4.12–4.16
4.12–Cellular respiration converts food molecules into ATP, a universal source of energy for living organisms.
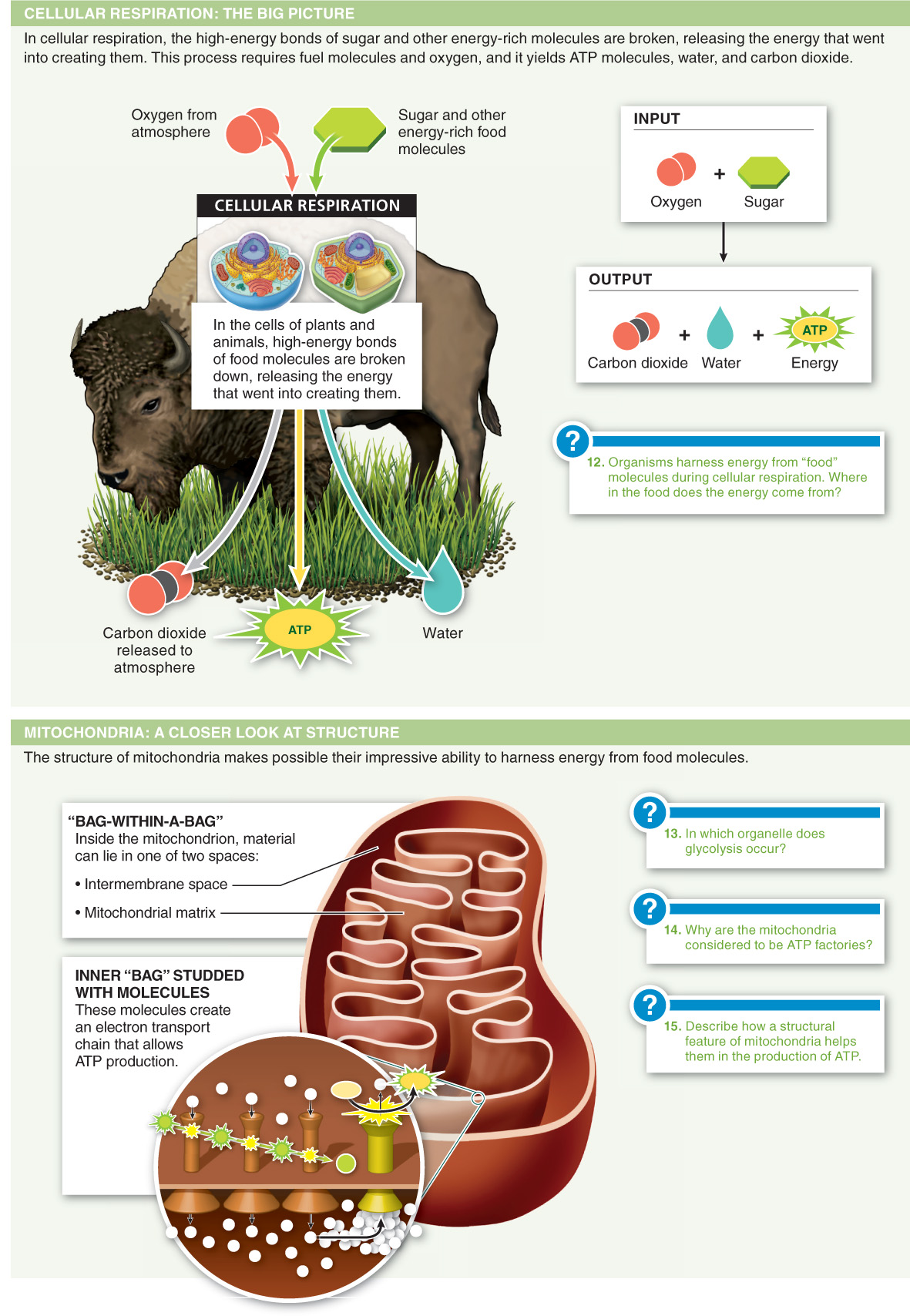
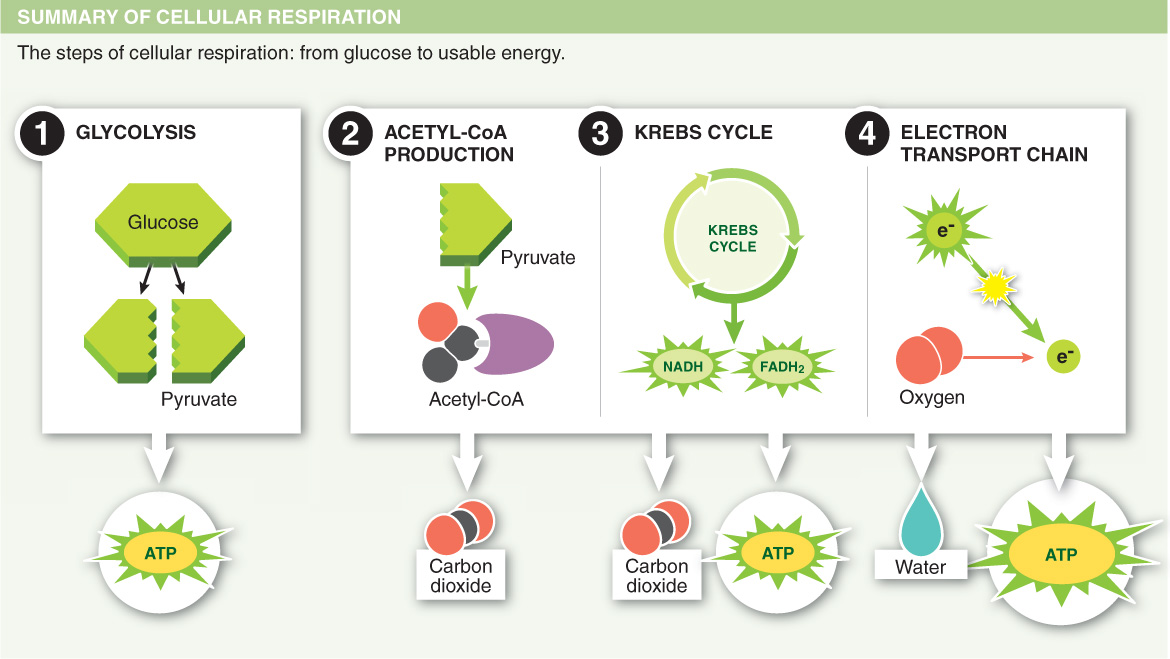
Living organisms extract energy through a process called cellular respiration in which glucose and oxygen are converted to carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
Q
Plants rely on water:
- a) to provide the protons necessary to produce chlorophyll.
- b) to concentrate beams of sunlight on the reaction center.
- c) to replenish oxygen molecules that are lost during photosynthesis.
- d) to replace electrons that are excited by light energy and passed down an electron transport chain.
- e) to serve as an energy source.

During photosynthesis, which step is most responsible for a plant’s acquisition of new organic material?
- a) the “building” of NADPH during the Calvin cycle
- b) the excitation of chlorophyll molecules by photons of light
- c) the “plucking” of carbon atoms from the air and fixing of the carbons to organic molecules within the chloroplast
- d) the loss of water through evaporation
- e) ATP made during the light reactions

During C4 photosynthesis:
- a) plants use less ATP in making sugar.
- b) plants can produce sugars even when they close their stomata to reduce water loss on hot days.
- c) plants are able to generate water molecules to cool their leaves.
- d) plants produce more rubisco.
- e) plants are able to produce sugars without any input of carbon dioxide.

During cellular respiration:
- a) oxygen is used to transport chemical energy throughout the body.
- b) metabolic oxygen is produced.
- c) light is converted to kinetic energy.
- d) ATP is converted to water and sugar.
- e) energy from the chemical bonds of food molecules is captured.

During cellular respiration, most of the energy contained within the bonds of food molecules is captured in:
- a) the conversion of the kinetic energy of food to the potential energy of ATP.
- b) the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain.
- c) digestion.
- d) glycolysis.
- e) None of the above. Energy is lost, not gained, during cellular respiration.

175