
Which parent determines a baby’s sex? Why?
In humans, the sex of a baby is determined by its father. The sequence of events involved in sex determination is instigated by one special pair of chromosomes, the sex chromosomes, which carry information that directs a growing fetus to develop as a male or as a female.
Let’s take a closer look at the human sex chromosomes. We noted that there are 23 pairs of chromosomes in every somatic cell. These can be divided into two different types: 1 pair of sex chromosomes and 22 pairs of non-
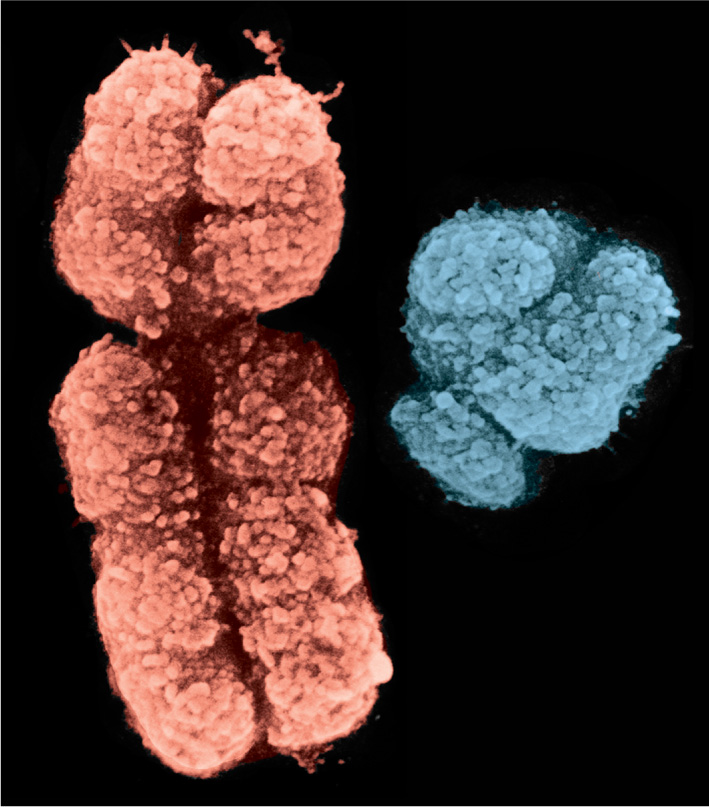
How do the X and Y chromosomes differ from the other chromosomes? All of the genetic information is stored on the chromosomes in all the cells of an organism’s body. But most of this information is not sex specific—
An individual has two copies of all the non-
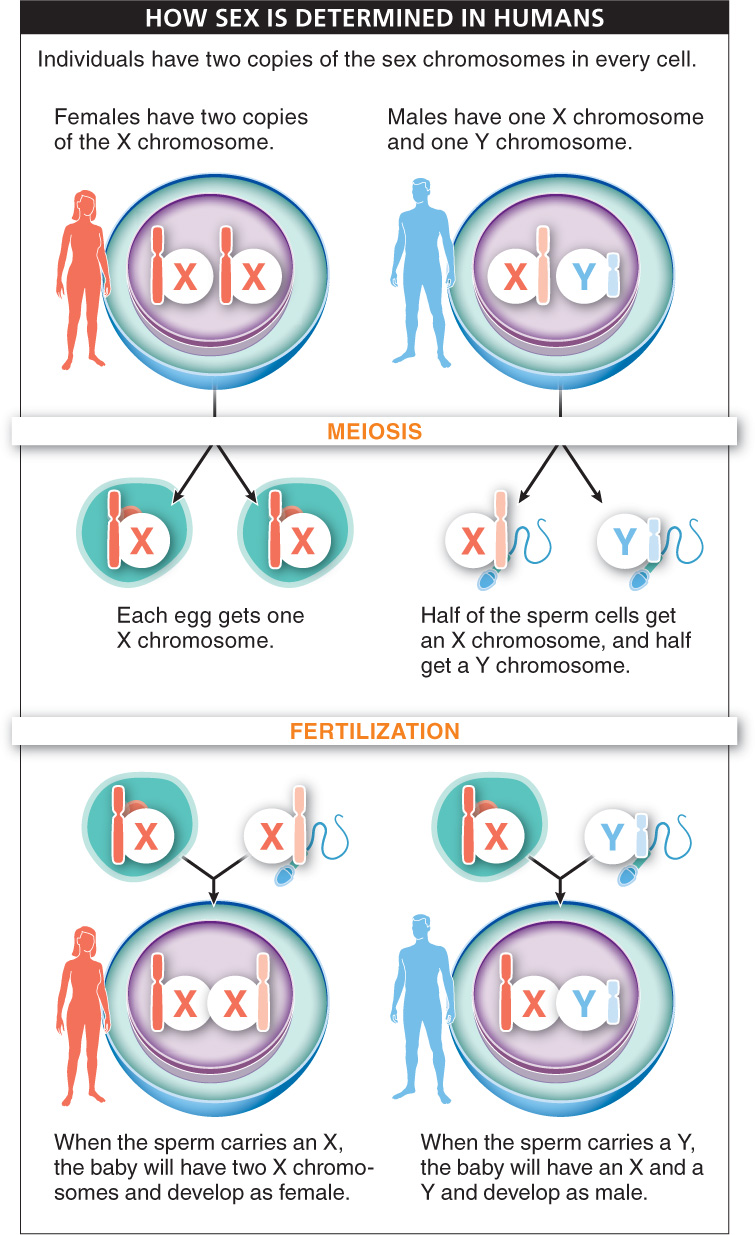
So how does the father determine the sex of the baby? During meiosis in females, the gametes that are produced carry only one copy of each chromosome. This is true for the sex chromosomes, too. So from the two copies of the X chromosome carried by females, half of the gametes end up with a copy of one of those X chromosomes while the rest of the gametes inherit the other X chromosome. Thus, every egg has an X for its one sex chromosome. During meiosis in males, the sperm that are produced also carry one copy of each chromosome, including the sex chromosomes, but in this case, half of the sperm produced inherit the X chromosome and the other half inherit the Y chromosome. At fertilization, an egg bearing a single X chromosome (and one copy of all the non-
31
We know that no genetic information on the Y chromosome is essential for producing a normally functioning human. Why?
Given the distribution of X and Y chromosomes into males and females, it must be true that no essential genetic information is carried on the Y chromosome. Why? Because females don’t have a Y chromosome in any of their cells, yet they are able to develop and live normal, healthy lives. For this reason, we know that nothing on the Y chromosome is absolutely necessary for the development of a normally functioning human.
Physically, the X and Y chromosomes look very different from each other. The X chromosome is relatively large and carries a great deal of genetic information relating to a large number of non-
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 6.14
In humans, the sex chromosomes carry information that directs a growing fetus to develop as either a male (if a Y chromosome is present) or a female (if no Y chromosome is present). Sex determination depends on the sex chromosome inherited from the father.
In humans, what combination of chromosomes produces a female? How about a male?
Females possess two X chromosomes, while males possess one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.
32