14.14–14.16
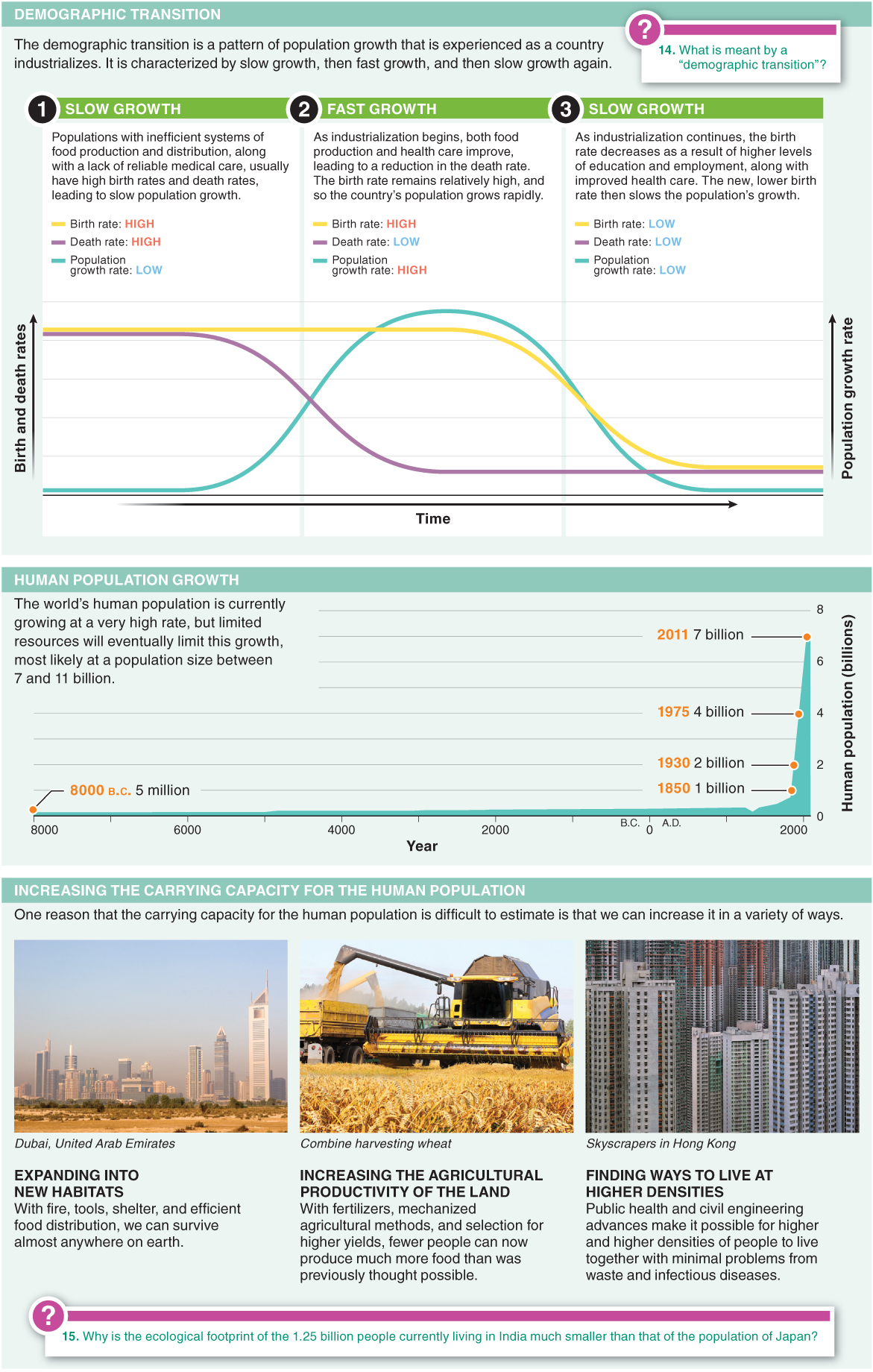
14.14–The human population is growing rapidly.
In humans, current birth rates exceed death rates by so much that we add 80 million people to the world population each year!
607
Q
Life extension:
- a) is not possible, because natural selection cannot weed out disease-
causing alleles that have an effect only at an age when reproduction is no longer possible. - b) can be achieved by selectively breeding those individuals that have the earliest age of maturity.
- c) works in insects but could not work in humans.
- d) has been achieved using laboratory selection for delayed reproduction.
- e) None of the above are true.

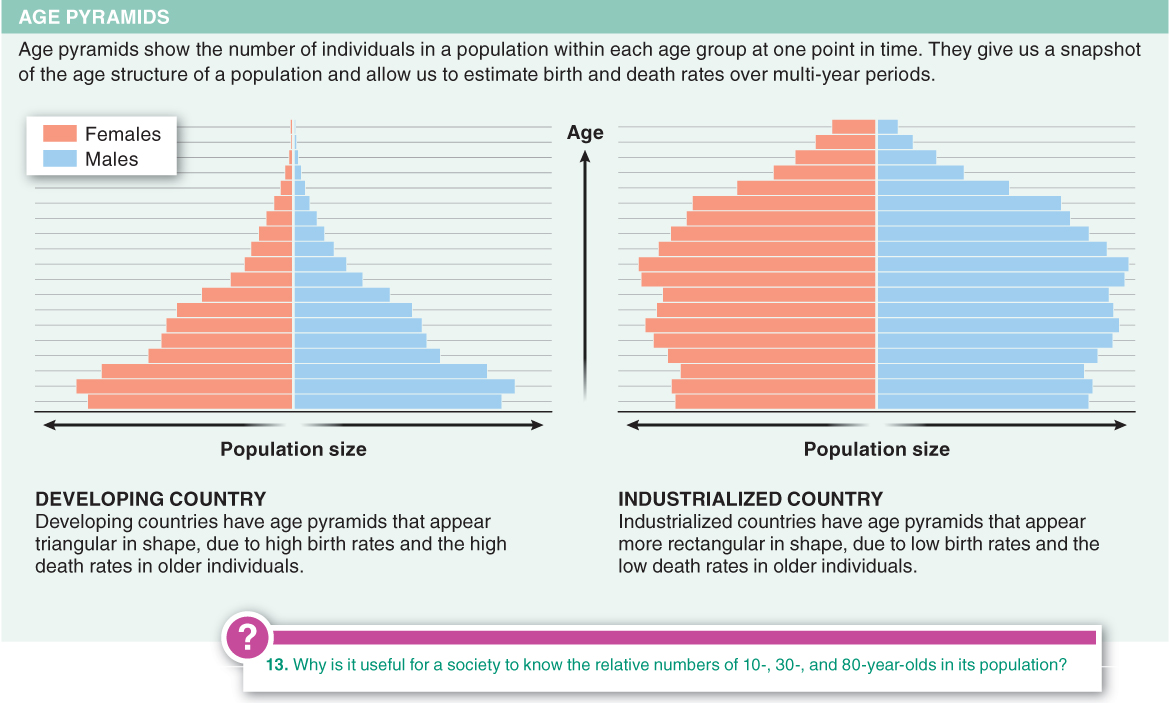
A population pyramid:
- a) represents the number of individuals in various age groups in a population.
- b) can be constructed from the data in a life table.
- c) directly predicts future age distributions of the population.
- d) shows the current birth and death rates of a population.
- e) predicts survival and mortality rates for an individual at a given age.

A primary difference between the age pyramids of industrialized and developing countries is that:
- a) mean longevity is significantly greater in developing countries.
- b) in developing countries, much larger proportions of the population are in the youngest age groups.
- c) developing countries show a characteristic “bulge” that indicates a baby boom.
- d) in developing countries, females live significantly longer than males, whereas in industrialized countries the reverse is true.
- e) developing countries have significantly more individuals than industrialized countries.

Which statement best describes expectations for the world’s human population by the year 2015?
- a) It will exceed 10 billion if the current rate of increase continues.
- b) Negative growth in the United States and Europe will counterbalance positive growth in the developing countries.
- c) It will exceed 7.5 billion if the current rate of increase continues.
- d) It will drop below 6 billion if the current rate of decrease continues.
- e) The problem is too complex to make any predictions.
