
Chapter 5. Chapter 5: DNA, Gene Expression, and Biotechnology
Review & Rehearse

Instructions
Review the visual summaries and answer the essay questions below.
Make sure to enter a brief response that completely answers each question and explains your reasoning. When you click "Submit," you will be provided instant feedback, allowing you to check if your response is correct.
(This activity contains 15 total essay questions. Each new question will be revealed once you complete the preceding question.)
1.

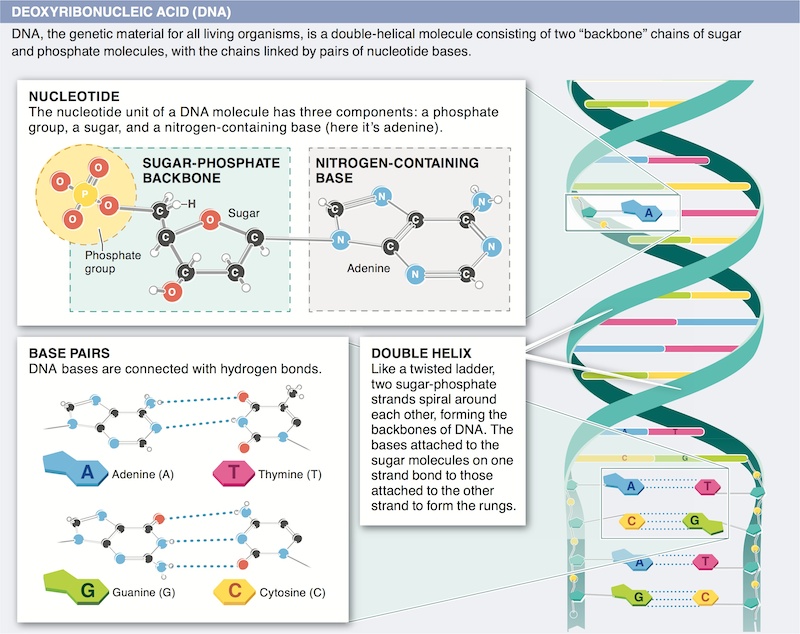
1. How and why is DNA helpful in ensuring greater justice in our society?
2.
2. After sequencing a molecule of DNA, you discover that 20% of the bases are cytosine. What percentage of the bases would you expect to be thymine? Why?
3.
3. What function does the sugar-phosphate backbone of a DNA molecule serve?
4.
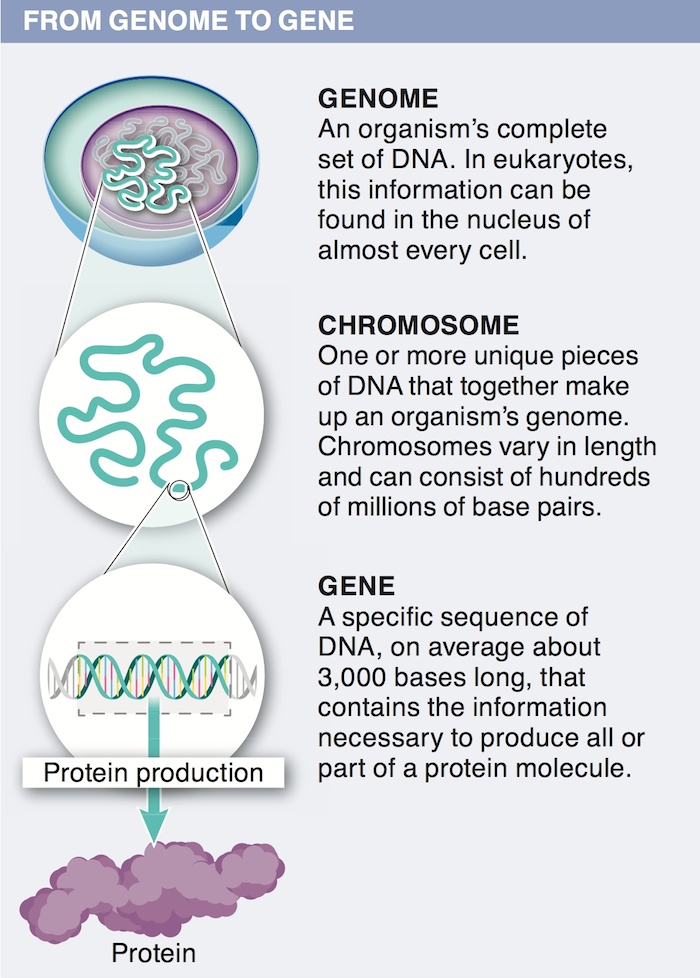
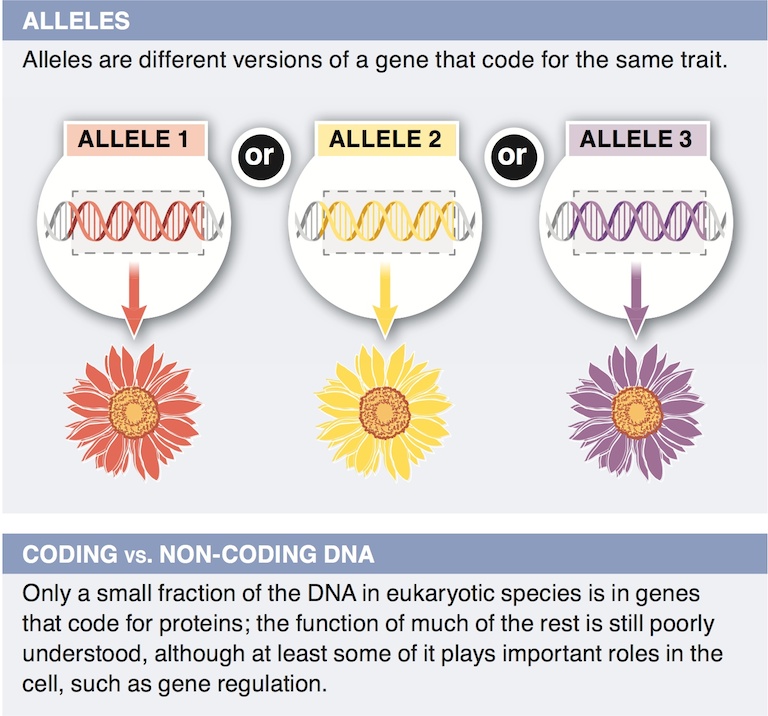
4. Only a small fraction of the DNA in eukaryotic species codes for proteins. The remainder is sometimes referred to as “junk” DNA. Why is this a poor description of the non-coding DNA?
5.

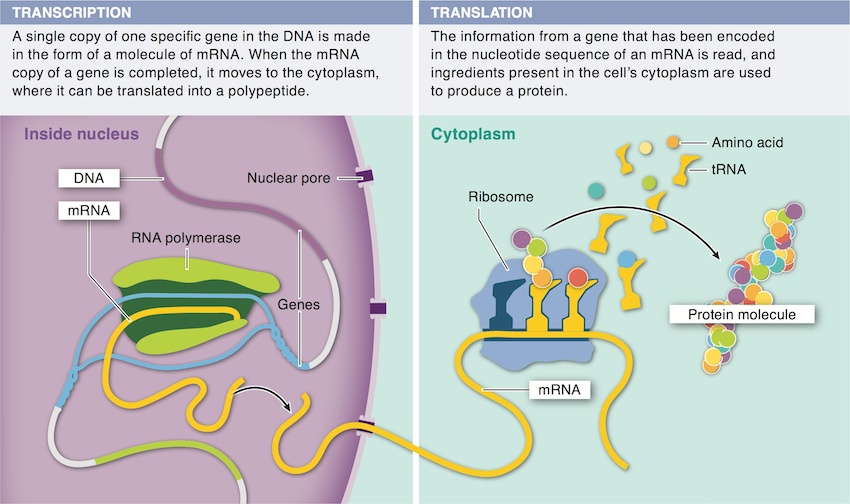
5. What is the role of transcription? Why is this step is necessary and translation is not the first step in using DNA information to build a new organism?
6.
6. When the mRNA copy of a gene is completed, why does it move to the cytoplasm?
7.
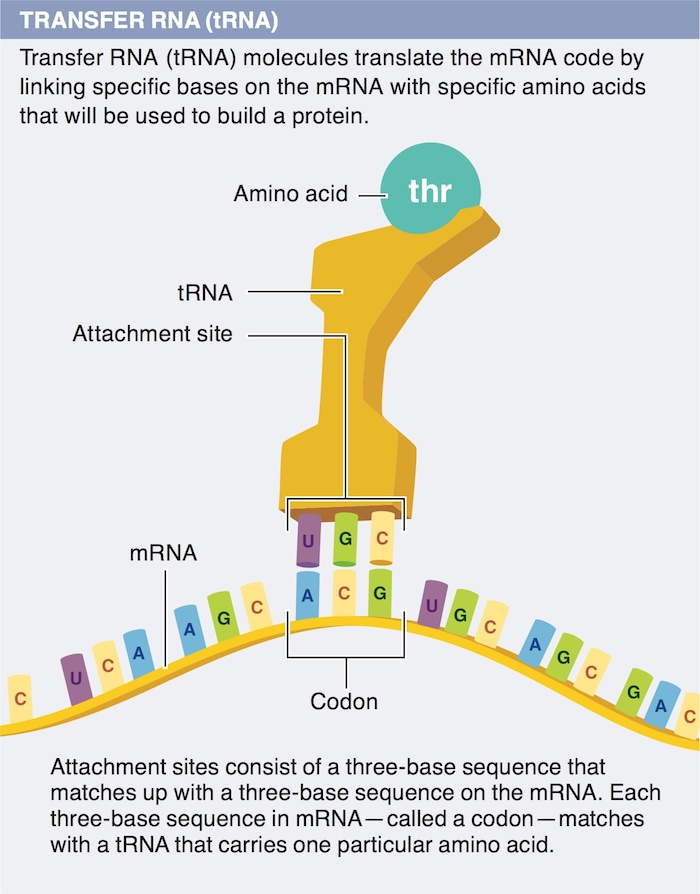
7. What is the function of tRNA in translation?
8.
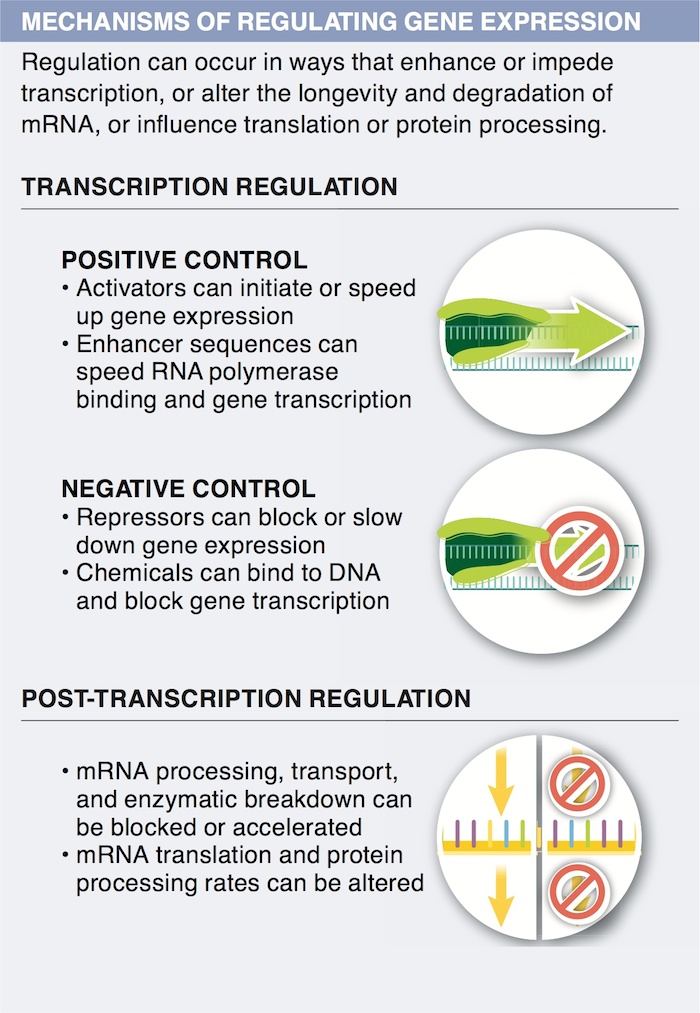
8. E.coli prefer glucose as an energy source. If lactose, and not glucose, is present, the E.coli are able to survive. How are E.coli able to respond to this environmental change?
9.

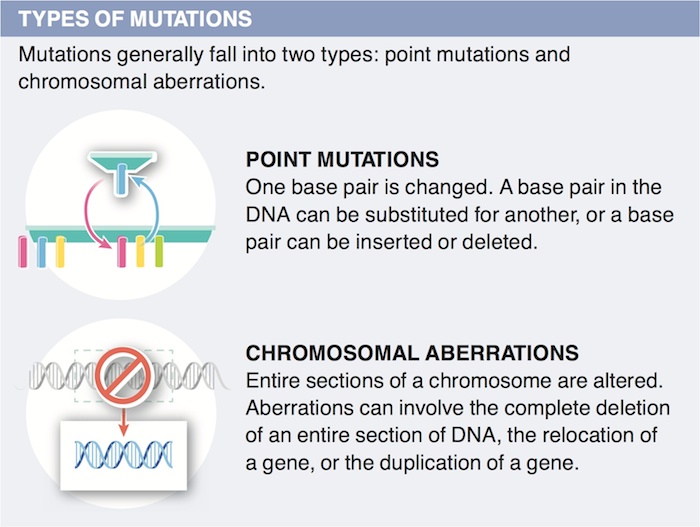
9. Mutations often are considered negative events with bad consequences. Why is this view of mutations somewhat of a paradox?
10.
10. Which step in a metabolic pathway is disrupted in Tay-Sachs disease?
11.

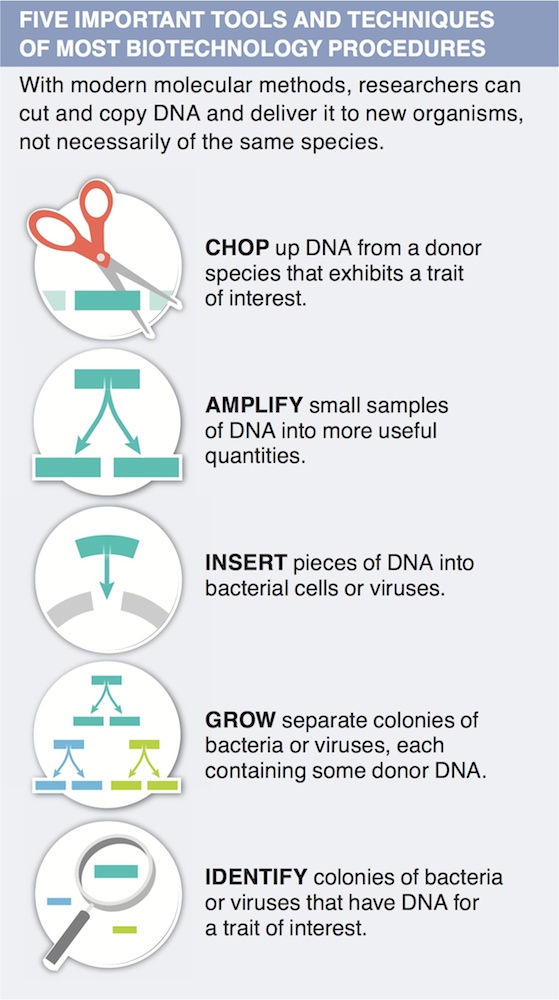

11. Describe two ways in which advances in biotechnology have helped make farming more efficient.
12.

12. The creation of genetically modified foods raises many concerns, including that the loss of genetic diversity may have bad consequences. Why this is a concern?
13.


13. Describe three major applications of biotechnology and their impact on human health.
14.

14. How has the advent of genetic screening for prospective parents led to decreases in the incidence of fatal genetic diseases?
15.
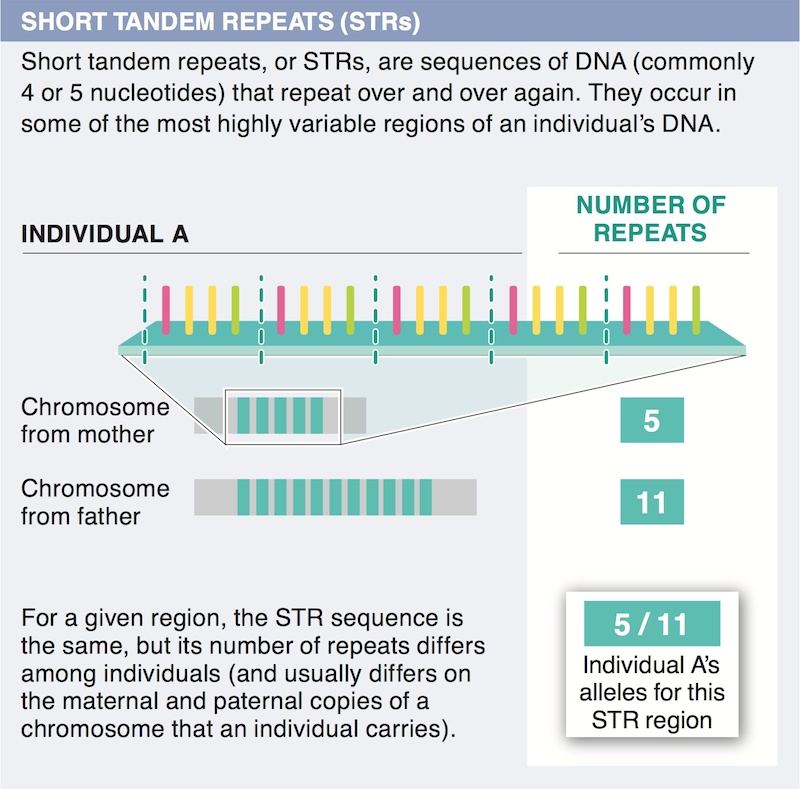
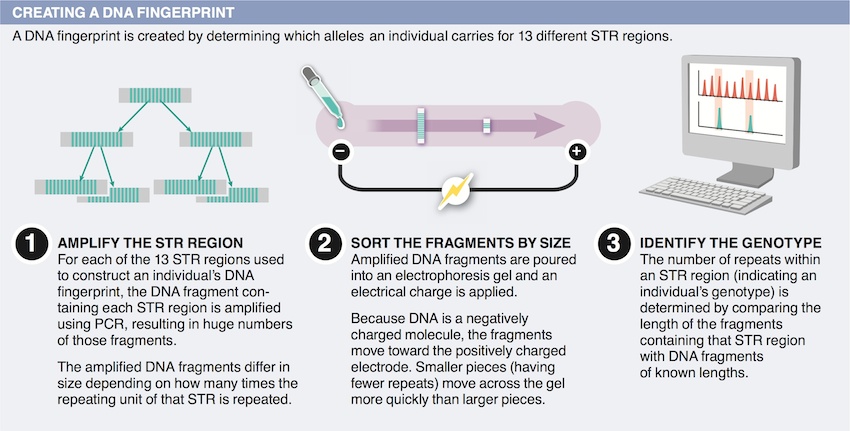
15. What is a potential benefit to farmers of cloning technology?
Activity results are being submitted...