle takes invisible molecules of CO2 from the air and uses them to assemble visible—
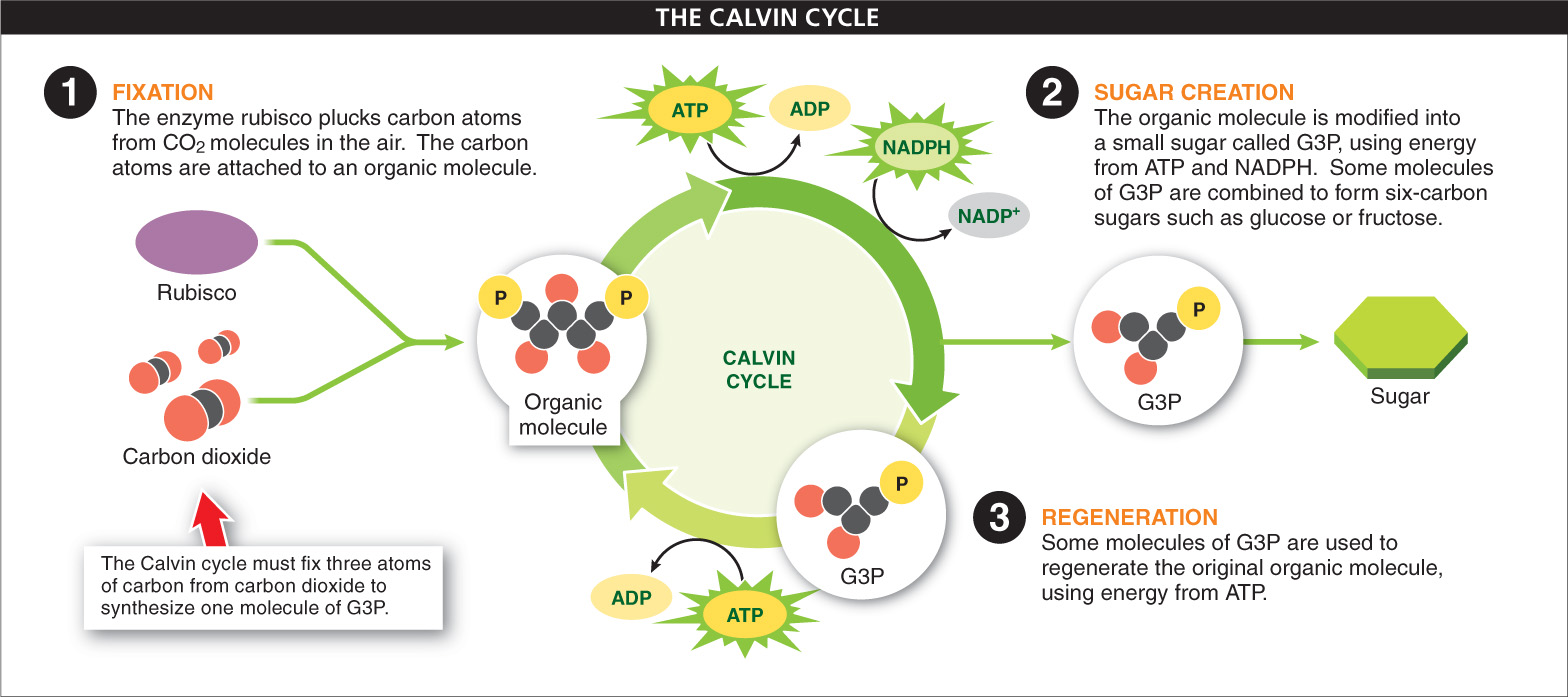
Fixation. First, using an enzyme called rubisco, plants pluck carbon from the air, where it occurs in the form of carbon dioxide (which has one carbon), and then attach, or “fix,” it to a visible organic molecule (which has five carbon atoms) within the chloroplast. Not surprisingly, given its role as the critical chemical that enables plants to build food molecules, rubisco is the most abundant protein on earth.
1. Sugar creation. The newly built molecule is chemically modified: a phosphate from ATP is added, and the molecule receives some high-
Some of the G3P molecules are combined to make the six-
2. Regeneration. Not all of the G3P molecules are used to produce sugars. In the third and final phase of the Calvin cycle, some G3P molecules are rearranged to regenerate the original five-
153
Ultimately, to synthesize one molecule of G3P, the Calvin cycle requires three “turns” of the Calvin cycle and fixation of three atoms of carbon from carbon dioxide to the initial organic molecule; this process consumes nine molecules of ATP and six molecules of NADPH generated in the “photo” reactions of photosynthesis.
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 4.10
The second part, or “synthesis” part, of photosynthesis is the Calvin cycle, which occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts. During this phase, carbon from CO2 in the atmosphere is attached (fixed) to molecules in the chloroplasts, sugars are built, and molecules are regenerated to be used again in the Calvin cycle. The fixation, building, and regeneration processes consume energy from ATP and NADPH (the products of the “photo” part of photosynthesis).
Describe the three steps in the Calvin cycle.
The first step of the Calvin cycle is carbon fixation, in which carbon dioxide molecules are attached to organic molecules. The next step is sugar creation, in which these organic molecules are modified into sugars. The third and final step is regeneration, where some of these sugars are used to regenerate the original organic molecules.