
Chapter 7. Chapter 7: Genes and Inheritance
Review and Rehearse

Instructions
Review the visual summaries and answer the essay questions below.
Make sure to enter a brief response that completely answers each question and explains your reasoning. When you click "Submit," you will be provided instant feedback, allowing you to check if your response is correct.
(This activity contains 15 total essay questions. Each new question will be revealed once you complete the preceding question.)
1.

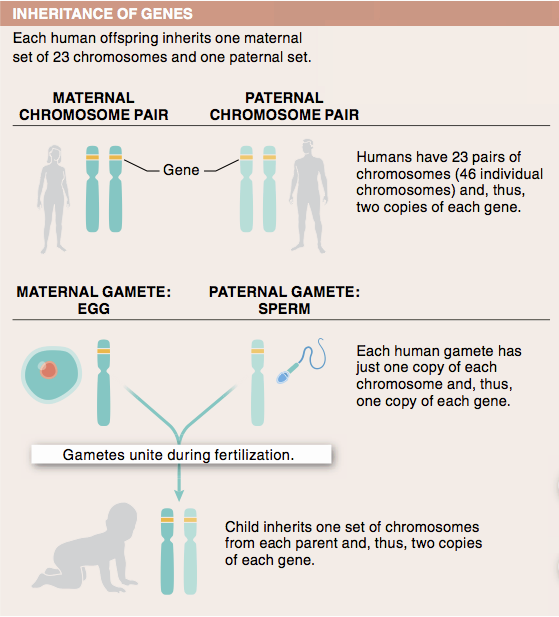
1. Why do offspring resemble their parents?
2.

2. Why is it simpler to describe heredity using single-gene traits?
3.
3. Describe the main focus of Mendel's research on pea plants.
4.
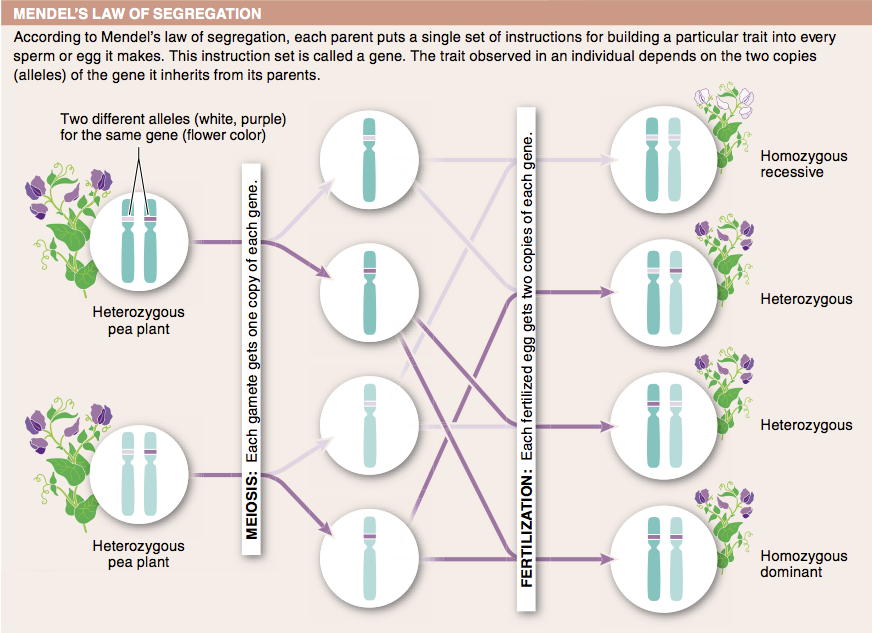
4. Why does a sperm or egg only have one copy of a gene?
5.
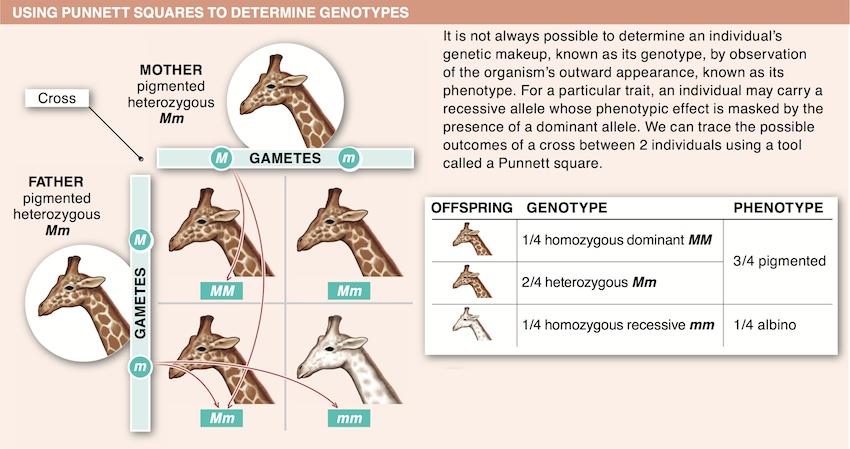
5. Compare and contrast the terms phenotype and genotype.
6.

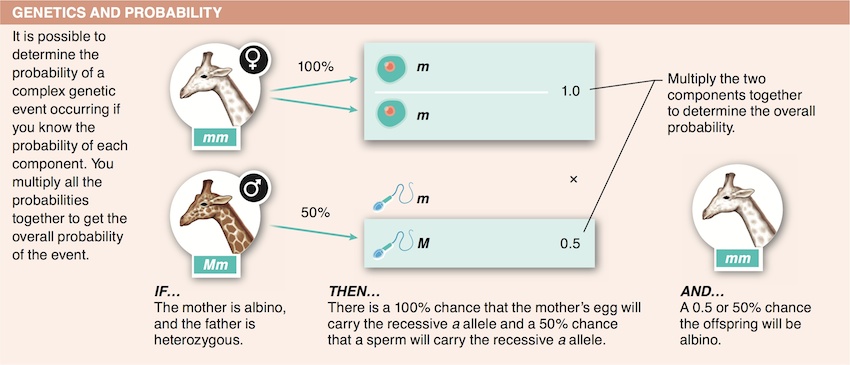
6. If an individual is homozygous for a trait, what percentage of his/her gametes will carry that allele?
7.
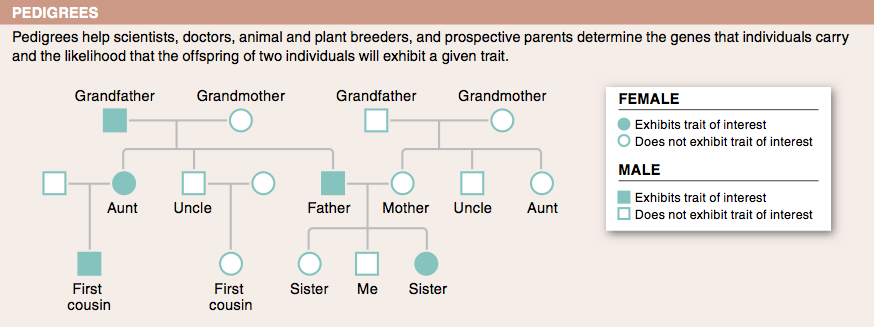
7. In what situation is a test-cross helpful in determining an individual's genotype?
8.
8. What does it mean to be the "carrier of a trait"?
9.

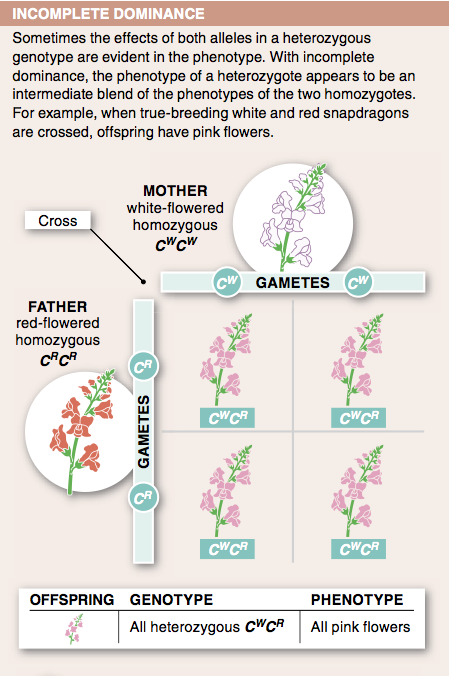
9. Describe the phenotype of an individual heterozygous for an allele with incomplete dominance.
10.
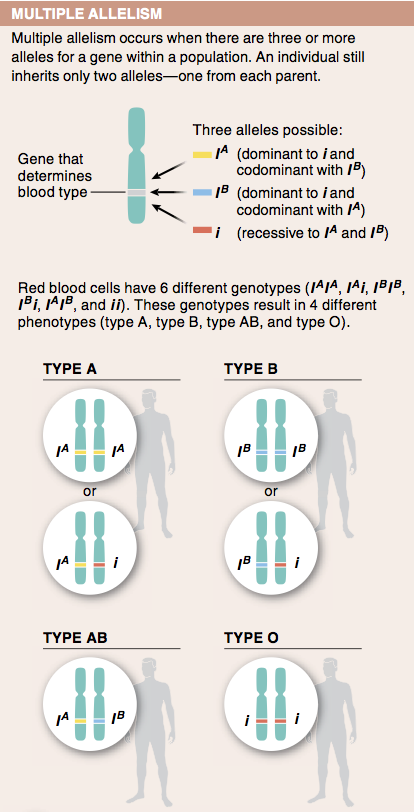
10. For a gene with four alleles, what is the largest number of different alleles that one individual can carry? Why?
11.

11. What does it mean for a trait to be polygenic?
12.
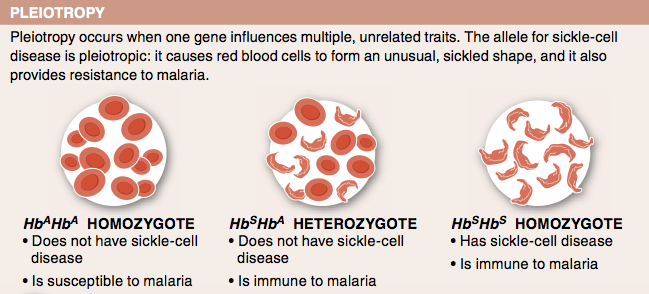
12. Describe how being heterozygous for the sickle-cell allele can help provide resistance to malaria.
13.

13. Why are sex-linked recessive traits more commonly observed in males than females?
14.

14. How does the case of PKU support the notion that our phenotype is a product of our genotype in combination with the effect of our environment?
15.

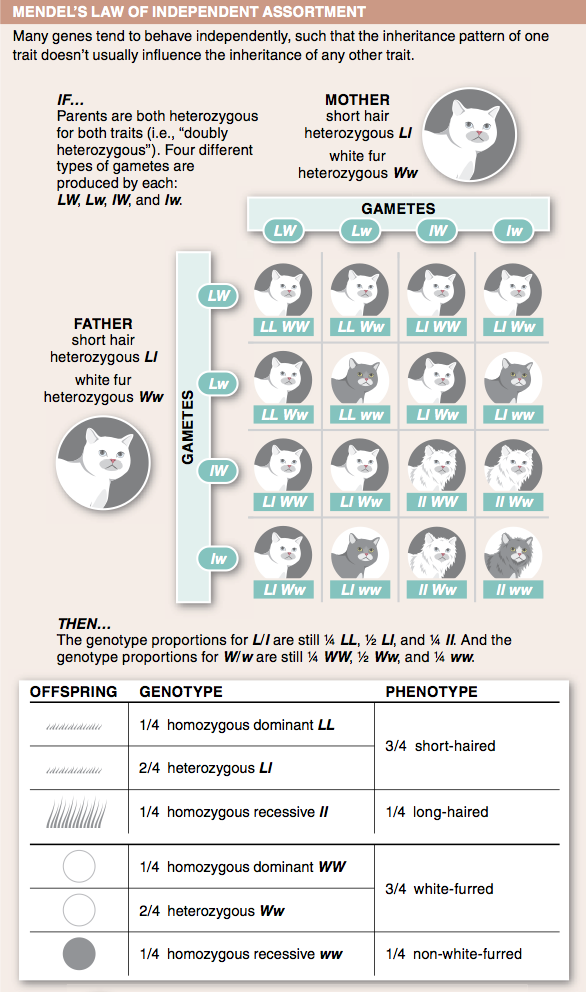
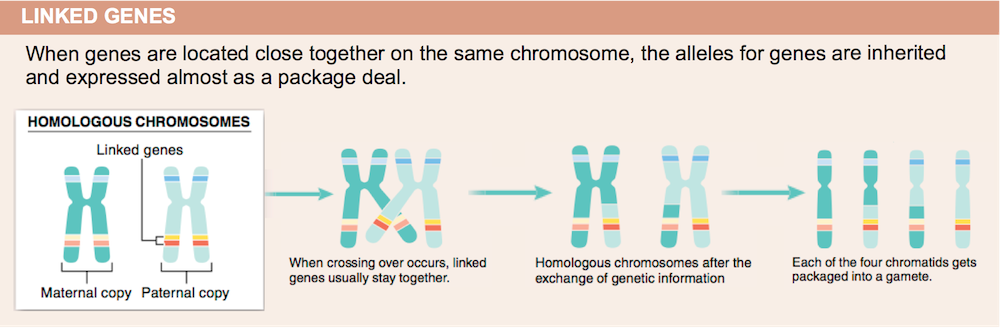
15. What is Mendel's second law? Why doesn't it apply for all traits?
Activity results are being submitted...