13.6–13.10
13.6–In humans, bacteria can have harmful or beneficial health effects
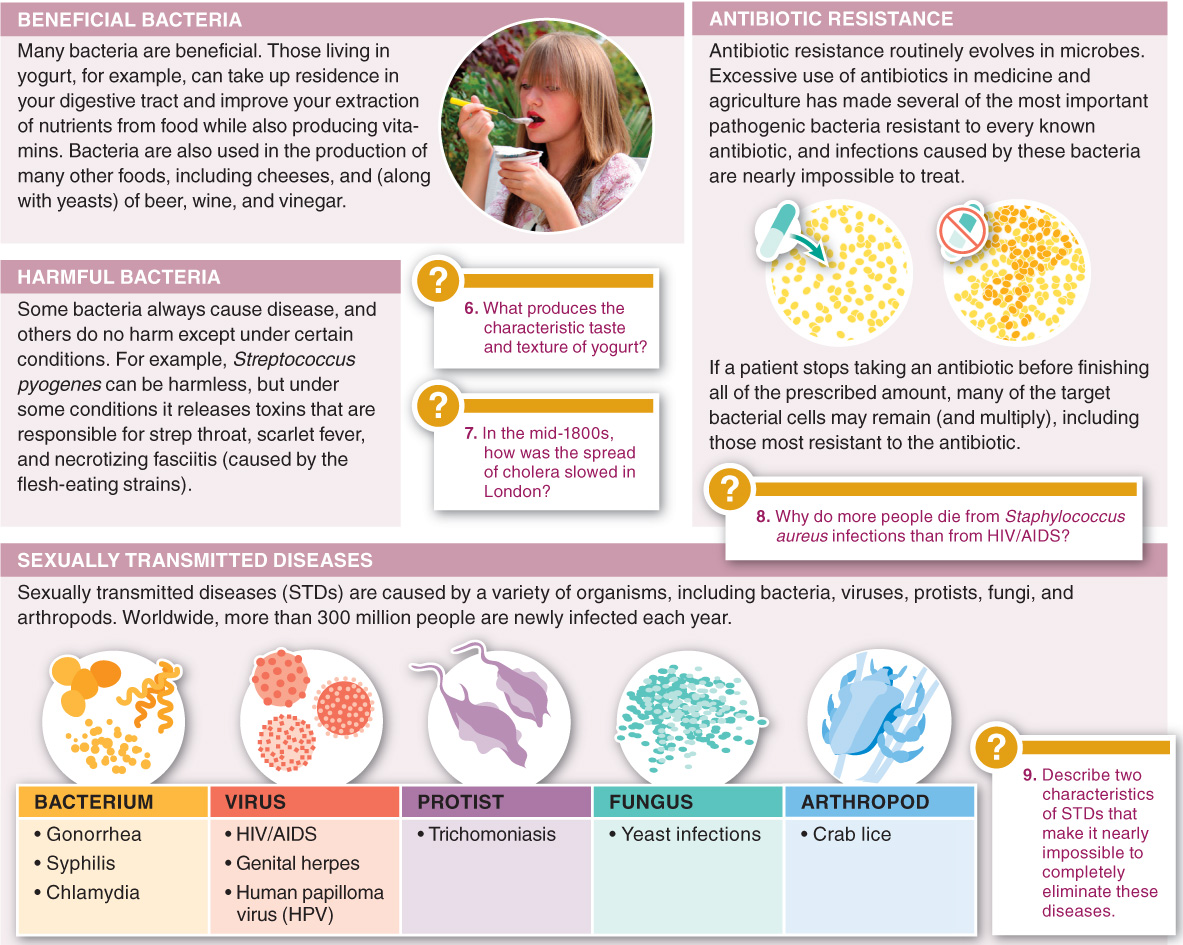
Bacterial effects on human health vary widely. Many are beneficial and many are neutral, while some can be harmful.
Q
A population of Escherichia coli can double every ________ in an ideal laboratory culture.
- a) 20 seconds
- b) 2 minutes
- c) 2 days
- d) 20 minutes
- e) 2 hours

Plasmids containing genes for antibiotic resistance can be exchanged between bacterial cells in a culture by:
- a) conjugation.
- b) artificial exchange.
- c) cloning.
- d) transduction.
- e) conduction.

Which group of organisms utilizes the largest variety of energy sources?
- a) prokaryotes
- b) fungi
- c) protists
- d) invertebrate animals
- e) vertebrate animals

Which of the following statements about antibiotics is incorrect?
- a) Penicillin was the first antibiotic widely used to fight bacterial infections.
- b) Antibiotics help microbes compete with other microbes.
- c) Antibiotic-
resistant microbes are selected for in humans who are taking antibiotics. - d) Antibiotics, though effective against viruses, are not effective against bacteria.
- e) Antibiotics are used not just in human health care but also in agriculture.

Which of the following domains are the most closely related, in that they share a unique common ancestor?
- a) archaea and bacteria
- b) archaea and eukarya
- c) bacteria and eukarya
- d) None of the above; all three domains evolved from different ancestors.
- e) None of the above; all three domains are equally related to one another.

568