10.4–10.7
10.4–Species are the basic units of biodiversity.
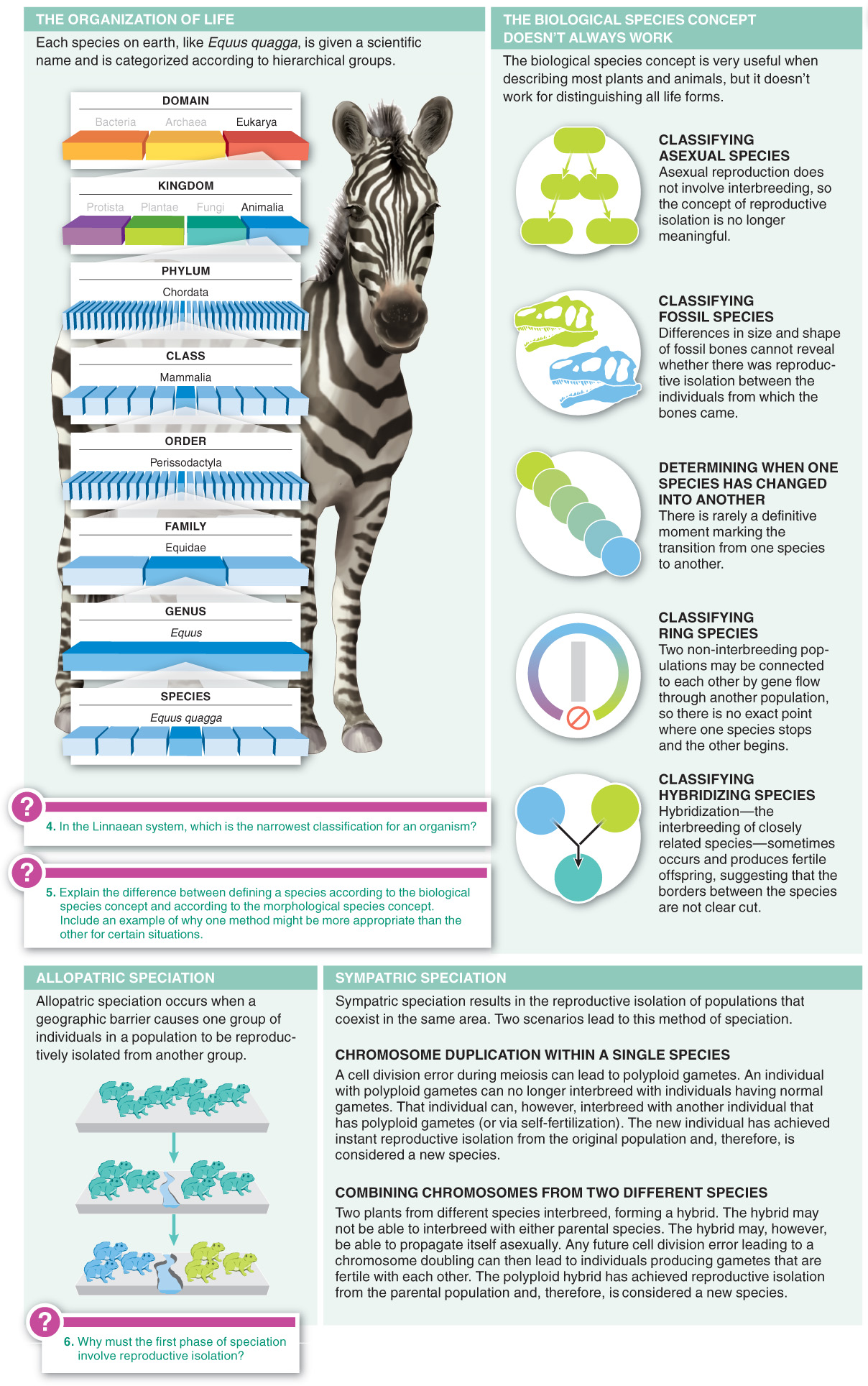
Species are distinct biological entities, named using a hierarchical system of classification.

441
Q
Populations of Larus gulls around the North Pole show an unusual pattern of reproductive isolation: each population is able to interbreed with its neighboring populations, but populations separated by larger geographic distances are not able to interbreed. Larus gulls are an example of a(n) __________ species.
- a) ring
- b) polyploid
- c) circular
- d) Escher
- e) linked

In animals, it is believed that the most common mode of speciation is:
- a) autopolyploidy.
- b) chromosomal.
- c) directional.
- d) allopatric.
- e) sympatric.

Polyploidy:
- a) arises only when an error in meiosis results in diploid gametes instead of haploid gametes.
- b) is a common method of sympatric speciation for animals.
- c) arises when allopatric speciation causes plants to have fewer sets of chromosomes than their parent plants.
- d) is an increased number of sets of chromosomes.
- e) always results in allopatric speciation.

In the plant kingdom, all of the species are descended from a single common ancestor. In terms of phylogeny, what type of tree of life is this?
- a) monophyletic
- b) uniphyletic
- c) punctuated
- d) sympatric
- e) allopatric

442