Invertebrates, defined as animals without a backbone, are the largest and most diverse group of animals comprising 96% of all living animal species. The invertebrates are not a monophyletic group, however, and include protostomes and some (but not all) of the deuterostomes.
489
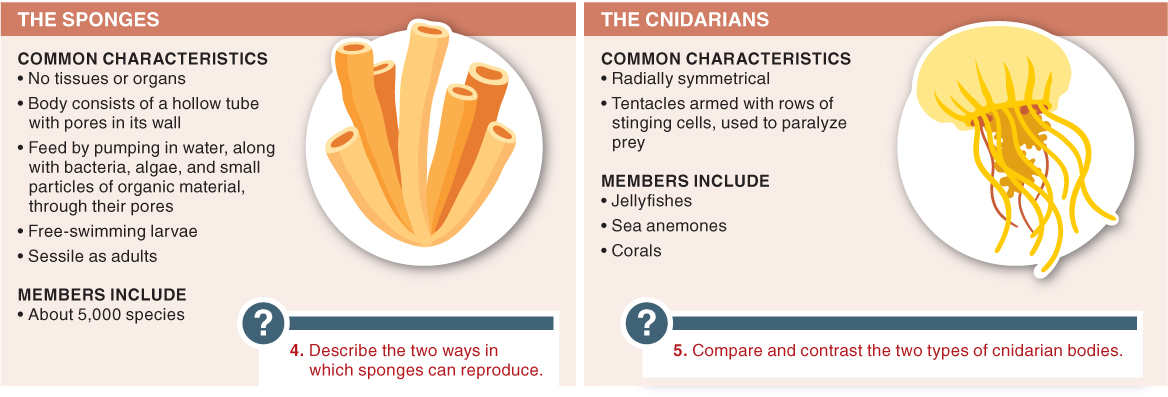
Sponges are sessile, meaning that they:
- a) reproduce asexually.
- b) are parasitic and depend on their host for a constant supply of nutrients.
- c) have exoskeletons that they must shed as they grow.
- d) live within shells they find on the ocean floor.
- e) live attached to a solid structure and do not move around.

In cnidarians, cnidocytes are primarily used for:
- a) creation of water flow across the body wall.
- b) formation of free-
living medusas. - c) secretion of digestive enzymes.
- d) prey capture and defense.
- e) muscular contraction during movement.

The mollusk’s mantle is used primarily for:
- a) feeding.
- b) gas exchange.
- c) producing the shell.
- d) excretion.
- e) reproduction.

The phylum Arthropoda includes all of the following kinds of animals except:
- a) snails.
- b) crabs.
- c) crayfish.
- d) butterflies.
- e) scorpions.

For which of the following groups of organisms is it most difficult to estimate species numbers?
- a) bees, wasps, and ants
- b) bacteria
- c) tropical trees
- d) beetles
- e) mammals


490
Which of the following echinoderms has radial symmetry during its larval stage?
- a) sea star
- b) brittle star
- c) sea urchin
- d) sand dollar
- e) None of the above have radial symmetry during the larval stage.

Which one of the following characteristics distinguishes all chordates from all other animals?
- a) a vertebral column
- b) a dorsal hollow nerve cord
- c) collar cells
- d) bilateral symmetry during embryonic or larval development
- e) an amniotic egg

Which of the following are chordates?
- a) fishes
- b) humans
- c) frogs
- d) All of the above are chordates.
- e) Only a) and c) are chordates.

Which of these animals is a tetrapod that does not produce amniotic eggs?
- a) salamander
- b) human
- c) monkey
- d) elephant
- e) python

Why is the amniotic egg considered a key evolutionary innovation?
- a) It prohibits external fertilization thereby facilitating the evolutionary innovation of internal fertilization.
- b) It has an unbreakable shell.
- c) It greatly increases the likelihood of survival of the eggs in a terrestrial environment.
- d) It enables eggs to float in an aquatic medium.
- e) It extends the time of embryonic development.
